目录
导入
为什么要学习pandas
numpy已经能够帮助我们处理数据,能够结合matplotlib解决我们数据分析的问题,那么pandas学习的目的在什么地方呢?
numpy能够帮我们处理处理数值型数据,但是这还不够
很多时候,我们的数据除了数值之外,还有字符串,还有时间序列等
比如:我们通过爬虫获取到了存储在数据库中的数据
比如:之前youtube的例子中除了数值之外还有国家的信息,视频的分类(tag)信息,标题信息等
所以,numpy能够帮助我们处理数值,但是pandas除了处理数值之外(基于numpy),还能够帮助我们处理其他类型的数据
什么是pandas
pandas is an open source, BSD-licensed library providing high-performance, easy-to-use data structures and data analysis tools for the Python programming language.
pandas的基本操作
pandas的常用数据类型
1.Series 一维,带标签数组
2.DataFrame 二维,Series容器
pandas之Series创建
In [2]: import string
In [3]: import numpy as np
In [4]: import pandas as pd
In [5]: t=pd.Series(np.arange(10),index=list(string.ascii_uppercase[:10]))
In [6]: t
Out[6]:
A 0
B 1
C 2
D 3
E 4
F 5
G 6
H 7
I 8
J 9
dtype: int32
In [7]: type(t)
Out[7]: pandas.core.series.Series注意这样几个问题:
pd.Serises能干什么,能够传入什么类型的数据让其变为series结构
index是什么,在什么位置,对于我们常见的数据库数据或者ndarray来说,index到底是什么
如何给一组数据指定index
In [9]: #字典推导式创建一个字典,通过字典创建一个series,注意其中的索引就是字典的键
In [10]: a={string.ascii_uppercase[i]:i for i in range(10)}
In [11]: a
Out[11]:
{'A': 0,
'B': 1,
'C': 2,
'D': 3,
'E': 4,
'F': 5,
'G': 6,
'H': 7,
'I': 8,
'J': 9}重新给其制定其他的索引之后,如果能够对应上,就取其值,如果不能,就返回Nan
为什么类型是float呢,pandas会自动根据数据类型更改series的dtype类型
In [14]: pd.Series(a,index=list(string.ascii_uppercase[5:15]))
Out[14]:
F 5.0
G 6.0
H 7.0
I 8.0
J 9.0
K NaN
L NaN
M NaN
N NaN
O NaN
dtype: float64
#重新给其制定其他的索引之后,如果能够对应上,就取其值,如果不能,就返回Nan
#为什么类型是float呢,pandas会自动根据数据类型更改series的dtype类型pandas之Series切片和索引
In [15]: t
Out[15]:
A 0
B 1
C 2
D 3
E 4
F 5
G 6
H 7
I 8
J 9
dtype: int32
In [16]: t[2:10:2]
Out[16]:
C 2
E 4
G 6
I 8
dtype: int32
In [17]: t[2:10:2] # 索引2-10,以2为步长
Out[17]:
C 2
E 4
G 6
I 8
dtype: int32
In [18]: t[1] #索引下标为1的值
Out[18]: 1
In [20]: t[[2,3,6]] #索引下标为2 3 6的值
Out[20]:
C 2
D 3
G 6
dtype: int32
In [21]: t[t>4]
Out[21]:
F 5
G 6
H 7
I 8
J 9
dtype: int32
In [22]: t["F"] #指定索引值为F对应的值
Out[22]: 5
In [23]: t[["A","F","g"]] #指定索引值为AFg对应的值 没有个所以返回nan
E:\ProgramData\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\series.py:851: FutureWarning:
Passing list-likes to .loc or [] with any missing label will raise
KeyError in the future, you can use .reindex() as an alternative.
See the documentation here:
https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#deprecate-loc-reindex-listlike
return self.loc[key]
Out[23]:
A 0.0
F 5.0
g NaN
dtype: float64切片:直接传入start end或者步长即可
索引:一个的时候直接传入序号或者index 多个的时候传入序号或者index的列表
对于一个陌生的series类型,我们如何知道他的索引和具体的值呢?
In [24]: t.index
Out[24]: Index(['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J'], dtype='object')
In [25]: t.values
Out[25]: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
In [26]: type(t.index)
Out[26]: pandas.core.indexes.base.Index
In [27]: type(t.values)
Out[27]: numpy.ndarraySeries对象本质上由两个数组成
一个数组构成对象的键(index、索引),一个数组构成对象的值(values) 键—>值
ndarrary的很多方法都可以运用于series类型,比如argmax,clip
series具有where方法,但是结果和ndarray不同
pandas之读取外部数据
现在假设我们有一个组关于狗的名字的统计数据,那么为了观察这组数据的情况,我们应该怎么做呢?
数据来源:https://www.kaggle.com/new-york-city/nyc-dog-names/data
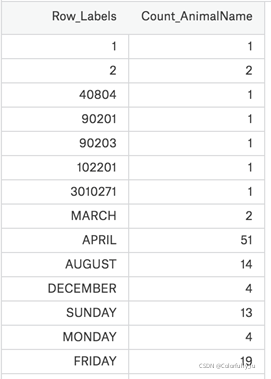
我们的这组数据存在csv





 本文详细介绍了Pandas库的使用,包括为什么要学习Pandas、Pandas的基本操作如Series和DataFrame的创建、切片、索引,以及数据处理、统计方法、数据合并等。通过实例展示了读取CSV数据、处理缺失数据、数据排序、布尔索引等功能,是学习Pandas的实用教程。
本文详细介绍了Pandas库的使用,包括为什么要学习Pandas、Pandas的基本操作如Series和DataFrame的创建、切片、索引,以及数据处理、统计方法、数据合并等。通过实例展示了读取CSV数据、处理缺失数据、数据排序、布尔索引等功能,是学习Pandas的实用教程。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1108
1108

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








