1.概述
对Linux memory子系统有基本了解的都知道,linux内核通过LRU管理物理内存,不知道是否有思考过如下问题:LRU是全局一套,还是说每个memory cgroup拥有单独的一套LRU链表?直接揭晓答案:每个memory cgroup都会单独的LRU链表
2.怎么查到memcg对应的LRU链表
内核5.15可通过mem_cgroup_lruvec获得mem_cgroup对应的lru链表,函数定义在内核include/linux/memcontrol.h:

首先从memcg的nodeinfo中获取一个mem_cgroup_per_node指针 mz,mz中可以取到lruvec,所以关键就是分析memcg->nodeinfo是什么初始化的,答案是:这个memcg 创建的时候就需要初始化nodeinfo,而memcg初始化是在mem_cgroup_alloc函数中,所以接下来重点分析此函数。
3. memcg对应的LRU链表是什么时候初始化的
mem_cgroup_alloc --->alloc_mem_cgroup_per_node_info
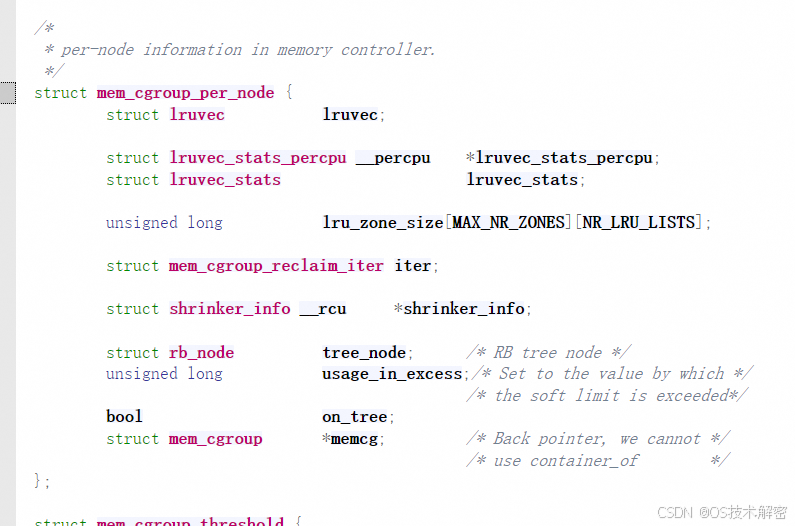
可以看到在cgroup创建的时候,调用到mem_cgroup_alloc,进而调用alloc_mem_cgroup_per_node_info,然后memcg->nodeinfo[node] = pn和lruvec_init(&pn->lruvec)初始化了一套LRU链表,然后使用的时候通过mem_cgroup_lruvec取到这里初始化的lruvec,lruvec就包含了inactive file/active file, inactive anon,active anon等各种LRU链表,数据结构如下:























 1804
1804

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








