1.前言
https://docs.ultralytics.com/zh/中文官网
ultralytics训练yolo并导出onnx时经常需要符合一定的结构,如果直接导出onnx并不是我们想要的[1*8400*85]格式,
经典YOLOv5 的输出格式为 [batch, num_anchors, nc+5],如[1*8400*85]其中:
前4个值:边界框 (x_center, y_center, width, height)
第5个值:目标置信度
后80个值:类别概率
如果是自己数据,类别为7,那么最后值应该是4+1+7=12
https://netron.app/可以直接查看导出的onnx结构、输入输出
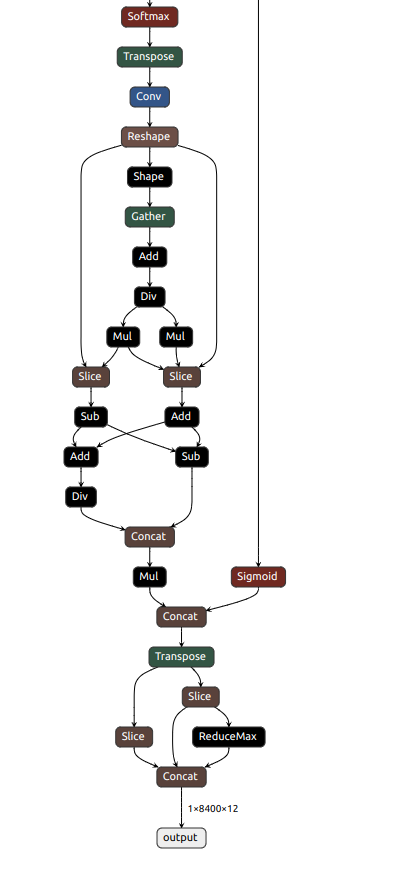
2.训练
现在训练yolo系列很简单了,导入库、准备好数据、迁移学习就行
如果没有GPU环境可以下载官方docker,已经有的话直接pip install ultralytics即可:
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
#model = YOLO("yolov5n.pt")
#model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
#model = YOLO("yolo11n.pt")
model = YOLO("yolov12n.pt") # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
# Train the model
results = model.train(data="data.yaml", epochs=100, imgsz=640)
#data.yaml cfg如下
path: /path_to/datasets/data
train: images/train # 训练集图像路径
val: images/val # 验证集图像路径
test: images/test # 测试集路径(可选)
#nc: 7
# 类别数量及名称
names:
0: aaa
1: bbb
2: ccc
3: ddd
4: eee
5: fff
6: ggg
3.部署
最新的导出代码如下,这种结果是封装好的:
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
model = YOLO("path/to/your/best.pt") # load a custom trained model
# Export the model
model.export(format="onnx")
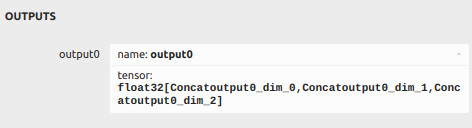
(以下内容节选)
如果想要以前的那种输出[batch, num_anchors,nc+5],可以加一段预处理再导出我们想要的格式:
# 确保模型处于评估模式
model.model.eval()
# 自定义转换模块
class OutputAdapter(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model):
super().__init__()
self.model = model
# 直接从模型中获取类别数量
self.nc = model.model[-1].nc # 获取最后一层(检测头)的类别数
def forward(self, x):
# 获取原始输出
raw_output = self.model(x)
# 处理可能的元组输出情况
if isinstance(raw_output, tuple):
# YOLOv8可能返回多个输出,我们只需要第一个(检测结果)
output = raw_output[0] # 提取第一个输出(主要检测结果)
else:
output = raw_output # 直接使用单个输出
# 原始输出应为张量:[batch, channels, num_predictions]
# 转换为:[batch, num_predictions, channels]
output = output.permute(0, 2, 1)
# 提取各组成部分
boxes = output[..., :4] # 边界框 (cx, cy, w, h)
class_probs = output[..., 4:4+self.nc] # 类别概率(根据实际类别数)
# 计算置信度(取各类别概率的最大值)
conf = torch.max(class_probs, dim=-1, keepdim=True).values
# 拼接为 [x_c, y_c, w, h, conf, cls_prob1, ..., cls_probN]
return torch.cat([boxes, conf, class_probs], dim=-1) # 形状 [1, 8400, 5+nc]
# 创建虚拟输入
dummy_input = torch.randn(1, 3, 640, 640)
# 封装模型
wrapped_model = OutputAdapter(model.model)
wrapped_model.eval() # 强制设置为评估模式
# 定义动态轴设置 - 这里我们设置为False(静态尺寸)
dynamic = False # 定义dynamic变量
test_output = wrapped_model(torch.randn(1, 3, 640, 640))
print("Test output shape:", test_output.shape)
#然后再导出onnx。
完整代码如下:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import os
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the YOLO11 model
model = YOLO('runs/train/yolov5/weights/best.pt')
# Export the model to ONNX format
# model.export(format="onnx") # creates 'onnx'
# 确保模型处于评估模式
model.model.eval()
# 自定义转换模块
class OutputAdapter(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model):
super().__init__()
self.model = model
# 直接从模型中获取类别数量
self.nc = model.model[-1].nc # 获取最后一层(检测头)的类别数
def forward(self, x):
# 获取原始输出
raw_output = self.model(x)
# 处理可能的元组输出情况
if isinstance(raw_output, tuple):
# YOLOv8可能返回多个输出,我们只需要第一个(检测结果)
output = raw_output[0] # 提取第一个输出(主要检测结果)
else:
output = raw_output # 直接使用单个输出
# 原始输出应为张量:[batch, channels, num_predictions]
# 转换为:[batch, num_predictions, channels]
output = output.permute(0, 2, 1)
# 提取各组成部分
boxes = output[..., :4] # 边界框 (cx, cy, w, h)
class_probs = output[..., 4:4+self.nc] # 类别概率(根据实际类别数)
# 计算置信度(取各类别概率的最大值)
conf = torch.max(class_probs, dim=-1, keepdim=True).values
# 拼接为 [x_c, y_c, w, h, conf, cls_prob1, ..., cls_probN]
return torch.cat([boxes, conf, class_probs], dim=-1) # 形状 [1, 8400, 5+nc]
# 创建虚拟输入
dummy_input = torch.randn(1, 3, 640, 640)
# 封装模型
wrapped_model = OutputAdapter(model.model)
wrapped_model.eval() # 强制设置为评估模式
# 定义动态轴设置 - 这里我们设置为False(静态尺寸)
dynamic = False # 定义dynamic变量
test_output = wrapped_model(torch.randn(1, 3, 640, 640))
print("Test output shape:", test_output.shape)
# 导出ONNX模型
torch.onnx.export(
wrapped_model,
dummy_input,
"yolov5_custom.onnx",
input_names=["images"],
output_names=["output"],
opset_version=12,
dynamic_axes={
'images': {0: 'batch_size'},
'output': {0: 'batch_size', 1: 'num_boxes'}
} if dynamic else None # 根据dynamic变量决定是否使用动态轴
)
print("ONNX模型导出成功!")
4.预测预处理
def postprocess(self, out):
# 获取batch中的第一个结果
batch_output = out[0] # [25200, 85]
# 筛选置信度高于阈值的预测
conf_mask = batch_output[:, 4] > self.config.confidence.thresh
preds = batch_output[conf_mask]
if preds.size == 0:
return np.array([]), np.array([]), np.array([])
# 计算调整后的置信度 = obj_conf * max_cls_conf
class_confs = preds[:, 5:]
max_class_conf = np.max(class_confs, axis=1)
adjusted_conf = preds[:, 4] * max_class_conf
# 获取边界框
bboxes = bbox_cxywh_to_xyxy(preds[:, :4])
# 获取类别
class_ids = np.argmax(class_confs, axis=1)
return class_ids, adjusted_conf, bboxes
5.预处理模型配置
yolov5:
不需要归一化
{
"base": {
"framework": "onnx",
"model_name": "yolov5",
"model_root": null,
"model_path": "YOLOV8/yolov5/yolov5.onnx",
"gpu_id": 0,
"mean": [
0.0,
0.0,
0.0
],
"std": [
1.0,
1.0,
1.0
],
"input_names": [
"images"
],
"input_shape": [
[
1,
3,
640,
640
]
],
"output_shape": null,
"output_names": [
"output"
],
"asnumpy": true,
"dtype": "float32",
"enable_batch_inference": false,
"extensions": false,
"encrypted": true,
"tensorrt": {
"calib": {
"batch_size": 32,
"input_shape": [
3,
224,
224
],
"max_samples": null,
"calib_data": null,
"cache_file": null,
"mean": [
0.0,
0.0,
0.0
],
"std": [
1.0,
1.0,
1.0
]
},
"dynamic_shapes": null
}
},
"task": "detect",
"task_inputs": [
"image",
"bbox"
],
"task_outputs": [
"label",
"confidence",
"bbox"
],
"save_dir": "results",
"image_dir": "figures",
"data_processor": "YOLOV5",
"normalize": true,
"patches": null,
"keep_ratio": true,
"bbox_resize_scale": 1.0,
"merge_batch_result": true,
"label": {
"target_name": null,
"target_num": null
},
"confidence": {
"thresh": 0.3
},
"keypoint_confidence": {
"thresh": 0.3
},
"bbox": {
"h_range": null,
"w_range": null,
"area_range": null,
"aspect_ratio_range": null,
"nms_thresh": 0.45,
"nms_topk": 100
},
"rbbox": {
"h_range": null,
"w_range": null,
"area_range": null,
"aspect_ratio_range": null,
"nms_thresh": 0.45,
"nms_topk": 100
},
"mask": {
"thresh": 0.3,
"return_type": "mask",
"fast_resize": false,
"nms_thresh": null
},
"semantic_mask": {
"thresh": 0.3,
"fallback": -1
},
"class_names": [
"your_label",
],
"_BaseModel_": "infer.detect.DetectBase",
"_version_": "3.3.0"
}
yolov8:
{
"base": {
"framework": "onnx",
"model_name": "yolov8",
"model_root": null,
"model_path": "YOLOV8/yolov8/yolov8_custom.onnx",
"gpu_id": 0,
"mean": [
0.485,
0.456,
0.406
],
"std": [
0.229,
0.224,
0.225
],
"input_names": [
"images"
],
"input_shape": [
[
1,
3,
640,
640
]
],
"output_shape": [
1,
8400,
12
],
"output_names": [
"output"
],
"asnumpy": true,
"dtype": "float32",
"enable_batch_inference": true,
"extensions": false,
"encrypted": true,
"tensorrt": {
"calib": {
"batch_size": 32,
"input_shape": [
3,
640,
640
],
"max_samples": null,
"calib_data": null,
"cache_file": null,
"mean": [
0.0,
0.0,
0.0
],
"std": [
1.0,
1.0,
1.0
]
},
"dynamic_shapes": null
}
},
"task": "detect",
"task_inputs": [
"image",
"bbox"
],
"task_outputs": [
"label",
"confidence",
"bbox"
],
"save_dir": "results",
"image_dir": "figures",
"data_processor": "YOLOV5",
"normalize": true,
"patches": null,
"keep_ratio": true,
"bbox_resize_scale": 1.0,
"merge_batch_result": true,
"label": {
"target_name": null,
"target_num": null
},
"confidence": {
"thresh": 0.1
},
"keypoint_confidence": {
"thresh": 0.3
},
"bbox": {
"h_range": null,
"w_range": null,
"area_range": null,
"aspect_ratio_range": null,
"nms_thresh": 0.6,
"nms_topk": 100
},
"rbbox": {
"h_range": null,
"w_range": null,
"area_range": null,
"aspect_ratio_range": null,
"nms_thresh": 0.45,
"nms_topk": 100
},
"mask": {
"thresh": 0.3,
"return_type": "mask",
"fast_resize": false,
"nms_thresh": null
},
"semantic_mask": {
"thresh": 0.3,
"fallback": -1
},
"class_names": [
"your_label"
],
"_BaseModel_": "infer.detect.DetectBase",
"_version_": "3.3.0"
}























 1269
1269

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








