Orthogonality of the four subspaces

- The row space is perpendicular to the nullspace
- The column space is perpendicular to the nullspace of
A
T
A^T
AT
- The column space C(A) , a subspace of R m R^m Rm, dimention r
- The leftnull space N( A T A^T AT) , a subspace of R m R^m Rm ,dimention m-r
- The row space C( A T A^T AT) , a subspace of R n R^n Rn ,dimention r
- The null space N(A) , a subspace of
R
n
R^n
Rn ,dimention n-r
Definition of orthogonal subspace
- Two subspace V V V and W W W of a vector space are orthogonal if every vector v v v in V V V is perpendicular to every vector w w w in W W W
- Every vector x in the nullspace is perpendicular to every row of A A A, because A x = 0 Ax=0 Ax=0 ,the nullspace N ( A ) N(A) N(A) and row space C ( A T ) C(A^T) C(AT) are orthogonal subspace of R n R^n Rn
- Every vector
y
y
y in the nullspace of
A
T
A^T
AT is perpendicular to every column of
A
A
A, because
A
T
x
=
0
A^Tx=0
ATx=0 , ,The leftnull space N(
A
T
A^T
AT) and the column space C(A) are orthogonal in
R
m
R^m
Rm
Definition of orthogonal complements(正交补)
- The orthogonal complement of a subspace V V V contains every vector that is perpendicular to V V V
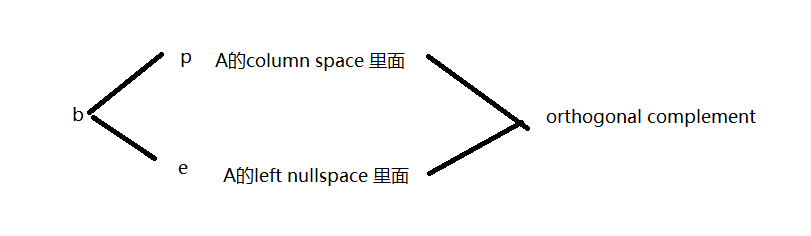
- Nullspace N(A) is the orthogonal complement of the row space C( A T A^T AT) in R n R^n Rn
- LeftNull space N( A T A^T AT) is the orthogonal complement of the column space C(A) in R m R^m Rm
Projections
- The projection matrix P(由A得到投影矩阵) multiplies b(被投影的向量) to give p (b在A上的投影) on A
Projection onto a line
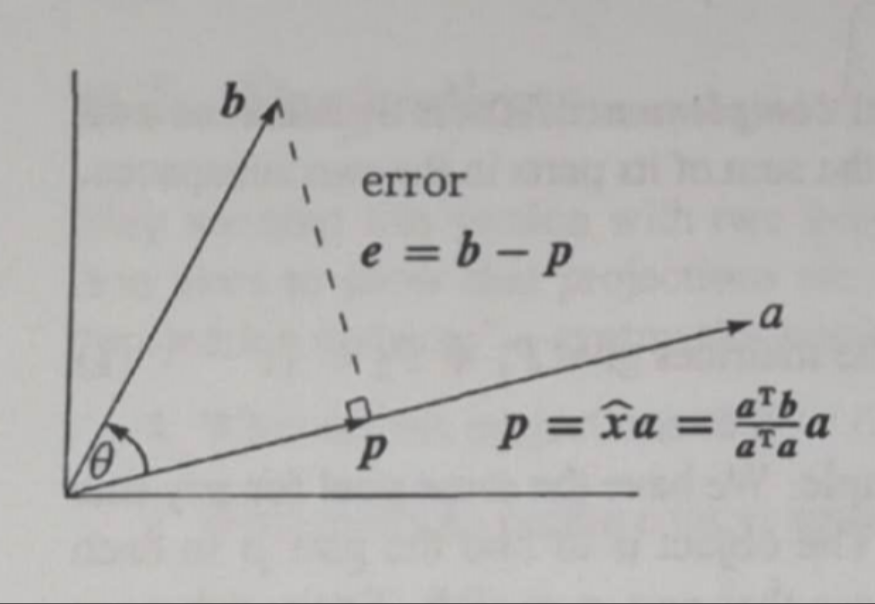
projection matrix : P = a a T a T a P=\frac{aa^T}{a^Ta} P=aTaaaT
例子:
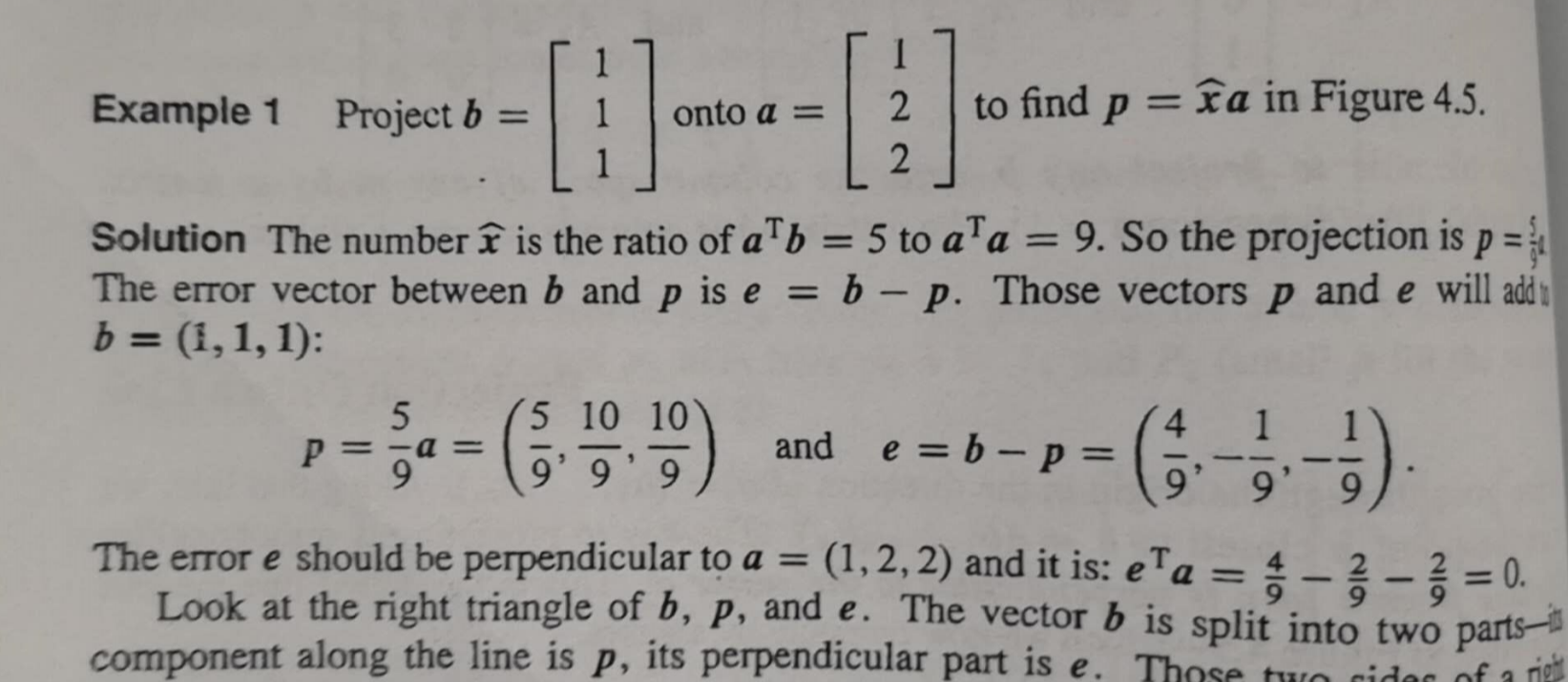
Projection onto a subspace
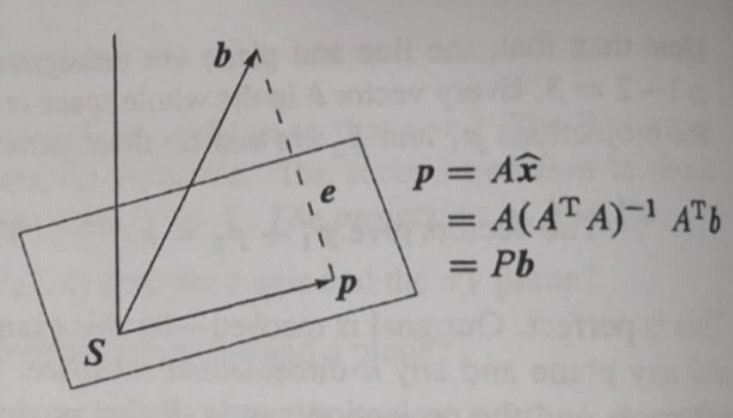
( I − P ) b = e (I-P)b=e (I−P)b=e : I − P I-P I−P 也是投影矩阵,将b 投影到 plane perpendicular to A to get e
实例

Orthogonal bases and Gram-Schmidt
Orthonomal bases and matrix(标准正交基、正交矩阵)
-
标准正交基

-
(orthogonal matrix)正交矩阵:方阵
由上面标准正交基构成的方阵:正交矩阵

the inverse is the transpose , In the square case we call Q an orthogonal matrix
Projection Using Orthonormal Bases:Q replace A
- Suppose the basis are orthonomal. that means A is Q ,
A
T
A
A^TA
ATA is
Q
T
Q
=
I
Q^TQ=I
QTQ=I
投影向量: p = Q x ^ = Q Q T b p=Q\hat{x}=QQ^Tb p=Qx^=QQTb
x ^ = Q T b \hat{x}=Q^Tb x^=QTb
projection matrix: P = Q Q T P=QQ^T P=QQT

- When Q is square m=n , (subspace Q is whole space, 任何一个向量投影到整个整个空间,都是其本身,所以投影矩阵是
I
I
I)
Q T = Q − 1 Q^T=Q^{-1} QT=Q−1
x ^ = Q − 1 b \hat{x}=Q^{-1}b x^=Q−1b
projection matrix: P = Q Q T = I P=QQ^T=I P=QQT=I
The Gram-Schmidt
- 假设 a , b , c a,b,c a,b,c三个向量不是标准正交基, 转化成正交基(基的长度不是1) A , B , C A,B,C A,B,C
- 第一步:选 A = a A=a A=a , B = b − A T b A T A A = e ( 误 差 ) B=b-\frac{A^Tb}{A^TA}A=e(误差) B=b−ATAATbA=e(误差),因为b与A的误差是与A垂直的
- 第二步: C = c − A T c A T A A − B T c B T B B C=c-\frac{A^Tc}{A^TA}A-\frac{B^Tc}{B^TB}B C=c−ATAATcA−BTBBTcB,取c 在 A , B A,B A,B平面投影的误差e
- 重复下去
例子:






 本文探讨了矩阵空间中四个子空间的正交性,解释了正交子空间和正交补的概念。此外,详细阐述了投影理论,包括在直线和平面上的投影,以及正交基在投影中的作用。通过Gram-Schmidt过程展示了如何将非正交基转化为正交基,并介绍了正交矩阵及其在投影矩阵中的应用。
本文探讨了矩阵空间中四个子空间的正交性,解释了正交子空间和正交补的概念。此外,详细阐述了投影理论,包括在直线和平面上的投影,以及正交基在投影中的作用。通过Gram-Schmidt过程展示了如何将非正交基转化为正交基,并介绍了正交矩阵及其在投影矩阵中的应用。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








