单链表
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/code/content/42977/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
// head 表示头结点的下标
// e[i] 表示节点i的值
// ne[i] 表示节点i的next指针是多少
// idx 存储当前已经用到了哪个点
int head, e[N], ne[N], idx;
// 初始化
void init()
{
head = -1;
idx = 0;
}
// 将x插到头结点
void add_to_head(int x)
{
e[idx] = x, ne[idx] = head, head = idx ++ ;
}
// 将x插到下标是k的点后面
void add(int k, int x)
{
e[idx] = x, ne[idx] = ne[k], ne[k] = idx ++ ;
}
// 将下标是k的点后面的点删掉
void remove(int k)
{
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
int main()
{
int m;
cin >> m;
init();
while (m -- )
{
int k, x;
char op;
cin >> op;
if (op == 'H')
{
cin >> x;
add_to_head(x);
}
else if (op == 'D')
{
cin >> k;
if (!k) head = ne[head];
else remove(k - 1);
}
else
{
cin >> k >> x;
add(k - 1, x);
}
}
for (int i = head; i != -1; i = ne[i]) cout << e[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
双链表
邻接表
1.将每个节点相邻的边存下来
2.实质:n个单链表
栈
tt表示栈顶下标

队列
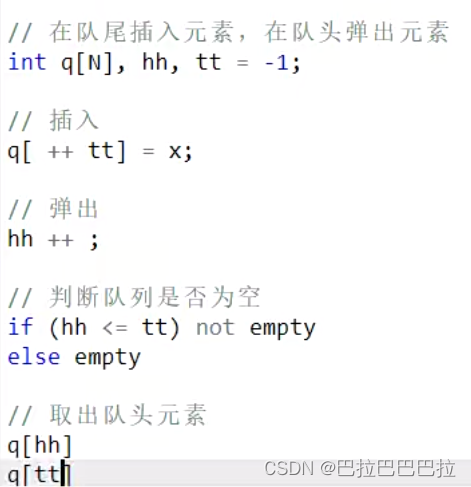
hh表示队头指针,tt表示队尾指针
单调栈
在一个数组中找到一个左(右)边离它最近(远)的数

暴力做法:把a1~an-1所有的数存在一个栈顶中,从栈顶开始找符合题意的点

本题代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n;
int stk[N], tt;
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
while (tt && stk[tt] >= x)tt--;
if (tt)cout << stk[tt] << ' ';
else cout << "-1" << ' ';
stk[++tt] = x;
}
return 0;
}
单调队列(滑动窗口)
模型:求滑动窗口中的最大值和最小值

队列当中仅存储滑动窗口里的数,每次滑动分两步进行,第一步将新的数从队尾插入,第二步将队头的数弹出
注:队列当中存的不是值,而是下标
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
int n, k;
int a[N], q[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)cin >> a[i];
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (hh <= tt && i - k + 1 > q[hh])hh++;//判断队头元素是否已经滑出窗口
while (hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] >= a[i])tt--;
q[++tt] = i;//因为i有可能是最小的
if (i >= k - 1)cout << a[q[hh]]<<' ';
}
hh = 0, tt = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (hh <= tt && i - k + 1 > q[hh])hh++;//判断队头元素是否已经滑出窗口
while (hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] <= a[i])tt--;
q[++tt] = i;//因为i有可能是最小的
if (i >= k - 1)cout << a[q[hh]]<<' ';
}
return 0;
}
KMP
1.下标按个人习惯,此处主串的i从1开始,子串的j从0开始
2.朴素做法


3.若匹配成功,则返回首位置

4.举例:求next的过程-----实际上就是求前缀=后缀时的最长长度








 文章介绍了如何在C++中使用单链表和双链表进行操作,包括添加、删除节点,以及邻接表的运用。还讨论了栈、队列和单调栈的概念,以及滑动窗口问题的单调队列解决方案。最后提及了KMP算法的基本概念和应用实例。
文章介绍了如何在C++中使用单链表和双链表进行操作,包括添加、删除节点,以及邻接表的运用。还讨论了栈、队列和单调栈的概念,以及滑动窗口问题的单调队列解决方案。最后提及了KMP算法的基本概念和应用实例。

















 186
186

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








