Qnx IPC通信 Message-passing
Message-passing介绍
QNX提供了多种IPC(Interprocess Communication )通信方式,包括Message-passing、Plus(脉冲)、Event、Signal、共享内存、Pipe,当然还有socket。
Message-passing是Qnx IPC的主要形式。
Synchronous messaging is the main form of IPC in the QNX Neutrino RTOS.
Message-passing提供了主从直接同步的双向消息传输,类似于Android 同步Binder。
客户端向服务端请求(Request),服务端向客户端(Reply)。
官网链接:
https://www.qnx.com/developers/docs/7.1/#com.qnx.doc.neutrino.sys_arch/topic/ipc_Sync_messaging.html
通信状态迁移图
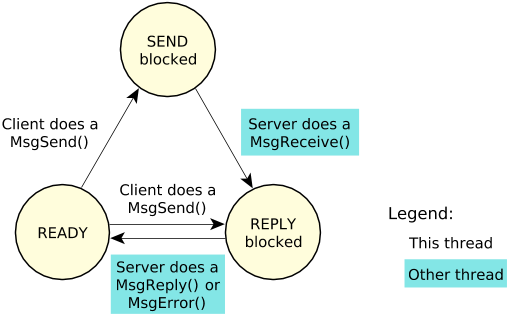
Qnx官网给出的客户端状态迁移图。
- 客户端调用MsgSend(Qnx提供的函数),客户执行函数的所在线程,进入SednBlocked的阻塞状态(等待服务端回复)
- 服务端执行MsgRecevice,接收客户端的请求后。Qnx kernel会将Client端的Thread调度为Repley blocked状态。
- 服务端处理完客户端的请求后,调用MsgReply或者MsgError,返回结果给Client端。Client从blocked阻塞状态,变为Ready非阻塞状态。
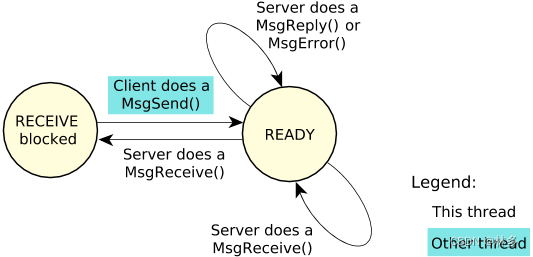
Qnx官网给出的服务端状态迁移图
- 服务端调用MsgReceive接收客户端请求(阻塞)
- 客户端端调用MessageSend后,服务端收到调用,从阻塞状态中退出。处理请求后,通过MsgReply()/MsgError回复客户端。
- 服务端重新调用MsgReceive,监听客户端请求。
Channels and connections
Qnx中消息传递(Message-passing)是基于通道/连接 这种方式,进行传输的。
- 一个thread(看做任务的基本调度单位)想要接收消息,必须创建一个通道(Channels)
- 一个thread 想要发送消息,必须连接(connections)到这个通道。
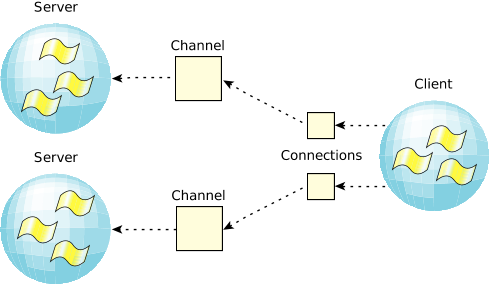
Qnx官网关于Channels and connections的说明图片。
关于性能
根据QNX官网的介绍,Message-passing时,Qnx Kernel基于地址空间,直接把消息从当前线程的地址,复制到接收线程的地址,没有额外的中间拷贝。所以接近于硬件上内存的带宽(很快)
Since our messaging services copy a message directly from the address space of one thread to another without intermediate buffering, the message-delivery performance approaches the memory bandwidth of the underlying hardware.
Message-passing例子
Qnx官网给出了例子,这里借用分析一下例子。
- 服务端
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/dispatch.h>
#define ATTACH_POINT "myname"
// 定义消息数据的类型
typedef struct _my_data
{
uint16_t type;
int value;
} my_data_t;
// 在特殊情况下,比如客户端断开,会收到来自Qnx Kernel的消息。





 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 3362
3362

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










