前言
RocketMQ的API实战实例,需要引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.rocketmq</groupId>
<artifactId>rocketmq-client</artifactId>
<version>5.1.4</version>
</dependency>
一、客户端消息确认机制
消息生产者分别通过三种方式发送消息:
- 单向发送:只负责发送消息,不管是否接收
public class OnewayProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//使用生产者组名称进行实例化。
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer("please_rename_unique_group_name");
// 指定名称服务器地址。
producer.setNamesrvAddr("localhost:9876");
//启动实例。
producer.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
//创建消息实例,指定主题、标签和消息正文。
Message msg = new Message("TopicTest" /* Topic */,
"TagA" /* Tag */,
("Hello RocketMQ " +
i).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8) /* Message body */
);
//调用 send message 将消息投递到其中一个 broker。
producer.sendOneway(msg);
}
//等待发送完成
Thread.sleep(5000);
producer.shutdown();
}
}
- 同步发送:等待消息返回再继续
/*
* 同步发送
* */
public class Producer {
public static final String PRODUCER_GROUP = "ProducerGroupName";
public static final String DEFAULT_NAMESRVADDR = "127.0.0.1:9876";
public static final String TOPIC = "TopicTest";
public static final String TAG = "TagA";
public static void main(String[] args) throws MQClientException, InterruptedException {
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer(PRODUCER_GROUP);
// namesrvAddr 应设置为您的本地地址
producer.setNamesrvAddr(DEFAULT_NAMESRVADDR);
producer.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 128; i++) {
try {
Message msg = new Message(TOPIC, TAG, "OrderID188", "Hello world".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));/
//同步发送可以接收到结果
SendResult sendResult = producer.send(msg);
System.out.printf("%s%n", sendResult);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
producer.shutdown();
}
}
- 异步发送:发送消息后,另启线程接收消息返回结果
/*
* 异步发送
* */
public class AsyncProducer {
public static final String TOPIC = "TopicTest";
public static void main(
String[] args) throws MQClientException, InterruptedException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer("Jodie_Daily_test");
producer.setNamesrvAddr("localhost:9876");
producer.start();
// 建议在流量较大的 enableBackpressureForAsyncMode 上启用,默认为 false
producer.setEnableBackpressureForAsyncMode(true);
producer.setRetryTimesWhenSendAsyncFailed(0);
int messageCount = 100;
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(messageCount);
for (int i = 0; i < messageCount; i++) {
try {
final int index = i;
Message msg = new Message(TOPIC,
"TagA",
"OrderID188",
"Hello world".getBytes(RemotingHelper.DEFAULT_CHARSET));
producer.send(msg, new SendCallback() {
//异步成功之后方法
@Override
public void onSuccess(SendResult sendResult) {
countDownLatch.countDown();
System.out.printf("%-10d OK %s %n", index, sendResult.getMsgId());
}
//异常方法
@Override
public void onException(Throwable e) {
countDownLatch.countDown();
System.out.printf("%-10d Exception %s %n", index, e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
countDownLatch.await(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
producer.shutdown();
}
}
消费者消费消息分两种:
- 拉模式:消费者主动去broker拉取消息
/*
* 拉模式消费消息
* 核心逻辑:循环一直拉取messageQueues,每次遍历获取32条数据,继续下一次messageQueue的消费位点(NextBeginOffset)
* */
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public class PullConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws MQClientException {
DefaultMQPullConsumer consumer = new DefaultMQPullConsumer("PullConsumerName1");
consumer.setNamesrvAddr("127.0.0.1:9876");
Set<String> topics = new HashSet<>();
//你最好注册 topic,它会在启动时使用 rebalance
topics.add("TopicTest");
consumer.setRegisterTopics(topics);
consumer.start();
ExecutorService executors = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(topics.size(), new ThreadFactoryImpl("PullConsumerThread"));
for (String topic : consumer.getRegisterTopics()) {
executors.execute(new Runnable() {
public void doSomething(List<MessageExt> msgs) {
//do your business
System.out.printf("%s Receive New Messages: %s %n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), msgs);
}
@Override
public void run() {
//循环一直拉取messageQueues,每次遍历获取32条数据,继续下一次messageQueue的消费位点(NextBeginOffset)
while (true) {
try {
Set<MessageQueue> messageQueues = consumer.fetchMessageQueuesInBalance(topic);
if (messageQueues == null || messageQueues.isEmpty()) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
continue;
}
PullResult pullResult = null;
for (MessageQueue messageQueue : messageQueues) {
try {
//获取messageQueue的偏移量
long offset = this.consumeFromOffset(messageQueue);
//设置了一次拉取的消息数量32
pullResult = consumer.pull(messageQueue, "*", offset, 32);
switch (pullResult.getPullStatus()) {
case FOUND:
List<MessageExt> msgs = pullResult.getMsgFoundList();
if (msgs != null && !msgs.isEmpty()) {
this.doSomething(msgs);
//更新 offset 到 本地内存,最终到 broker
consumer.updateConsumeOffset(messageQueue, pullResult.getNextBeginOffset());
//打印拉的TPS
this.incPullTPS(topic, pullResult.getMsgFoundList().size());
}
break;
case OFFSET_ILLEGAL:
consumer.updateConsumeOffset(messageQueue, pullResult.getNextBeginOffset());
break;
case NO_NEW_MSG:
Thread.sleep(1);
consumer.updateConsumeOffset(messageQueue, pullResult.getNextBeginOffset());
break;
case NO_MATCHED_MSG:
consumer.updateConsumeOffset(messageQueue, pullResult.getNextBeginOffset());
break;
default:
}
} catch (RemotingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (MQBrokerException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (MQClientException e) {
//reblance error
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public long consumeFromOffset(MessageQueue messageQueue) throws MQClientException {
//-1启动时
long offset = consumer.getOffsetStore().readOffset(messageQueue, ReadOffsetType.READ_FROM_MEMORY);
if (offset < 0) {
//来自 broker 的查询
offset = consumer.getOffsetStore().readOffset(messageQueue, ReadOffsetType.READ_FROM_STORE);
}
if (offset < 0) {
//First Time Start from Last Offset (第一次从最后一个偏移开始)
offset = consumer.maxOffset(messageQueue);
}
//确定
if (offset < 0) {
offset = 0;
}
return offset;
}
public void incPullTPS(String topic, int pullSize) {
consumer.getDefaultMQPullConsumerImpl().getRebalanceImpl().getmQClientFactory()
.getConsumerStatsManager().incPullTPS(consumer.getConsumerGroup(), topic, pullSize);
}
});
}
// executors.shutdown();
// consumer.shutdown();
}
}
- 推模式:broker向消费者主动推消息
/*
* 推模式消费消息
* */
public class PushConsumer {
public static final String TOPIC = "TopicTest";
public static final String CONSUMER_GROUP = "CONSUMER_GROUP_NAME1";
public static final String NAMESRV_ADDR = "127.0.0.1:9876";
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, MQClientException {
DefaultMQPushConsumer consumer = new DefaultMQPushConsumer(CONSUMER_GROUP);
consumer.setNamesrvAddr(NAMESRV_ADDR);
//消费者订阅topic
consumer.subscribe(TOPIC, "*");
//消费者消费起始位点offset //如果MessageQueue 的最小位点为0,则设置CONSUME_FROM_LAST_OFFSET也不会从最终消费位点消费,也会从头开始消费
consumer.setConsumeFromWhere(ConsumeFromWhere.CONSUME_FROM_LAST_OFFSET);
//错误的时间格式 2017_0422_221800
consumer.setConsumeTimestamp("20181109221800");
//注册监听器
consumer.registerMessageListener(new MessageListenerConcurrently() {
@Override
public ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus consumeMessage(List<MessageExt> msgs, ConsumeConcurrentlyContext context) {
System.out.printf("%s Receive New Messages: %s %n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), msgs);
return ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus.CONSUME_SUCCESS;
}
});
consumer.start();
System.out.printf("Consumer Started.%n");
}
}
二、广播消息
广播模式需要在消费者代码上设置MessageModel,默认是集群模式CLUSTERING
- MessageModel.BROADCASTING:广播消息。一条消息会发给所有订阅了对应主题的消费者,不管消费者是不是同一个消费者组。
- MessageModel.CLUSTERING:集群消息。每一条消息只会被同一个消费者组中的一个实例消费。
/*
* 广播模式
*
* */
public class PushConsumer {
public static final String CONSUMER_GROUP = "broadcast_CONSUMER_GROUP";
public static final String DEFAULT_NAMESRVADDR = "127.0.0.1:9876";
public static final String TOPIC = "TopicTestBroadcast";
public static final String SUB_EXPRESSION = "*";
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, MQClientException {
DefaultMQPushConsumer consumer = new DefaultMQPushConsumer(CONSUMER_GROUP);
// Uncomment the following line while debugging, namesrvAddr should be set to your local address
consumer.setNamesrvAddr(DEFAULT_NAMESRVADDR);
consumer.setConsumeFromWhere(ConsumeFromWhere.CONSUME_FROM_FIRST_OFFSET);
// 广播模式 MessageModel.BROADCASTING
//集群模式(默认) MessageModel.CLUSTERING
consumer.setMessageModel(MessageModel.BROADCASTING);
consumer.subscribe(TOPIC, SUB_EXPRESSION);
consumer.registerMessageListener((MessageListenerConcurrently) (msgs, context) -> {
System.out.printf("%s Receive New Messages: %s %n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), msgs);
return ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus.CONSUME_SUCCESS;
});
consumer.start();
System.out.printf("Broadcast Consumer Started.%n");
}
}
可以看到两个消费者实例都收到消息了
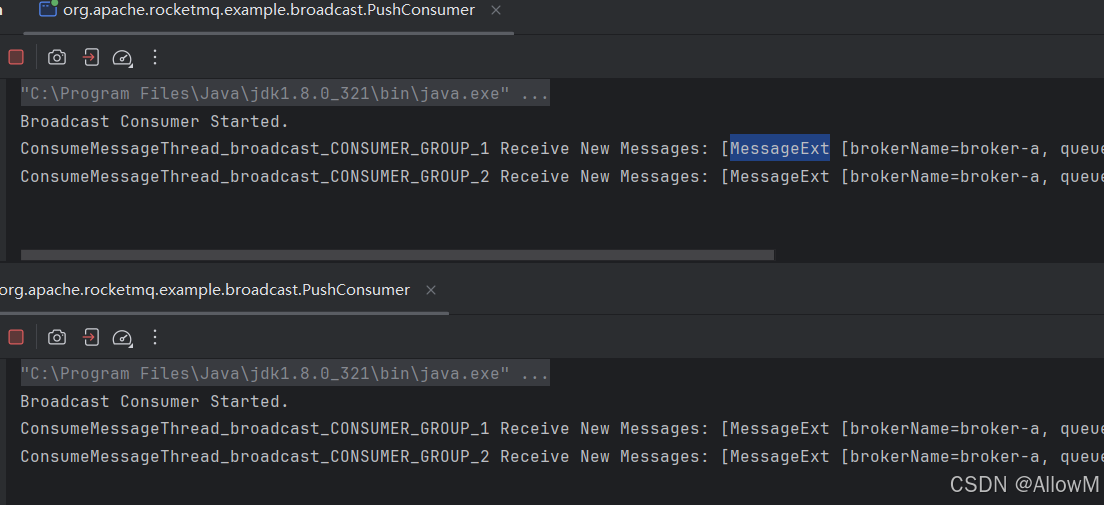
1、广播模式消费位点问题
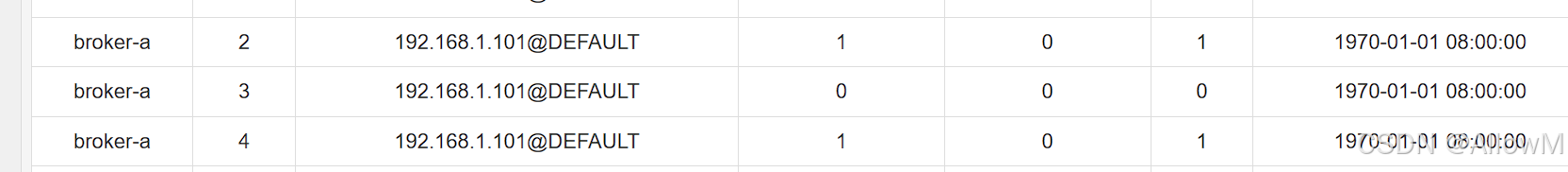
图上可以看出广播消息的消费位点不由服务端broker来维护了,由对应的客户端来维护消费位点。
客户端会在服务器对应目录下创建offsets.json文件夹来保存节点信息
地址:根目录.rocketmq_offsets\192.168.1.101@DEFAULT\broadcast_CONSUMER_GROUP
offsets.json
{
"offsetTable":{{
"brokerName":"broker-a",
"queueId":7,
"topic":"TopicTestBroadcast"
}:0,{
"brokerName":"broker-a",
"queueId":6,
"topic":"TopicTestBroadcast"
}:0,{
"brokerName":"broker-a",
"queueId":5,
"topic":"TopicTestBroadcast"
}:0,{
"brokerName":"broker-a",
"queueId":4,
"topic":"TopicTestBroadcast"
}:1,{
"brokerName":"broker-a",
"queueId":3,
"topic":"TopicTestBroadcast"
}:0,{
"brokerName":"broker-a",
"queueId":2,
"topic":"TopicTestBroadcast"
}:1,{
"brokerName":"broker-a",
"queueId":1,
"topic":"TopicTestBroadcast"
}:0,{
"brokerName":"broker-a",
"queueId":0,
"topic":"TopicTestBroadcast"
}:0
}
}
三、消息过滤机制
在大多数情况下,可以使用Message的Tag属性来简单快速的过滤信息。
1、使用Tag方式过滤消息
- tag消息过滤-生产者TagFilterProducer
/*
* tag过滤生产者
* */
public class TagFilterProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer("TagFilterTestProduceName");
producer.setNamesrvAddr("127.0.0.1:9876");
producer.start();
String[] tags = new String[] {"TagA", "TagB", "TagC"};
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
Message msg = new Message("TagFilterTest",
tags[i % tags.length],
"Hello world".getBytes(RemotingHelper.DEFAULT_CHARSET));
SendResult sendResult = producer.send(msg);
System.out.printf("%s%n", sendResult);
}
producer.shutdown();
}
}
- tag消息过滤-消费者TagFilterConsumer
/*
* tag过滤消费者
* */
public class TagFilterConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws MQClientException {
DefaultMQPushConsumer consumer = new DefaultMQPushConsumer("TagFilterTestConsumerName");
consumer.setNamesrvAddr("127.0.0.1:9876");
//过滤出TagA || TagC
consumer.subscribe("TagFilterTest", "TagA || TagC");
consumer.registerMessageListener(new MessageListenerConcurrently() {
@Override
public ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus consumeMessage(List<MessageExt> msgs,
ConsumeConcurrentlyContext context) {
System.out.printf("%s Receive New Messages: %s %n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), msgs);
return ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus.CONSUME_SUCCESS;
}
});
consumer.start();
System.out.printf("Consumer Started.%n");
}
}
Tag是RocketMQ中特有的一个消息属性,一个应用可以就用一个Topic,而应用中的不同业务就用Tag来区分。
但是Tag方式有一个很大的限制,就是一个消息只能有一个Tag,这在一些比较复杂的场景就有点不足了。 这时候可以使用SQL表达式来对消息进行过滤。
2、使用Sql方式过滤
- sql过滤消息-生产者SqlFilterProducer
/*
* sql消息生产者
*
* */
public class SqlFilterProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer("SqlFilterProducer");
producer.setNamesrvAddr("localhost:9876");
producer.start();
String[] tags = new String[] {"TagA", "TagB", "TagC"};
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Message msg = new Message("SqlFilterTest",
tags[i % tags.length],
("Hello RocketMQ " + i).getBytes(RemotingHelper.DEFAULT_CHARSET)
);
msg.putUserProperty("a", String.valueOf(i));
SendResult sendResult = producer.send(msg);
System.out.printf("%s%n", sendResult);
}
producer.shutdown();
}
}
- sql过滤消息-消费者SqlFilterConsumer
/*
* sql消息消费者
* */
public class SqlFilterConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DefaultMQPushConsumer consumer = new DefaultMQPushConsumer("SqlFilterConsumer");
//不要忘记在 broker 中设置 enablePropertyFilter=true,需要在broker.conf设置,重启broker
consumer.subscribe("SqlFilterTest",
MessageSelector.bySql("(TAGS is not null and TAGS in ('TagA', 'TagB'))" +
"and (a is not null and a between 0 and 3)"));
consumer.registerMessageListener(new MessageListenerConcurrently() {
@Override
public ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus consumeMessage(List<MessageExt> msgs,
ConsumeConcurrentlyContext context) {
System.out.printf("%s Receive New Messages: %s %n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), msgs);
return ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus.CONSUME_SUCCESS;
}
});
consumer.start();
System.out.printf("Consumer Started.%n");
}
}
如果需要使用sql过滤,需要配置broker.conf文件,设置enablePropertyFilter=true,默认为false

enablePropertyFilter=true
SQL92语法:
RocketMQ只定义了一些基本语法来支持这个特性。我们可以很容易地扩展它。
- 数值比较,比如:>,>=,<,<=,BETWEEN,=;
- 字符比较,比如:=,<>,IN;
- IS NULL ,IS NOT NULL;
- 逻辑符号 AND,OR,NOT;
常量支持类型为:
- 数值,比如:123,3.1415;
- 字符,比如:‘abc’,必须用单引号包裹起来;
- NULL,特殊的常量
- 布尔值,TRUE 或 FALSE
使用注意:
- 只有推模式的消费者可以使用SQL过滤。拉模式是用不了的;
- 另外消息过滤是在Broker端进行的,提升网络传输性能,但是broker服务会比较繁忙。(consumer将过滤条件推送给broker端)
四、顺序消息
1、介绍
顺序消息是一种对消息发送和消费顺序有严格要求的消息。对于一个指定的Topic,消息严格按照先进先出(FIFO)的原则进行消息发布和消费,即先发布的消息先消费,后发布的消息后消费。在 Apache RocketMQ 中支持分区顺序消息,如下图所示。我们可以按照某一个标准对消息进行分区(比如图中的ShardingKey),同一个ShardingKey的消息会被分配到同一个队列中,并按照顺序被消费。
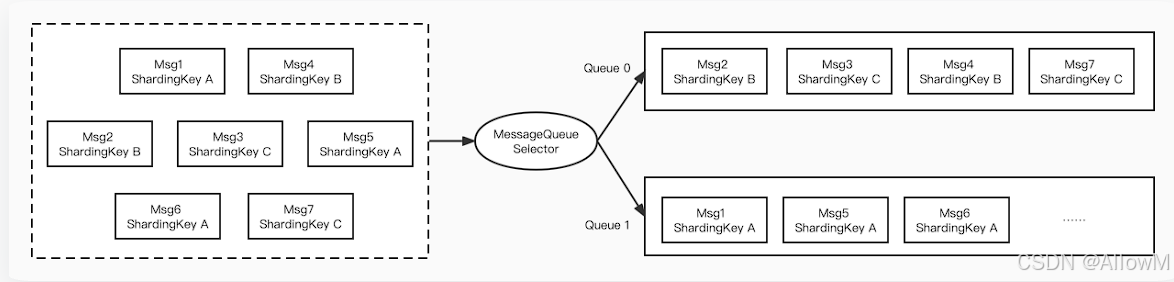
需要注意的是 RocketMQ 消息的顺序性分为两部分,生产顺序性和消费顺序性。只有同时满足了生产顺序性和消费顺序性才能达到顺序消息。
生产者顺序性:
- 单一生产者: 消息生产的顺序性仅支持单一生产者,不同生产者分布在不同的系统,即使设置相同的分区键,不同生产者之间产生的消息也无法判定其先后顺序。
- 串行发送:生产者客户端支持多线程安全访问,但如果生产者使用多线程并行发送,则不同线程间产生的消息将无法判定其先后顺序。
满足上述两条的生产者在将顺序消息发送至服务端后,会保证设置了同一分区键的消息,按照发送顺序存储在同一队列中
2、生产者实例
顺序消费生产者java代码
/*
* 顺序消费生产者
* */
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws MQClientException {
try {
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer("order_producer_group_name");
producer.setNamesrvAddr("127.0.0.1:9876");
producer.start();
//设置过滤消息tags组
String[] tags = new String[] {"TagA", "TagB", "TagC", "TagD", "TagE"};
//
for (int i = 0; i < 80; i++) {
//i = 0 10 20 30 40等这些值取余10后的值是一样的,会被放到同一个MessageQueue中
int orderId = i % 10;
Message msg =
new Message("TopicTestOrder", tags[i % tags.length], "KEY" + i,
("Hello RocketMQ " + i).getBytes(RemotingHelper.DEFAULT_CHARSET));
SendResult sendResult = producer.send(msg, new MessageQueueSelector() {
// MessageQueue的选择器逻辑
@Override
public MessageQueue select(List<MessageQueue> mqs, Message msg, Object arg) {
// orderId入参
Integer id = (Integer) arg;
//** 根据orderId取余获得MessageQueue的索引,
int index = id % mqs.size();
//把orderId相同的消息放到同一个MessageQueue中
return mqs.get(index);
}
}, orderId);
System.out.printf("%s%n", sendResult);
}
producer.shutdown();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new MQClientException(e.getMessage(), null);
}
}
}
MessageQueueSelector 是队列选择器,arg 是一个 Java Object 对象,可以传入作为消息发送分区的分类标准。
MessageQueueSelector的接口如下:
public interface MessageQueueSelector { MessageQueue select(final List<MessageQueue> mqs, final Message msg, final Object arg); }
其中 mqs 是可以发送的队列,msg是消息,arg是上述send接口中传入的Object对象,返回的是该消息需要发送到的队列。上述例子里,是以orderId作为分区分类标准,对所有队列个数取余,来对将相同orderId的消息发送到同一个队列中。
生产环境中建议选择最细粒度的分区键进行拆分,例如,将订单ID、用户ID作为分区键关键字,可实现同一终端用户的消息按照顺序处理,不同用户的消息无需保证顺序。
3、消费者实例
顺序消费消费者java代码
/*
*
* 顺序消费消费者
* */
public class Consumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws MQClientException {
DefaultMQPushConsumer consumer = new DefaultMQPushConsumer("order_consumer_group_name1");
consumer.setNamesrvAddr("127.0.0.1:9876");
consumer.setConsumeFromWhere(ConsumeFromWhere.CONSUME_FROM_FIRST_OFFSET);
consumer.subscribe("TopicTestOrder", "*");
// MessageListenerOrderly 顺序消费者监听器
consumer.registerMessageListener(new MessageListenerOrderly() {
AtomicLong consumeTimes = new AtomicLong(0);
@Override
public ConsumeOrderlyStatus consumeMessage(List<MessageExt> msgs, ConsumeOrderlyContext context) {
context.setAutoCommit(true);
//每次消费一条消息
System.out.printf("%s---%s Receive New Messages: %s %n", msgs.size(),Thread.currentThread().getName(), msgs);
this.consumeTimes.incrementAndGet();
if ((this.consumeTimes.get() % 2) == 0) {
return ConsumeOrderlyStatus.SUCCESS;
} else if ((this.consumeTimes.get() % 5) == 0) {
context.setSuspendCurrentQueueTimeMillis(3000);
//阻塞当前队列
return ConsumeOrderlyStatus.SUSPEND_CURRENT_QUEUE_A_MOMENT;
}
return ConsumeOrderlyStatus.SUCCESS;
}
});
consumer.start();
System.out.printf("Consumer Started.%n");
}
}
MessageListenerOrderly 顺序消费者监听器,
实现原理:实际上是服务端会在处理MessageListenerOrderly时给MessageQueue加锁,拿到MessageQueue上所有的消息再去读下一个MessageQueue
注意事项:当消费者处理业务逻辑时出现问题,不建议抛出异常,可以使用ConsumeOrderlyStatus.SUSPEND_CURRENT_QUEUE_A_MOMENT来代替
五、延迟消息
延迟消息实现的效果就是在调用producer.send方法后,消息并不会立即发送出去,而是会等一段时间再发送出去
-
message.setDelayTimeLevel(3):预定日常定时发送。1到18分别对应messageDelayLevel=1s 5s 10s 30s 1m 2m 3m 4m 5m 6m 7m 8m 9m 10m 20m 30m 1h 2h;可以在dashboard中broker配置查看。

-
msg.setDelayTimeMs(10L):指定时间定时发送。默认支持最大延迟时间为3天,可以根据broker配置:timerMaxDelaySec修改。
当前rocketMQ实现了两种延迟消息的机制,一种是设置延迟级别,一种是指定消息发送时间
核心代码
1、设置延迟级别发送
Message message = new Message(TOPIC, ("Hello scheduled message " + i).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
// 此消息将在 10 秒后发送给消费者。 默认的延迟级别有18种 1-18
message.setDelayTimeLevel(3);
// 发送消息
SendResult result = producer.send(message);
2、指定消息发送时间
3种设置方式
message.setDelayTimeSec(10);
message.setDelayTimeMs(10_000L);
message.setDeliverTimeMs(System.currentTimeMillis() + 10_000L);
Message message = new Message(TOPIC, ("Hello scheduled message " + i).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
// 此消息将在 10 秒后发送给消费者。
//message.setDelayTimeSec(10);
// 此消息将在 10 秒后发送给消费者。
// message.setDelayTimeMs(10_000L);
// 3种都可以实现同一效果
message.setDeliverTimeMs(System.currentTimeMillis() + 10_000L);
// Send the message
SendResult result = producer.send(message);
六、批量消息
批量消息是指将多条消息合并成一个批量消息,一次发送出去。这样的好处是可以减少网络IO,提升吞吐量。
批量消息的使用限制:
- 消息大小不能超过4M,虽然源码注释不能超1M,但是实际使用不超过4M即可。平衡整体的性能,建议保持1M左右。
- 相同的Topic,
- 相同的waitStoreMsgOK
- 不能是延迟消息、事务消息等
1、批量消息生产者
/*
*
* 批量消息生产者
* */
public class SimpleBatchProducer {
public static final String PRODUCER_GROUP = "BatchProducerGroupName";
public static final String DEFAULT_NAMESRVADDR = "127.0.0.1:9876";
public static final String TOPIC = "BatchTest";
public static final String TAG = "Tag";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer(PRODUCER_GROUP);
producer.setNamesrvAddr(DEFAULT_NAMESRVADDR);
producer.start();
//如果您一次只发送不超过 1MiB 的消息,则很容易使用 batch
//同一批次的消息应具有:相同的主题、相同的 waitStoreMsgOK 且不支持延迟计划。
List<Message> messages = new ArrayList<>();
messages.add(new Message(TOPIC, TAG, "OrderID001", "Hello world 0".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
messages.add(new Message(TOPIC, TAG, "OrderID002", "Hello world 1".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
messages.add(new Message(TOPIC, TAG, "OrderID003", "Hello world 2".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
SendResult sendResult = producer.send(messages);
System.out.printf("%s", sendResult);
}
}
2、分批发送生产者
如果要发送大批量的数据,需要我们将大批量的数据拆分小批量的数据发送
/**
* 分批批量发送消息
* 注意修改SIZE_LIMIT为 = 10 * 1000,不然发送消息时会提示消息体积过大
*/
public class SplitBatchProducer {
public static final String PRODUCER_GROUP = "BatchProducerGroupName";
public static final String DEFAULT_NAMESRVADDR = "127.0.0.1:9876";
public static final int MESSAGE_COUNT = 100 * 1000;
public static final String TOPIC = "BatchTest";
public static final String TAG = "Tag";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer(PRODUCER_GROUP);
producer.setNamesrvAddr(DEFAULT_NAMESRVADDR);
producer.start();
//大批量
List<Message> messages = new ArrayList<>(MESSAGE_COUNT);
for (int i = 0; i < MESSAGE_COUNT; i++) {
messages.add(new Message(TOPIC, TAG, "OrderID" + i, ("Hello world " + i).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
}
//将大批量拆分为小批量:
ListSplitter splitter = new ListSplitter(messages);
while (splitter.hasNext()) {
List<Message> listItem = splitter.next();
SendResult sendResult = producer.send(listItem);
System.out.printf("%s", sendResult);
}
}
}
class ListSplitter implements Iterator<List<Message>> {
private static final int SIZE_LIMIT = 1000 * 1000; //每个消息批次的最大大小
private final List<Message> messages;// 待发送的消息列表
private int currIndex;// 当前拆分到的位置
public ListSplitter(List<Message> messages) {
this.messages = messages;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return currIndex < messages.size();
}
@Override
public List<Message> next() {
int nextIndex = currIndex;
int totalSize = 0;
for (; nextIndex < messages.size(); nextIndex++) {
Message message = messages.get(nextIndex);
int tmpSize = message.getTopic().length() + message.getBody().length;
Map<String, String> properties = message.getProperties();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
tmpSize += entry.getKey().length() + entry.getValue().length();
}
tmpSize = tmpSize + 20;
// 如果超过了单个批次所允许的大小,就将此消息之前的消息作为下一个子列表返回
if (tmpSize > SIZE_LIMIT) {
// 如果是第一条消息就超出大小限制,就跳过这条消息再继续扫描
if (nextIndex - currIndex == 0) {
nextIndex++;
}
break;
}
// 如果当前子列表大小已经超出所允许的单个批次大小,那么就暂停添加消息
if (tmpSize + totalSize > SIZE_LIMIT) {
break;
} else {
totalSize += tmpSize;
}
}
// 返回从currIndex到nextIndex之间的所有消息
List<Message> subList = messages.subList(currIndex, nextIndex);
currIndex = nextIndex;
return subList;
}
@Override
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not allowed to remove");
}
}
7、事务消息
1、什么是事务消息
事务消息是在分布式系统中保证最终一致性的两阶段提交的消息实现。他可以保证本地事务执行与消息发送两个操作的原子性,也就是这两个操作一起成功或者一起失败。
2、事务消息的实现机制
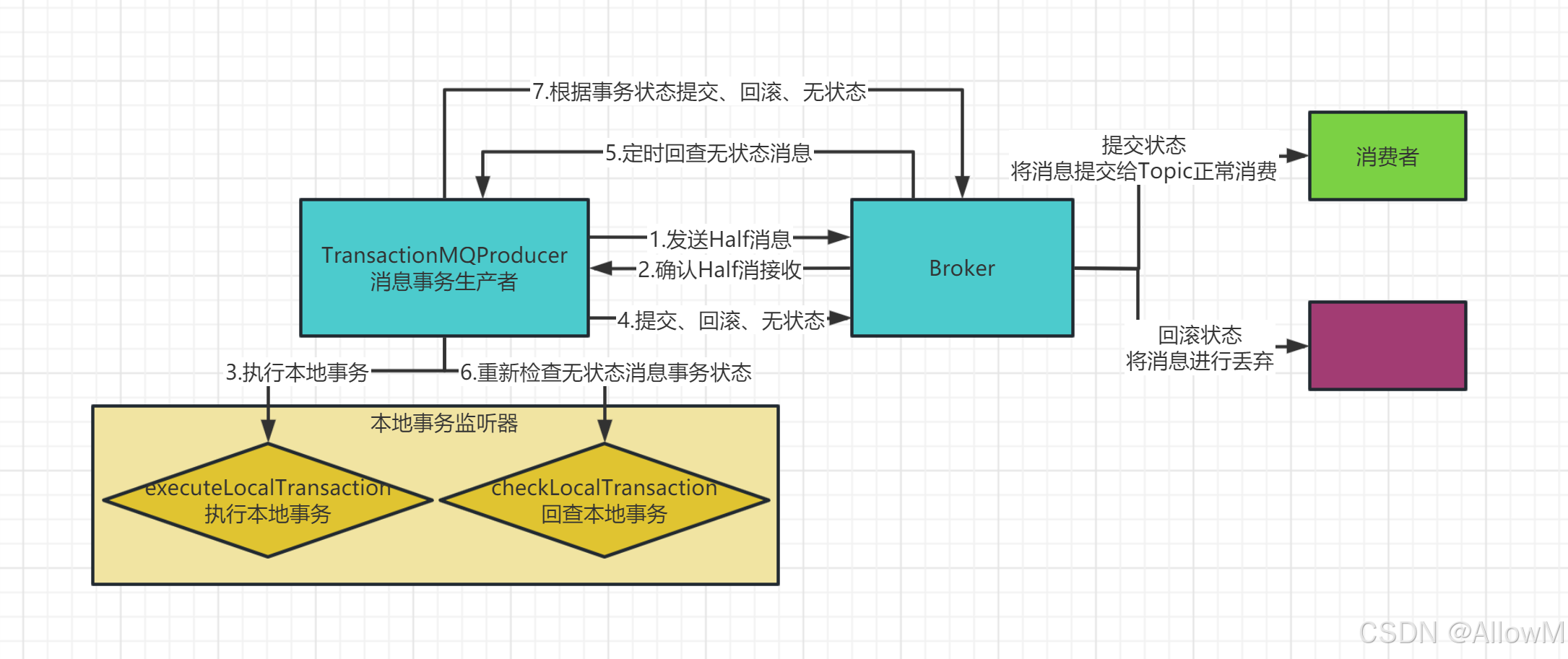
事务消息机制的关键是在发送消息时会将消息转为一个half半消息,并存入RocketMQ内部的一个Topic(RMQ_SYS_TRANS_HALF_TOPIC),这个Topic对消费者是不可见的。再经过一系列事务检查通过后,再将消息转存到目标Topic,这样对消费者就可见了。

3、事务消息的编程模型
事务消息只保证消息发送者的本地事务与发消息这两个操作的原子性,因此,事务消息的示例只涉及到消息发送者
事务消息的关键是在TransactionMQProducer中指定了一个TransactionListener事务监听器,这个事务监听器就是事务消息的关键控制器。
事务消息生产者代码
/*
* 事物消息生产者
* */
public class TransactionProducer {
public static final String PRODUCER_GROUP = "TransactionProducerGroup";
public static final String DEFAULT_NAMESRVADDR = "127.0.0.1:9876";
public static final String TOPIC = "TransTopic";
public static final int MESSAGE_COUNT = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) throws MQClientException, InterruptedException {
// 自定义的事务消息监听器
TransactionListener transactionListener = new TransactionListenerImpl();
TransactionMQProducer producer = new TransactionMQProducer(PRODUCER_GROUP, Arrays.asList(TOPIC));
producer.setNamesrvAddr(DEFAULT_NAMESRVADDR);
ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 5, 100, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2000), r -> {
Thread thread = new Thread(r);
thread.setName("client-transaction-msg-check-thread");
return thread;
});
producer.setExecutorService(executorService);
//注册事务监听器
producer.setTransactionListener(transactionListener);
producer.start();
String[] tags = new String[] {"TagA", "TagB", "TagC", "TagD", "TagE"};
for (int i = 0; i < MESSAGE_COUNT; i++) {
try {
Message msg =
new Message(TOPIC, tags[i % tags.length], "KEY" + i,
("Hello RocketMQ " + i).getBytes(RemotingHelper.DEFAULT_CHARSET));
//producer.sendMessageInTransaction(msg, null) 发送事务消息
SendResult sendResult = producer.sendMessageInTransaction(msg, null);
System.out.printf("%s%n", sendResult);
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (MQClientException | UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
Thread.sleep(1000); //等待broker端回调
}
producer.shutdown();
}
}
事务监听器
/*
* 注册监听器
* * */
public class TransactionListenerImpl implements TransactionListener {
@Override
/**
* 在提交完事务消息后执行。
* 返回COMMIT_MESSAGE状态的消息会立即被消费者消费到。
* 返回ROLLBACK_MESSAGE状态的消息会被丢弃。
* 返回UNKNOWN状态的消息会由Broker过一段时间再来回查事务的状态。
*/
public LocalTransactionState executeLocalTransaction(Message message, Object o) {
String tags = message.getTags();
System.out.println("executeLocalTransaction: " + tags);
//TagA的消息会立即被消费者消费到
if(StringUtils.contains(tags,"TagA")){
return LocalTransactionState.COMMIT_MESSAGE;
//TagB的消息会被丢弃
}else if(StringUtils.contains(tags,"TagB")){
return LocalTransactionState.ROLLBACK_MESSAGE;
//其他消息会等待Broker进行事务状态回查。
}else{
return LocalTransactionState.UNKNOW;
}
}
@Override
/**
* 在对UNKNOWN状态的消息进行状态回查时执行。
* 返回COMMIT_MESSAGE状态的消息会立即被消费者消费到。
* 返回ROLLBACK_MESSAGE状态的消息会被丢弃。
* 返回UNKNOWN状态的消息会由Broker过一段时间再来回查事务的状态。
*/
public LocalTransactionState checkLocalTransaction(MessageExt messageExt) {
String tags = messageExt.getTags();
System.out.println("checkLocalTransaction: " + tags);
//TagC的消息过一段时间会被消费者消费到
if(StringUtils.contains(tags,"TagC")){
return LocalTransactionState.COMMIT_MESSAGE;
//TagD的消息也会在状态回查时被丢弃掉
}else if(StringUtils.contains(tags,"TagD")){
return LocalTransactionState.ROLLBACK_MESSAGE;
//剩下TagE的消息会在多次状态回查后最终丢弃
}else{
return LocalTransactionState.UNKNOW;
}
}
}
4、事务消息的使用限制
-
事务消息不支持延迟消息和批量消息。
-
为了避免单个消息被检查太多次而导致半队列消息累积,我们默认将单个消息的检查次数限制为 15 次,但是用户可以通过 Broker 配置文件的transactionCheckMax参数来修改此限制。如果已经检查某条消息超过N次的话(N = transactionCheckMax)则 Broker 将丢弃此消息,并在默认情况下同时打印错误日志。可以通过重写AbstractTransactionCheckListener类来修改这个行为。
-
事务性消息可能不止一次被检查或消费。
检查消息
 RocketMQ API实战:消息特性与机制
RocketMQ API实战:消息特性与机制




















 931
931

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








