Trie树
1.定义:高效地存储和查找字符串
例:(标记表示在此处有一个以该字母结束的英文单词)
2.例题:插入和查找字符串在集合中出现了多少次
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int son[N][26], cnt[N]//表示以p结尾的单词数, idx;
char str[N];
void insert(char *str)
{
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i ++ )
{
int u = str[i] - 'a';//将英文字母映射到0~25
if (!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = ++ idx;//如果不存在则插入
p = son[p][u];
}
cnt[p] ++ ;
}
int query(char *str)
{
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i ++ )
{
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if (!son[p][u]) return 0;
p = son[p][u];
}
return cnt[p];
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n -- )
{
char op[2];
scanf("%s%s", op, str);//没有地址符号
if (*op == 'I') insert(str);//此处表示的是值
else printf("%d\n", query(str));
}
return 0;
}
并查集
1.belong[x]表示的是x属于哪个集合

2.优化:路径压缩()

3.例题:
例题一:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int p[N];
int find(int x)返回x的祖宗节点+路径压缩
{
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main()
{
int n, m;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) p[i] = i;
while (m -- )
{
char op[2];
int a, b;
scanf("%s%d%d", op, &a, &b);//用字符串读入字符,防止scanf读入空格之类的东西
if (*op == 'M') p[find(a)] = find(b);//合并
else//查找是否在同一个集合
{
if (find(a) == find(b)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
}
return 0;
}
例题二:


#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n, m;
int p[N], cnt[N];
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
此处的作用是:如果该点不是祖宗节点,则向上走一层,直到找到祖宗节点;
然后向下回溯,让每一个节点的父节点直接指向祖宗节点

int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
p[i] = i;
cnt[i] = 1;
}
while (m -- )
{
string op;
int a, b;
cin >> op;
if (op == "C")
{
cin >> a >> b;
a = find(a), b = find(b);
if (a != b)
{
p[a] = b;
cnt[b] += cnt[a];
}
}
else if (op == "Q1")
{
cin >> a >> b;
if (find(a) == find(b)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
else
{
cin >> a;
cout << cnt[find(a)] << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
按秩合并:将树的高度较低的插到树的高度较高的树上
堆
4.5操作在stl中无法直接实现
1.堆是一棵完全二叉树
2.小根堆:每一个点都是小于等于左右儿子的,则根节点是最小值
大根堆则相反
3.存储:以一维数组来存,下标从1开始
1号点是根节点,x的左儿子是2x,右儿子是2x+1

3.两个操作:up(x),down(x)
以小根堆为例,前者是某节点的值变小了需要向上移,后者是某一个点的值变大了需要向下移
4.

5.例题:
如果建立堆时,挨个往堆里插,时间复杂度是O(log n);
此处有时间复杂度为O(n)的做法:down(n/2~1)

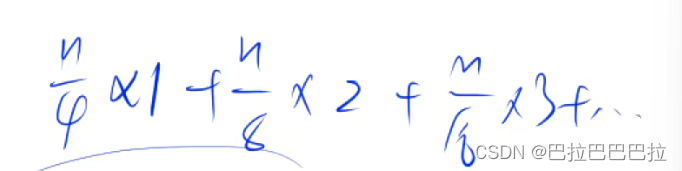
例一:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n, m;
int h[N], size;
void down(int u)
{
int t = u;//t表示最小值的下标
if (u * 2 <= cnt && h[u * 2] < h[t]) t = u * 2;//与左儿子比较,使得t是最小值的下标
if (u * 2 + 1 <= cnt && h[u * 2 + 1] < h[t]) t = u * 2 + 1;//与右儿子比较,使得t是最小值的下标
if (u != t)//说明根节点不是最小值
{
swap(h[u], h[t]);
down(t);
}
}
void up(int u)
{
while (u / 2 && h[u / 2] > h[u])
{
swap(h[u / 2], h[u]);
u /= 2;
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) scanf("%d", &h[i]);
size= n;
for (int i = n / 2; i; i -- ) down(i);
while (m -- )
{
printf("%d ", h[1]);
h[1] = h[size -- ];
down(1);
}
puts("");
return 0;
}
例二:
ph[k]表示第k个插入的某点在堆里面的下标是什么
hp[k]表示堆里面的某点是第几个插入的点

#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int h[N], ph[N], hp[N], size;
void heap_swap(int a, int b)//修改时,既要交换值,也要交换地址
{
swap(ph[hp[a]],ph[hp[b]]);
swap(hp[a], hp[b]);
swap(h[a], h[b]);
}
void down(int u)
{
int t = u;
if (u * 2 <= cnt && h[u * 2] < h[t]) t = u * 2;
if (u * 2 + 1 <= cnt && h[u * 2 + 1] < h[t]) t = u * 2 + 1;
if (u != t)
{
heap_swap(u, t);
down(t);
}
}
void up(int u)
{
while (u / 2 && h[u] < h[u / 2])
{
heap_swap(u, u / 2);
u >>= 1;
}
}
int main()
{
int n, m = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n -- )
{
char op[5];
int k, x;
scanf("%s", op);
if (!strcmp(op, "I"))
{
scanf("%d", &x);
size ++ ;
m ++ ;
ph[m] = size, hp[size] = m;
h[size] = x;
up(size);
}
else if (!strcmp(op, "PM")) printf("%d\n", h[1]);
else if (!strcmp(op, "DM"))
{
heap_swap(1, size);
size-- ;
down(1);
}
else if (!strcmp(op, "D"))
{
scanf("%d", &k);
k = ph[k];
heap_swap(k, size);
size -- ;
up(k);
down(k);
}
else
{
scanf("%d%d", &k, &x);
k = ph[k];
h[k] = x;
up(k);
down(k);
}
}
return 0;
}







 本文介绍了Trie树的高效字符串存储和查找方法,以及并查集的belong[]函数和路径压缩优化。同时展示了小根堆和大根堆的应用,包括堆排序和up/down操作的示例。
本文介绍了Trie树的高效字符串存储和查找方法,以及并查集的belong[]函数和路径压缩优化。同时展示了小根堆和大根堆的应用,包括堆排序和up/down操作的示例。
















 418
418

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








