1. XML、YAML文件的打开和关闭
XML\YAML文件在OpenCV中的数据结构为FileStorage,打开操作例如:
string filename = "I.xml";
FileStorage fs(filename, FileStorage::WRITE);
\\...
fs.open(filename, FileStorage::READ);
文件关闭操作会在FileStorage结构销毁时自动进行,但也可调用如下函数实现
fs.release();
2.文本和数字的输入和输出
写入文件使用 << 运算符,例如:
fs << "iterationNr" << 100;
读取文件,使用 >> 运算符,例如
int itNr;
fs["iterationNr"] >> itNr;
itNr = (int) fs["iterationNr"];
3. OpenCV数据结构的输入和输出,和基本的C++形式相同
Mat R = Mat_<uchar >::eye (3, 3),
T = Mat_<double>::zeros(3, 1);
fs << "R" << R; // Write cv::Mat
fs << "T" << T;
fs["R"] >> R; // Read cv::Mat
fs["T"] >> T;
4. vector(arrays) 和 maps的输入和输出
vector要注意在第一个元素前加上“[”,在最后一个元素前加上"]"。例如:
fs << "strings" << "["; // text - string sequence
fs << "image1.jpg" << "Awesomeness" << "baboon.jpg";
fs << "]"; // close sequence
对于map结构的操作使用的符号是"{“和”}",例如:
fs << "Mapping"; // text - mapping
fs << "{" << "One" << 1;
fs << "Two" << 2 << "}";
读取这些结构的时候,会用到FileNode和FileNodeIterator数据结构。对FileStorage类的[]操作符会返回FileNode数据类型,对于一连串的node,可以使用FileNodeIterator结构,例如:
FileNode n = fs["strings"]; // Read string sequence - Get node
if (n.type() != FileNode::SEQ)
{
cerr << "strings is not a sequence! FAIL" << endl;
return 1;
}
FileNodeIterator it = n.begin(), it_end = n.end(); // Go through the node
for (; it != it_end; ++it)
cout << (string)*it << endl;
XML和YAML文件的写入
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <time.h>
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
//初始化
FileStorage fs("test.yaml", FileStorage::WRITE);
//开始文件写入
fs << "frameCount" << 5;
time_t rawtime;
time(&rawtime);
fs << "calibrationDate" << asctime(localtime(&rawtime));
Mat cameraMatrix = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1000, 0, 320, 0, 1000, 240, 0, 0, 1);
Mat disCoeffs = (Mat_<double>(5, 1) << 0.1, 0.01, -0.001, 0, 0);
fs << "cameraMatrix" << cameraMatrix << "disCoeffs" << disCoeffs;
fs << "features" << "[";
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
int x = rand() % 640;
int y = rand() % 480;
uchar lbp = rand() % 256;
fs << "{:" << "x" << x << "y" << y << "lbp" << "[:";
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
fs << ((lbp >> j) & 1);
}
fs << "]" << "}";
}
fs << "]";
fs.release();
printf("文件读写完毕,请在工程目录下查看生成的文件~");
getchar();
return 0;
}
%YAML:1.0
---
frameCount: 5
calibrationDate: "Wed Aug 1 11:13:44 2018\n"
cameraMatrix: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 3
cols: 3
dt: d
data: [ 1000., 0., 320., 0., 1000., 240., 0., 0., 1. ]
disCoeffs: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 5
cols: 1
dt: d
data: [ 1.0000000000000001e-01, 1.0000000000000000e-02,
-1.0000000000000000e-03, 0., 0. ]
features:
- { x:41, y:227, lbp:[ 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1 ] }
- { x:260, y:449, lbp:[ 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0 ] }
- { x:598, y:78, lbp:[ 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 ] }
XML和YAML文件读取
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
// 改变console字体颜色
system("color 6F");
//初始化
FileStorage fs2("test.yaml", FileStorage::READ);
// 第一种方法 对FileNote操作
int frameCount = (int)fs2["frameCount"];
std::string date;
//第二种方法:使用 FileNote运算符
fs2["calibrationDate"] >> date;
Mat cameraMatrix2, disCoeffs2;
fs2["cameraMatrix"] >> cameraMatrix2;
fs2["disCoeffs"] >> disCoeffs2;
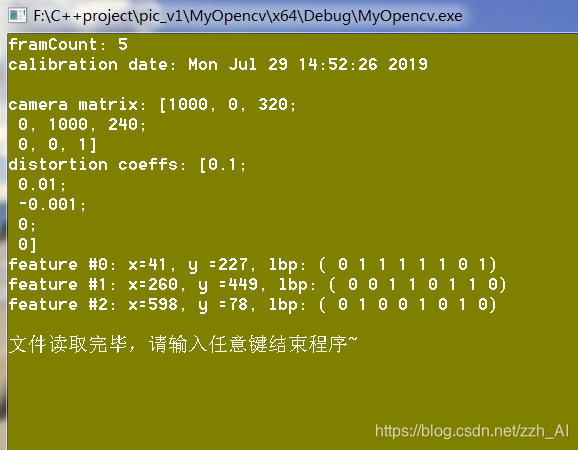
cout << "framCount: " << frameCount << endl
<< "calibration date: " << date << endl
<< "camera matrix: " << cameraMatrix2 << endl
<< "distortion coeffs: " << disCoeffs2 << endl;
FileNode features = fs2["features"];
FileNodeIterator it = features.begin(), it_end = features.end();
int idx = 0;
std::vector<uchar> lbpval;
//使用FileNoteIterator 遍历序列
for (; it != it_end; ++it, ++idx)
{
cout << "feature #" << idx << ": ";
cout << "x=" << (int)(*it)["x"] << ", y =" << (int)(*it)["y"] << ", lbp: (";
(*it)["lbp"] >> lbpval;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)lbpval.size(); i++)
{
cout << " " << (int)lbpval[i];
}
cout << ")" << endl;
}
fs2.release();
printf("\n文件读取完毕,请输入任意键结束程序~");
getchar();
return 0;
}





 本文介绍了如何在OpenCV中进行XML和YAML文件的读写操作,包括文件的打开和关闭、文本和数字的输入输出、OpenCV数据结构的处理、vector和maps的存取,以及利用FileNode和FileNodeIterator进行数据读取。
本文介绍了如何在OpenCV中进行XML和YAML文件的读写操作,包括文件的打开和关闭、文本和数字的输入输出、OpenCV数据结构的处理、vector和maps的存取,以及利用FileNode和FileNodeIterator进行数据读取。
















 594
594

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








