作者 | 南木 编辑 | 自动驾驶之心
原文链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/18239422064
点击下方卡片,关注“自动驾驶之心”公众号
戳我-> 领取自动驾驶近15个方向学习路线
本文只做学术分享,如有侵权,联系删文

0.1 什么是端到端?
首先定义端到端,当然有很多说法。我觉得,起码说相对于分阶段而言,规划不只是根据感知和预测的结果,而是其隐特征。进一步说,在前传和反传,planning可以直接触及输入信息。
0.2 为什么做端到端?
① 优势一:应对场景更多样;
② 优势二:上游出错的结果,不一定影响下游的planning;比如,如果看tesla的有些视频,就是这样,明显感知出错了,不影响planning;
③ 优势三,性能天花板够高,模型设计空间大:比如可以和大模型结合;比如,可以和无监督训练结合。因为,无监督,说明特征无倾向;数据量够大,说明特征泛化好。那分阶段的,一般是有监督训练,当然也可以无监督做个backbone,但还是需要有监督再调;
1、端到端技术路线划分及代表工作
① 直接端到端:就是说,不需要中间感知预测模块,比如mile、driveworld、dreamer-v1、dreamer-v2、sem2、bevplanner、transfuser、driveTransformer;可能需要监督,也可能不需要监督,但是,都没有中间模块了;
② 模块化端到端:以UniAD为代表,FusionAD,VAD,GenAD,都是;
③ 大语言模型路线:drive like a human, driveGPT4, LMDrive, EMMA,Senna;我认为是,这条路线在NLP和多模态的成功,具有启发意义;
④ 基于world model的路线:world models,dreamer-V1\V2, sem2,mile,driveworld, 这些的状态转移,其实就是world model。但是现在所说的world model,比如gaia-1, drivewm, 其实可以和端到端模型结合,比如drivewm做了一个比较粗糙的结合。我认为是趋势,是未来。
⑤ 基于Diffusion的路线:以DiffusionDrive为例;
按照学习范式,又可分为模仿学习和强化学习,这两个并不冲突,可以一起用。
以上,仅为梳理方便而人为划分,仅供参考。角度不同,划分也不同。我认为,每个研究领域都有其自己的生命力,不可硬性分为几个set的。
2、路线分析
2.1 直接端到端 和 模块化端到端 的对比
直接端到端,由传感器信息直接映射到action或者轨迹。由于action或轨迹都太稀疏,训练较为困难,因此,这条路线一般辅以感知的监督训练,如bevseg、occ、车道线、红绿灯等。比如mile、driveworld、dreamer-v1、dreamer-v2、sem2、bevplanner、transfuser、driveTransformer.
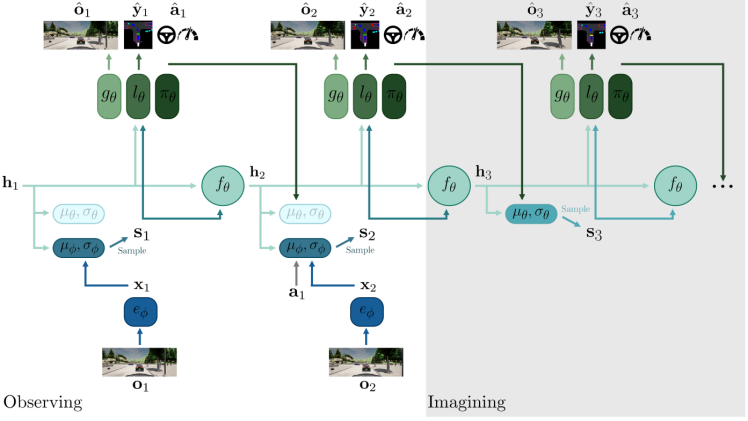
模块化端到端,传感器信息,经过若干感知模块,映射为action或轨迹。不同模块间可传梯度,共同训练。其类似于传统的分阶段自动驾驶,不过是把不同阶段通过transformer中的query机制连接. 以UniAD为代表,FusionAD,VAD,GenAD,都是;
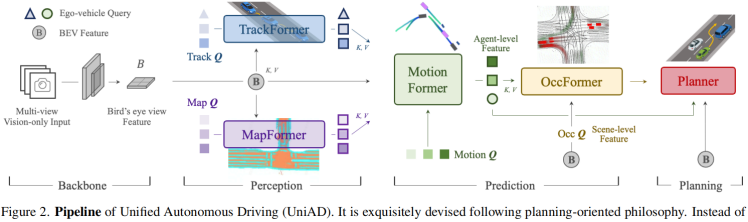
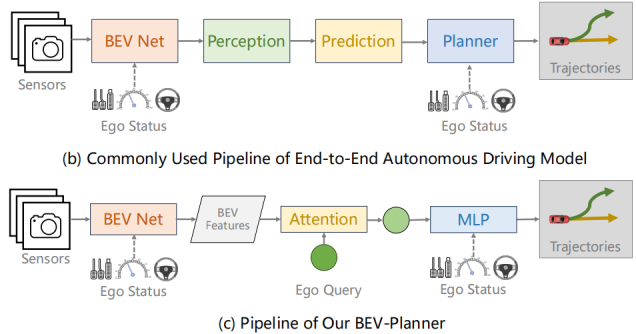
对比可知,由于现有直接端到端也会辅以感知的监督,直接端到端和模块化端到端的共同点是都需要感知监督。不同的是,直接端到端是并联形式,也就是基于共同的表征feature map,来学习感知和规划;模块化端到端的主线是串联形式,还是依赖于感知结果的。
因此,我认为是直接端到端的天花板更高,而模块化端到端更好训练一些。因为模块化端到端的中间模块,就是通过对应的感知,释加显示的约束,减小求解空间,那这带来的好处就是好训练,不好就是可能把更有效的规划结果给约束掉了。虽然直接端到端也辅以感知,但毕竟是隐式的,也就是感知是为了学习feature map, 规划还是直接基于feature map的。
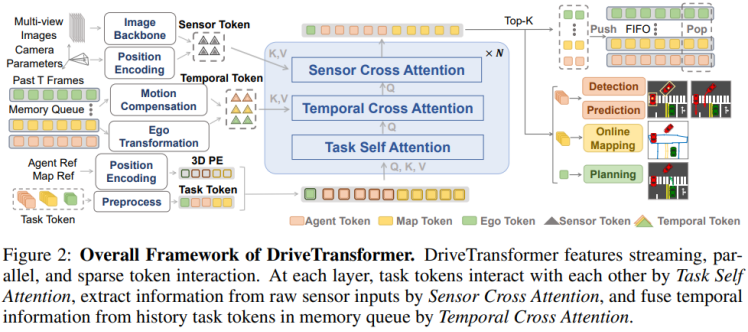
我认为这两条路线,没有本质区别,只是技术发展的一个顺序:模块化更好训,但最终收敛到直接端到端。但达到更好效果,还有不少工作要做。
2.2 基于VLM或LLM的端到端方案
比如drive like a human, driveGPT4, LMDrive, EMMA,Senna。
首先,我觉得VLM或LLM是有用的。
因为LLM或VLM,复杂场景理解、推理能力,这是很强的。另外一方面,在自动驾驶里,对于轨迹解释、VQA等,可能只能用VLM这样的技术来做。
但是,具体怎么用?是直接替代模块化端到端,还是和他们结合?我认为是后者。
VLM擅长场景理解和推理。所以在复杂场景,模块化端到端可能就傻眼了;VLM呢,泛化能力强,还能有个基本的场景理解。所以这些场景,VLM出决策建议,或者粗轨迹给模块化的端到端,或者直接给下游,应该是很有用的。
(1)双流架构的模型:
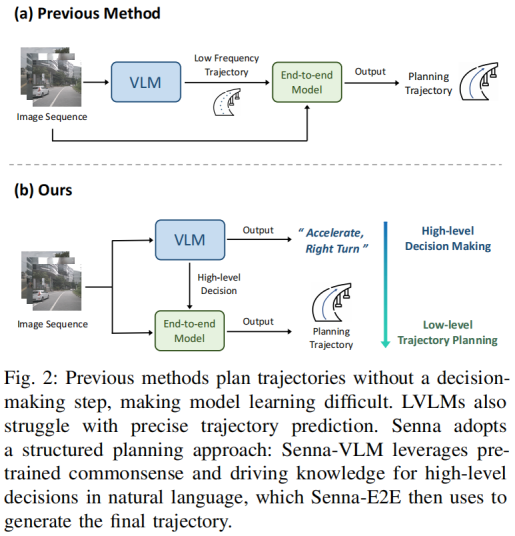
也就是一个运行快的模型,和一个运行慢的模型,并行运行;至于二者怎么分工和交互,每个工作各有所长,这个细节可以在讨论。相关工作,比如 DriveVLM、LeapAD、AsyncDriver。On the road虽然没做,但在future work中提到了感知部分需要融合传统方案和VLM方案的双流构思。Senna是做端到端规划,其逻辑和思想,与On the road一致。On the road和Senna都认为,VLM适合粗粒度的场景理解和推理,应结合具体任务的模型,实现专家模型泛化能力的增强。我个人非常赞同这个观点。
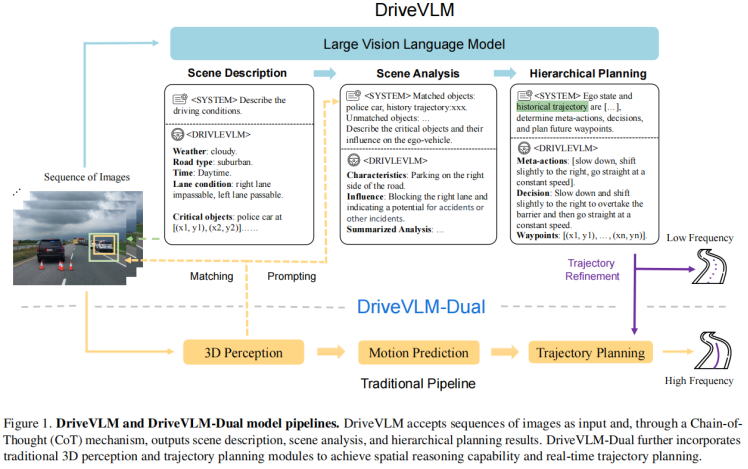
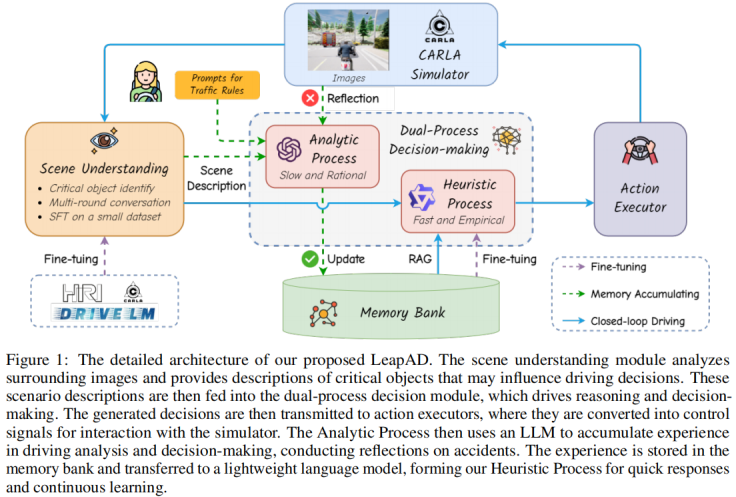
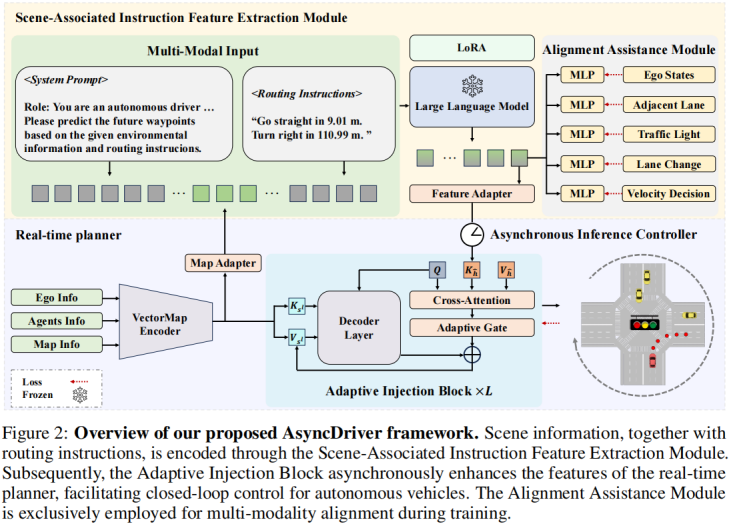
2024.06, Asynchronous Large Language Model Enhanced Planner for Autonomous Driving,和DriveVLM不同的是:这里的两个系统是做自适应融合,而DriveVLM是做switch.
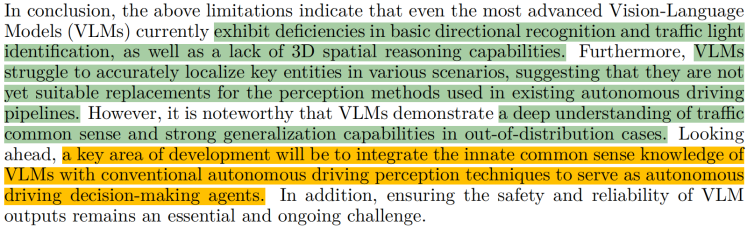
2023.11, On the Road with GPT-4V(ision): Explorations of Utilizing Visual-Language Model as Autonomous Driving Agent的conclusion部分, 总结的特别好:VLM适合粗粒度的场景理解和推理,可和具体任务模型(专家模型)结合,发挥二者优势。
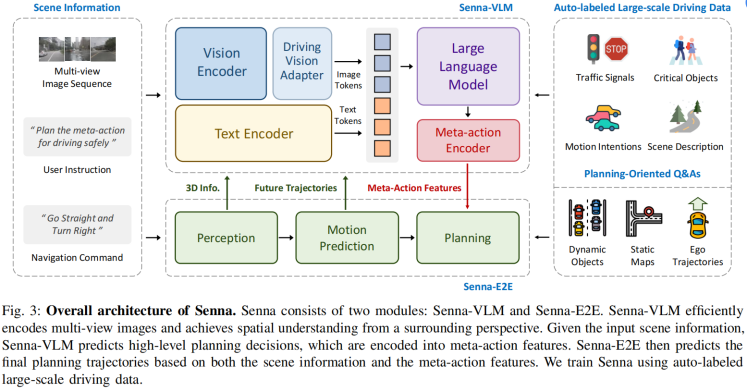
(2)3D信息:
有几篇工作,支撑需要3D信息的观点。至于这个3D,是显式的监督信息带来的,还是2D自监督带来的(如dinov2),是可以讨论的。比如"Is a 3D-Tokenized LLM the Key to Reliable Autonomous Driving? "、”Language-Image Models with 3D Understanding(Cube-LLM)“、”On the Road with GPT-4V(ision): Explorations of Utilizing Visual-Language Model as Autonomous Driving Agent“。前两篇,是正向支撑,证明了加了3D比较好;第三篇是反向支撑,证明没有3D的定位和空间推理能力弱。
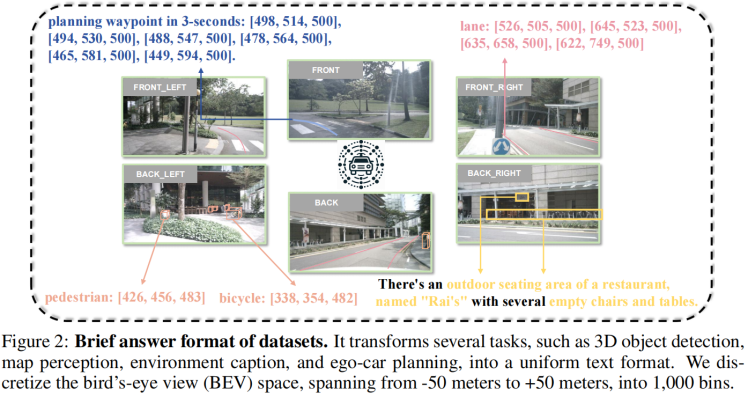
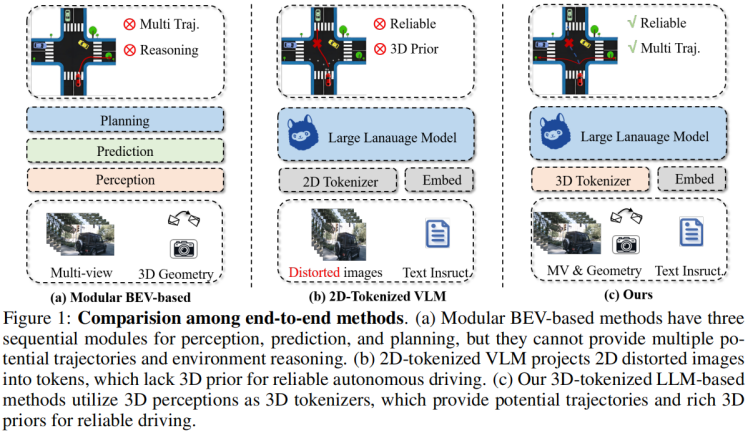
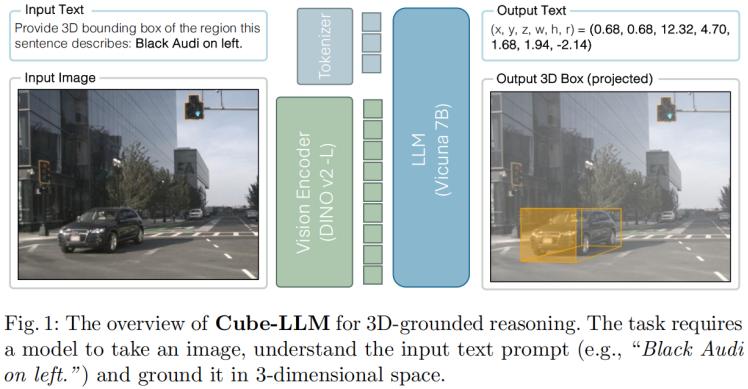
(3)总结:
总的来说,这条路线的发展趋势可能是:①和非大语言模型的方案形成双流架构;② 补充3D信息。
此外,On the Road with GPT-4V 和 Image Textualization这两篇论文都提到,现在VLM对环境的感知,属于粒度比较粗的场景理解。
当然,如 Image Textualization这样的方法,正在弥补VLM在细粒度问题上的不足。这条路线值得一直关注。
2.3 基于world model的端到端路线
World Model分为两类:端到端自动驾驶模型中的world model,数据生成中的world model。
world model的定义:
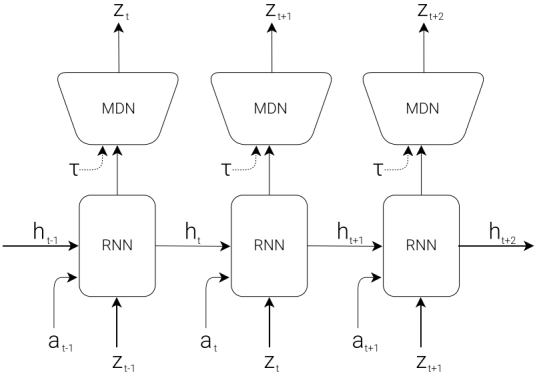
World Model要具备三个属性:预测、表征、可控。
(1)端到端自动驾驶模型中的world model
用于开车:探讨世界模型的集成如何使自动驾驶汽车能够预测并制定行动策略?
比如早期的world models,dreamr-V1, dream-V2, sem2, Fiery,mile, 近期的DriveWorld,以Mile为代表:
https://wayve.ai/thinking/learning-a-world-model-and-a-driving-policy/
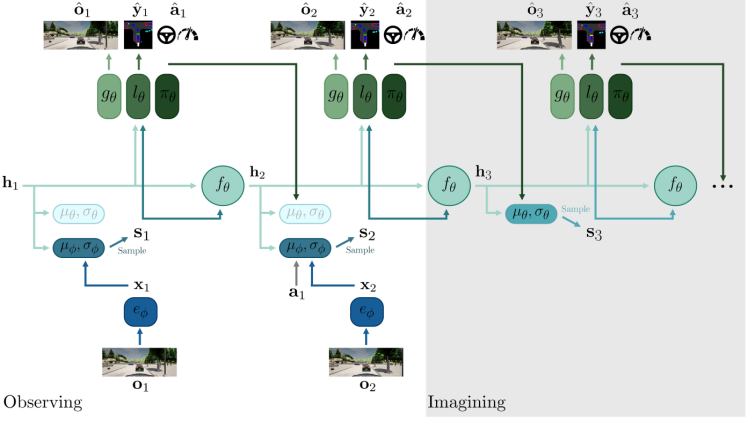
但是这条路线,好像是用到机器人的偏多,,,用到智驾有一个明显问题:累计误差。
目前,智驾领域的World Model,一般指基于action条件的驾驶场景数据生成。
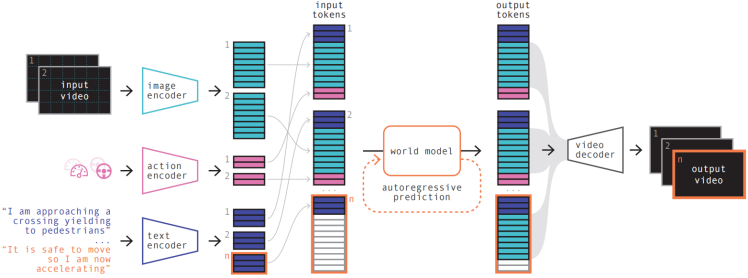
(2)数据生成中的world model
用于数据生成和驾驶行为理解:corner case的数据生成,模型或人类驾驶行为的理解
以GAIA-1为代表:
https://wayve.ai/thinking/scaling-gaia-1/
(3)二者的统一:Foundation Model
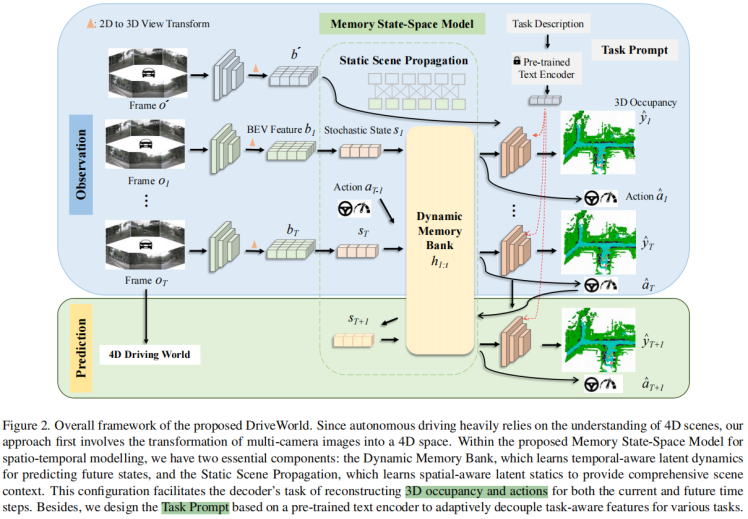
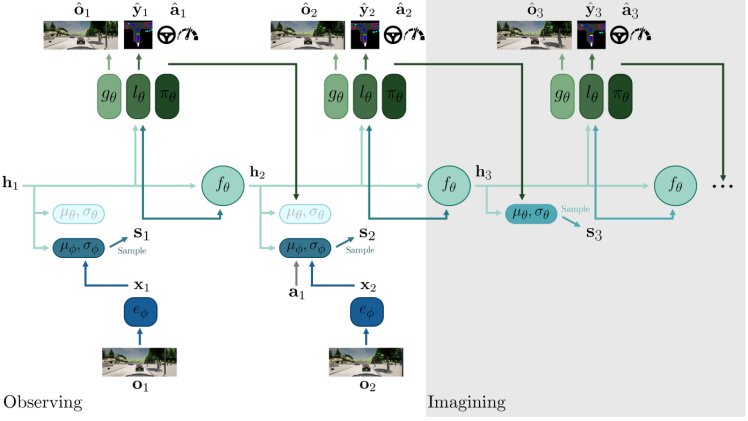
将生成和规划合二为一的,基本都可以作为foundation model。这类工作有个共性,就是生成的对象是有语义信息和几何信息的。按道理,也只有这样才能做规划。比如,Driveworld是生成Occ; Mile是生成BevSeg图。
值得说明,Mile本身不是Foundation model,但其范式非常具备自动驾驶Foundation Model的潜力。Mile是一篇非常好的学术工作,指的不是性能好,而是启发性强。后期很多端到端的工作,都有Mile的影子。DriveWorld里的MSSM和Mile也类似。
(4)总结world model的用处:
第一个是:端到端出planning或action
第二个是:数据生成,可控数据生成,corner case数据生成;给训练感知或端到端自动驾驶模型用;
第三个是:真实场景的闭环仿真系统,采集数据、评估模型、驾驶行为理解;
第四个是:Foundation Model。也就是基于这个模型,做一系列下游任务。这种范式的工作并不多,代表性的是DriveWorld。个人猜测特斯拉是基于worldmodel,,,因为tesla这么大的算力,我想不是训练模块化端到端,也不是训练VLM,,只有world model匹配如此大算力。仅为个人猜测。
个人认为:虽然这两年是模块化端到端和VLM端到端热闹,过两年可能就是world model了;world model是非常具备潜力的方向,端到端可以看做是world model的子集。
2.4 基于Diffusion的端到端路线
这方面看的不多,以DiffusionDrive举例
Motivation:扩散模型已被证明是机器人领域一种强大的生成决策策略;而扩散本身是连续空间的问题,和轨迹规划更契合,但Diffusion用于规划,不能实时;
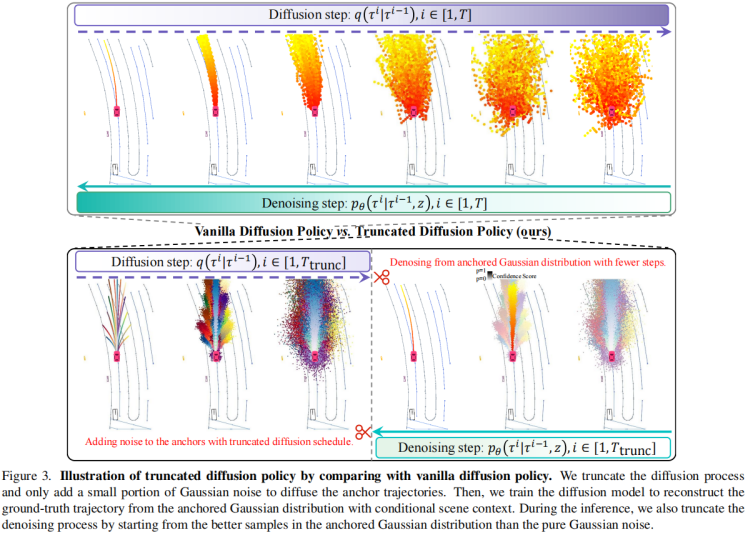
直接把Transfuser里的planning decoder换成diffusion,有两个问题:模式坍塌、时间太长;
因此提出,Truncated Diffusion:
① 添加anchor的概念,基于anchor做扩散;
② 前向扩散,只添加小部分高斯噪声,不要到全部是高斯噪声;
③ 其他细节:前向diffusion steps=50,反向denoising steps=2。
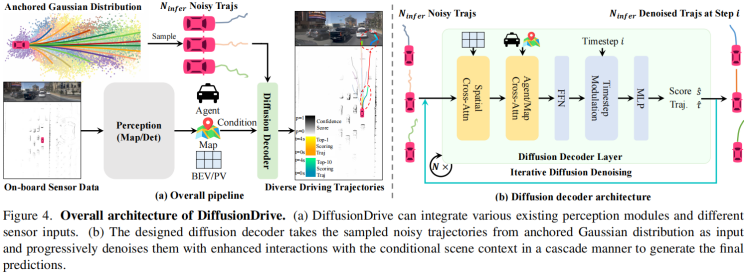
个人认为有两个地方疑惑:
消融实验,无从验证diffusion真正起到的作用;
为什么要用diffusion做规划?没有论述。个人认为,轨迹规划,本身可以看出是分布的问题,用Diffusion合情合理;但总感觉,杀鸡用牛刀,diffusion更适合分布复杂的情况,如图像生成、语音生成,而对于轨迹规划,可能不能凸显出diffusion的优势。
补充:基于Diffusion的方法,和前面所说的直接端到端、模块化端到端,甚至基于world model的端到端,不冲突,是结合使用的。简单说,就是把一步回归改为多步回归。
3、总结
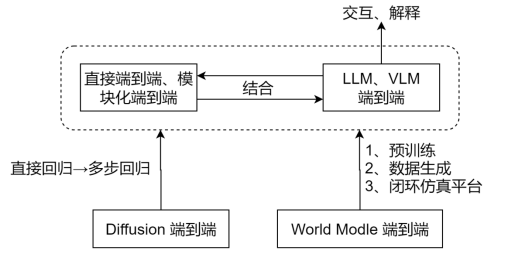
整体来说,这几条路线,统一大于对立。
参考文献:
(mile) Hu A, Corrado G, Griffiths N, et al. Model-based imitation learning for urban driving[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2022, 35: 20703-20716.
(Driveworld) Min C, Zhao D, Xiao L, et al. Driveworld: 4d pre-trained scene understanding via world models for autonomous driving[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2024: 15522-15533.
(Dreamer-v1) Hafner D, Lillicrap T, Ba J, et al. Dream to control: Learning behaviors by latent imagination[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.01603, 2019.
(Dreamer-v2) Hafner D, Lillicrap T, Norouzi M, et al. Mastering atari with discrete world models[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.02193, 2020.
(SEM2) Gao Z, Mu Y, Chen C, et al. Enhance sample efficiency and robustness of end-to-end urban autonomous driving via semantic masked world model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024.
(BevPlanner) Li Z, Yu Z, Lan S, et al. Is ego status all you need for open-loop end-to-end autonomous driving?[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2024: 14864-14873.
(TransFuser) Chitta K, Prakash A, Jaeger B, et al. Transfuser: Imitation with transformer-based sensor fusion for autonomous driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 45(11): 12878-12895.
(DriveTransformer) https://openreview.net/pdf?id=M42KR4W9P5
(UniAD) Hu Y, Yang J, Chen L, et al. Planning-oriented autonomous driving[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2023: 17853-17862.
(FusionAD) Ye T, Jing W, Hu C, et al. Fusionad: Multi-modality fusion for prediction and planning tasks of autonomous driving[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.01006, 2023.
(VAD) Jiang B, Chen S, Xu Q, et al. Vad: Vectorized scene representation for efficient autonomous driving[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 2023: 8340-8350.
(GenAD) Zheng W, Song R, Guo X, et al. Genad: Generative end-to-end autonomous driving[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Cham, 2025: 87-104.
(Drive like a human) Fu D, Li X, Wen L, et al. Drive like a human: Rethinking autonomous driving with large language models[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. 2024: 910-919.
(DriveGPT4) Xu Z, Zhang Y, Xie E, et al. Drivegpt4: Interpretable end-to-end autonomous driving via large language model[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2024.
(LMDrive) Shao H, Hu Y, Wang L, et al. Lmdrive: Closed-loop end-to-end driving with large language models[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2024: 15120-15130.
(EMMA) Hwang J J, Xu R, Lin H, et al. Emma: End-to-end multimodal model for autonomous driving[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.23262, 2024.
(Senna) Jiang B, Chen S, Liao B, et al. Senna: Bridging large vision-language models and end-to-end autonomous driving[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.22313, 2024.
(World Models) Ha D, Schmidhuber J. World models[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.10122, 2018.
(Gaia-1) Hu A, Russell L, Yeo H, et al. Gaia-1: A generative world model for autonomous driving[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.17080, 2023.
(DriveWM) Wang Y, He J, Fan L, et al. Driving into the future: Multiview visual forecasting and planning with world model for autonomous driving[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2024: 14749-14759.
(DiffusionDrive) Liao B, Chen S, Yin H, et al. DiffusionDrive: Truncated Diffusion Model for End-to-End Autonomous Driving[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.15139, 2024.
(DriveVLM) Tian X, Gu J, Li B, et al. Drivevlm: The convergence of autonomous driving and large vision-language models[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.12289, 2024.
(LeapAD) Mei J, Ma Y, Yang X, et al. Continuously Learning, Adapting, and Improving: A Dual-Process Approach to Autonomous Driving[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.15324, 2024.
(AsyncDriver) Chen Y, Ding Z, Wang Z, et al. Asynchronous large language model enhanced planner for autonomous driving[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Cham, 2025: 22-38.
(On the road) Wen L, Yang X, Fu D, et al. On the road with gpt-4v (ision): Early explorations of visual-language model on autonomous driving[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.05332, 2023.
(3D-Tokenized LLM) Bai Y, Wu D, Liu Y, et al. Is a 3D-Tokenized LLM the Key to Reliable Autonomous Driving?[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.18361, 2024.
(Cube-LLM) Cho J H, Ivanovic B, Cao Y, et al. Language-Image Models with 3D Understanding[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.03685, 2024.
(Image Textualization) Pi R, Zhang J, Zhang J, et al. Image Textualization: An Automatic Framework for Creating Accurate and Detailed Image Descriptions[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.07502, 2024.
(Fiery) Hu A, Murez Z, Mohan N, et al. Fiery: Future instance prediction in bird's-eye view from surround monocular cameras[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 2021: 15273-15282.
① 自动驾驶论文辅导来啦

② 国内首个自动驾驶学习社区
『自动驾驶之心知识星球』近4000人的交流社区,已得到大多数自动驾驶公司的认可!涉及30+自动驾驶技术栈学习路线,从0到一带你入门自动驾驶感知(端到端自动驾驶、世界模型、仿真闭环、2D/3D检测、语义分割、车道线、BEV感知、Occupancy、多传感器融合、多传感器标定、目标跟踪)、自动驾驶定位建图(SLAM、高精地图、局部在线地图)、自动驾驶规划控制/轨迹预测等领域技术方案、大模型,更有行业动态和岗位发布!欢迎扫描加入

③全网独家视频课程
端到端自动驾驶、仿真测试、自动驾驶C++、BEV感知、BEV模型部署、BEV目标跟踪、毫米波雷达视觉融合、多传感器标定、多传感器融合、多模态3D目标检测、车道线检测、轨迹预测、在线高精地图、世界模型、点云3D目标检测、目标跟踪、Occupancy、CUDA与TensorRT模型部署、大模型与自动驾驶、NeRF、语义分割、自动驾驶仿真、传感器部署、决策规划、轨迹预测等多个方向学习视频(扫码即可学习)

④【自动驾驶之心】全平台矩阵





















 769
769

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








