std::condition_variable cvWaitThread;
int a = 100;
std::mutex mt;
void tt()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lc(mt);
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
{
Sleep(1000);
printf("tt-%d\n",i);
}
}
void tt3()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 15; i++)
{
Sleep(1000);
printf("tt3-%d\n", i);
}
a = 10;
cvWaitThread.notify_all();
}
int main()
{
thread t(tt);
t.detach();
Sleep(2000);
thread t2(tt3);
t2.detach();
{
cout << "尝试锁住\n";
std::unique_lock<mutex>lc(mt);
cout << "已经锁住,等待条件\n";
cvWaitThread.wait(lc, []() {return a == 10; });
cout << "hello world 1\n";
}
{
cout << "尝试锁住\n";
std::unique_lock<mutex>lc(mt);
cout << "已经锁住,等待条件\n";
cvWaitThread.wait(lc, []() {return a == 10; });
cout << "hello world 2\n";
}
{
cout << "尝试锁住\n";
std::unique_lock<mutex>lc(mt);
cout << "已经锁住,等待条件\n";
cvWaitThread.wait(lc, []() {return a == 10; });
cout << "hello world 3\n";
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结果:
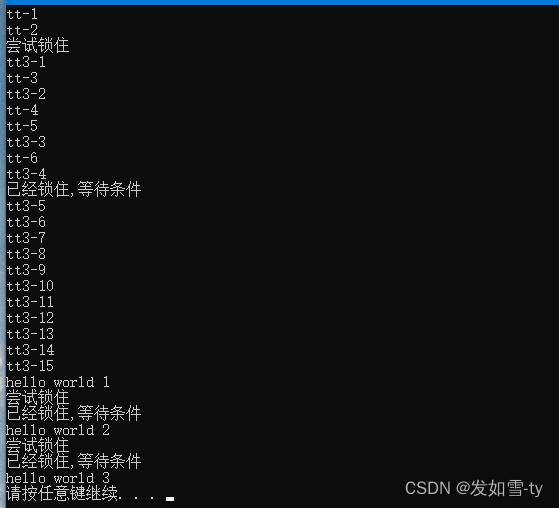
结论:如果当前锁已经被其它线程锁住,那么锁的时候会等待,直到其它线程释放锁。





 博客给出结论,在C++中若当前锁已被其他线程锁住,进行加锁操作时会等待,直至其他线程释放该锁。
博客给出结论,在C++中若当前锁已被其他线程锁住,进行加锁操作时会等待,直至其他线程释放该锁。

















 8402
8402

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










