这篇记录的目的,进一步从源码、流程的角度 梳理 UVC 开发流程,加速理解,快速迭代,迁移其它产品开发
文章目录
前言
假设已经对UVC了解,已经对能够写一个demo,或者用uvc 官方提供的demo 进行开发。但是遇到客户问题还是一知半解,那就还是有必要对 UVC Java层源码有一个了解,特别是流程上的,这样才能遇到问题针对性解决! 然后有自己的思考和一些想法。
一、参考资料
UVC for USBCamera in Android - 篇一
USB Camera open流程详解
Android中多USB摄像头解决方案——UVCCamera源码分析(一)
Android中多USB摄像头解决方案——UVCCamera源码分析(二)
Android中多USB摄像头解决方案——UVCCamera源码分析(三)
Android中多USB摄像头解决方案——UVCCamera源码分析(四)
Android中多USB摄像头解决方案——UVCCamera源码分析(五)
上面这些参考资料非常重要,都是在解析USBCamera 源码流程、分析,对着源码看 意义非常大。
USBCamera 本文源码对照分析
AndroidUSBCamera 方便快速集成的手机应用,这里提出来给出一种解决方案,适合自己的时候可以用一用。但是如再篇一中也讲过,有弊端,部分相机分辨率显示不出来 又无法更改,卡死,属于大佬封装的一个app , 仅供参考。
UVCCamera 最原始的UVCCamera Demo,方便二次封装。 太多的Demo 都是基于这个参考的。 里面的不同demo 对应不同使用场景,有借鉴的意义。
备注: 我们 本文源码流程参考的 就是 USBCamera 这个demo 基础上再进行二次封装 实现业务。 实际这个的基础也是 UVCCamera
二、核心关键类介绍
| 类 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| USBMonitor | 监听 USB 设备插拔,管理权限 |
| UsbControlBlock | 底层 USB 通信(控制传输) |
| OnDeviceConnectListener | USB 设备连接状态回调 |
| UVCCameraHandler | 封装 UVCCamera 操作(预览、拍照、录像) |
| CameraThread | 后台线程执行摄像头操作 |
这些类共同构成了 USBCamera 的核心框架,适用于 Android 上的 USB 摄像头开发。
USBMonitor(USB 设备监控与管理)
作用
-
负责 检测 USB 设备的插拔事件(如摄像头连接/断开)。
-
枚举已连接的 USB 设备,并检查是否有可用的摄像头设备。
-
申请 USB 设备权限(在 Android 上需要用户授权才能访问 USB 设备)。
-
管理 USB 设备的生命周期(如打开、关闭设备)。
关键方法
-
register() / unregister():注册/注销 USB 设备监听。
-
getDeviceList():获取当前连接的 USB 设备列表。
-
requestPermission(UsbDevice):请求用户授权访问 USB 设备。
-
openDevice(UsbDevice):打开 USB 设备,返回 UsbControlBlock。
UsbControlBlock(USB 设备控制块)
作用
- 代表一个 已打开的 USB 设备,用于 底层 USB 通信。
- 提供 USB 控制传输(Control Transfer) 功能,用于发送控制命令(如摄像头参数设置)。
- 管理 USB 接口(Interface) 和 端点(Endpoint)(用于数据传输)。
关键方法
- claimInterface(UsbInterface):声明 USB 接口(必须调用才能进行数据传输)。
- bulkTransfer(…):执行 USB 批量传输(Bulk Transfer)。
- close():关闭 USB 设备,释放资源。
OnDeviceConnectListener(USB 设备连接监听接口)
作用
- 定义 USB 设备连接/断开时的回调,用于处理设备状态变化。
- 通常由 USBMonitor 触发。
关键回调方法 - onAttach(UsbDevice):当 USB 设备插入时调用。
- onDetach(UsbDevice):当 USB 设备拔出时调用。
- onConnect(UsbDevice, UsbControlBlock, boolean):当 USB 设备成功连接并授权后调用。
- onDisconnect(UsbDevice, UsbControlBlock):当 USB 设备断开连接时调用。
示例
val usbMonitor = USBMonitor(context, object : OnDeviceConnectListener {
override fun onAttach(device: UsbDevice) {
Log.d("USB", "设备插入: ${device.deviceName}")
}
override fun onConnect(device: UsbDevice, ctrlBlock: UsbControlBlock, isNew: Boolean) {
Log.d("USB", "设备已连接: ${device.deviceName}")
// 可以在这里初始化摄像头
}
override fun onDisconnect(device: UsbDevice, ctrlBlock: UsbControlBlock) {
Log.d("USB", "设备已断开: ${device.deviceName}")
}
})
UVCCameraHandler(UVCCamera 控制与数据流处理)
作用
- 管理 UVCCamera 的预览、拍照、录像 等操作。
- 封装了 UVCCamera 的 API,提供更简单的调用方式。
- 通常运行在 CameraThread 中,避免阻塞 UI 线程。
关键方法 - startPreview(Surface):开始摄像头预览(传入 Surface 用于显示)。
- stopPreview():停止预览。
- captureStill(String):拍照并保存到指定路径。
- startRecording(String) / stopRecording():开始/停止录像。
示例
val cameraHandler = UVCCameraHandler.createHandler(
context,
UVCCamera.DEFAULT_PREVIEW_WIDTH,
UVCCamera.DEFAULT_PREVIEW_HEIGHT,
UVCCamera.FRAME_FORMAT_MJPEG
)
// 开始预览(传入 Surface,如 TextureView 的 Surface)
cameraHandler.startPreview(surface)
CameraThread(摄像头后台线程)
作用
- 用于 在后台线程执行摄像头操作(避免阻塞 UI 线程)。
- 通常由 UVCCameraHandler 内部使用,封装了 HandlerThread 的实现。
- 处理 USB 摄像头初始化、帧数据回调、录制存储 等耗时操作。
关键方法
-
run():线程运行逻辑(处理 UVCCamera 操作)。
-
queueEvent(Runnable):向线程发送任务(如 startPreview、captureStill)。
示例
// UVCCameraHandler 内部通常这样使用:
class UVCCameraHandler : HandlerThread("CameraThread") {
private val mWorkerHandler: Handler
init {
start()
mWorkerHandler = Handler(looper)
}
fun startPreview(surface: Surface) {
mWorkerHandler.post {
// 在后台线程执行摄像头初始化
mUVCCamera.startPreview(surface)
}
}
}
小结-完整流程示例
- USBMonitor 检测 USB 设备插入,并请求权限。
- OnDeviceConnectListener.onConnect 回调返回 UsbControlBlock。
- UVCCameraHandler 使用 UsbControlBlock 初始化 UVCCamera。
- CameraThread 在后台处理摄像头帧数据,并通过 Surface 显示预览。
- 用户操作(拍照、录像)通过 UVCCameraHandler 执行。
三、源码流程分析
open 打开USBCamera过程
上面我们了解了关键核心类,通过类的作用可以了解基本流程,这里总结的流程图如下,先有个大概了解
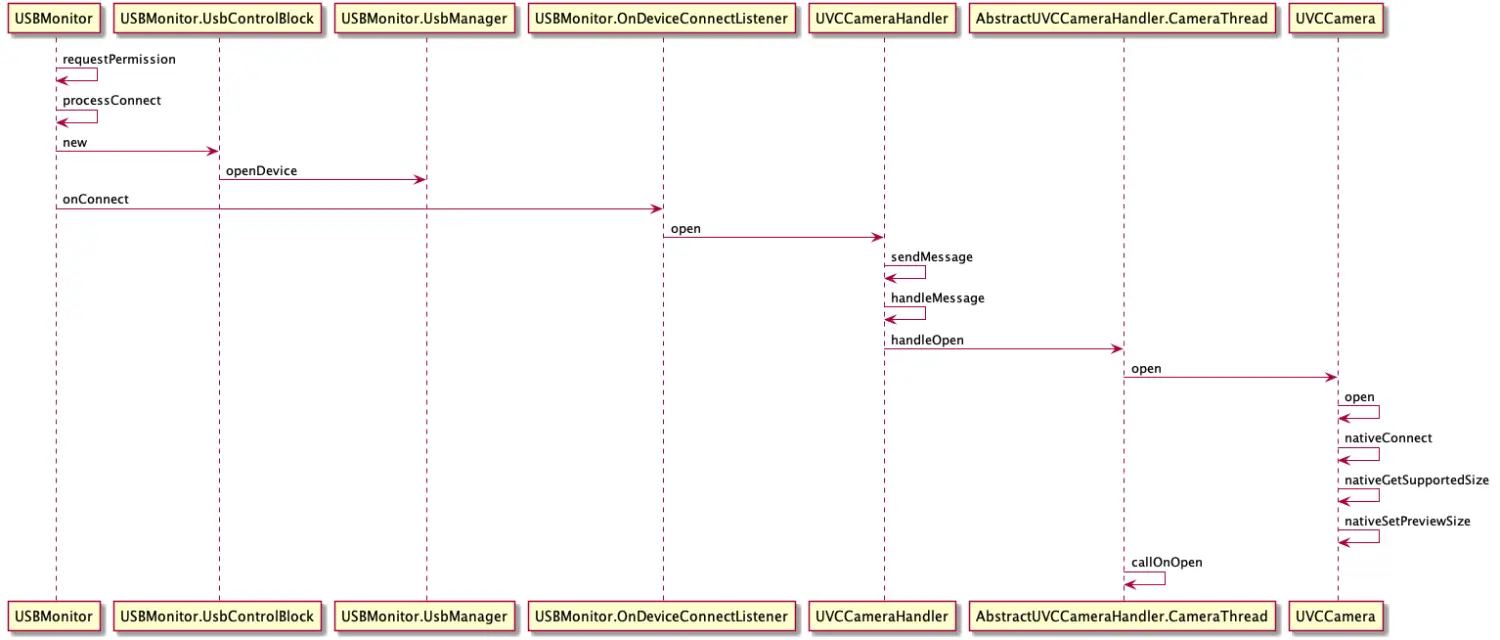
时序图是流程的总结,其实一就够了,对着源码一步一步分析即可,这里还是重点来分析下部分方法,代码。
USBMonitor - register 监听USB 事件
我们这么理解:当你插入USB的时候,系统是由USBEvent 事件的,作为应用你就必须知道由UsbDevice 插入了,所以应用端需要监听。 那么就是通过广播实现的,就是USBMonitor 监控器通过广播事件监听USB设备插入,UVCCamera 外设从硬件角度上来说就是一个USB 设备。
/**
* register BroadcastReceiver to monitor USB events
* @throws IllegalStateException
*/
public synchronized void register() throws IllegalStateException {
if (destroyed) throw new IllegalStateException("already destroyed");
Log.d(TAG," register");
if (mPermissionIntent == null) {
if (DEBUG) Log.i(TAG, "register:");
final Context context = mWeakContext.get();
if (context != null) {
//mPermissionIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, 0, new Intent(ACTION_USB_PERMISSION), 0);
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.S) {
mPermissionIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, 0, new Intent(ACTION_USB_PERMISSION), PendingIntent.FLAG_IMMUTABLE);
} else {
mPermissionIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, 0, new Intent(ACTION_USB_PERMISSION), PendingIntent.FLAG_ONE_SHOT | PendingIntent.FLAG_IMMUTABLE);
}
final IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter(ACTION_USB_PERMISSION);
// ACTION_USB_DEVICE_ATTACHED never comes on some devices so it should not be added here
filter.addAction(ACTION_USB_DEVICE_ATTACHED);
filter.addAction(UsbManager.ACTION_USB_DEVICE_DETACHED);
context.registerReceiver(mUsbReceiver, filter);
}
// start connection check
mDeviceCounts = 0;
mAsyncHandler.postDelayed(mDeviceCheckRunnable, 1000);
}
}
当 监听到USB插入事件,通过广播监听到后,如下: processAttach 方法 和 mOnDeviceConnectListener.onAttach(device); 回调
else if (UsbManager.ACTION_USB_DEVICE_ATTACHED.equals(action)) {
Log.d(TAG," ACTION_USB_DEVICE_ATTACHED");
final UsbDevice device = intent.getParcelableExtra(UsbManager.EXTRA_DEVICE);
updatePermission(device, hasPermission(device));
processAttach(device);
}
private final void processAttach(final UsbDevice device) {
if (destroyed) return;
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "processAttach: mOnDeviceConnectListener:"+mOnDeviceConnectListener);
if (mOnDeviceConnectListener != null) {
mAsyncHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Log.d(TAG," onAttach device");
mOnDeviceConnectListener.onAttach(device);
}
});
}
}
USBMonitor - onAttach 回调
mUSBMonitor = new USBMonitor(activity.getApplicationContext(), new USBMonitor.OnDeviceConnectListener() {
// called by checking usb device
// do request device permission
@Override
public void onAttach(UsbDevice device) {
Log.d(TAG," onAttach");
if (listener != null) {
listener.onAttachDev(device);
}
}
...........
}
private 




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 2407
2407

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










