点的定义:
为了便于理解,可以加一句 t y p e d e f p o i n t V e c t o r typedef\ \ point\ \ Vector typedef point Vector,即把点当成向量来处理。
struct point
{
double x,y;
point(double xx=0,double yy=0):x(xx),y(yy){}
};
typedef point Vector;
补充一些跟点有关的函数:
struct point
{
double x,y;
point(double a=0,double b=0)
{
x=a,y=b;
}
friend point operator * (point a,double b)
{
return point(a.x*b,a.y*b);
}
friend point operator * (double a,point b)
{
return point(b.x*a,b.y*a);
}
point operator - (const point &b)const
{
return point(x-b.x,y-b.y);
}
point operator + (const point &b)const
{
return point(x+b.x,y+b.y);
}
point operator / (const double b)const
{
return point(x/b,y/b);
}
bool operator < (const point &b)const//按坐标排序
{
if(fabs(x-b.x)<eps)
return y<b.y-eps;
return x<b.x-eps;
}
void transxy(double sinb,double cosb)//逆时针旋转b弧度
{ //若顺时针 在传入的sinb前加个-即可
double tx=x,ty=y;
x=tx*cosb-ty*sinb;
y=tx*sinb+ty*cosb;
}
void transxy(double b)//逆时针旋转b弧度
{ //若顺时针传入-b即可
double tx=x,ty=y;
x=tx*cos(b)-ty*sin(b);
y=tx*sin(b)+ty*cos(b);
}
double norm()
{
return sqrt(x*x+y*y);
}
};
一些细节问题:
P i Pi Pi用反三角函数计算出来,精度提前定义好。(精度很重要 尽量避免误差大的运算 如开方)
const double pi=acos(-1);//弧度pi
const double eps=1e-8;//精度
判断一个数与 0 0 0的关系:
inline int sgn(double x)
{
if(fabs(x)<eps)
return 0;
if(x>0)
return 1;
return -1;
}
如何表示一个圆?采用圆心+半径的形式:
p
a
i
r
<
p
o
i
n
t
,
d
o
u
b
l
e
>
pair<point,double>
pair<point,double>
注意使用
a
c
o
s
acos
acos这种函数时要保证传入的值在
[
−
1
,
1
]
[-1,1]
[−1,1]之间,因为精度问题我们要进行特判,可通过±eps来修改。同理使用
s
q
r
t
sqrt
sqrt时也要保证传入的是一个非负数。若答案为0最好也判断一下,防止输出
−
0.00
-0.00
−0.00。
叉积、点积、两点间的距离
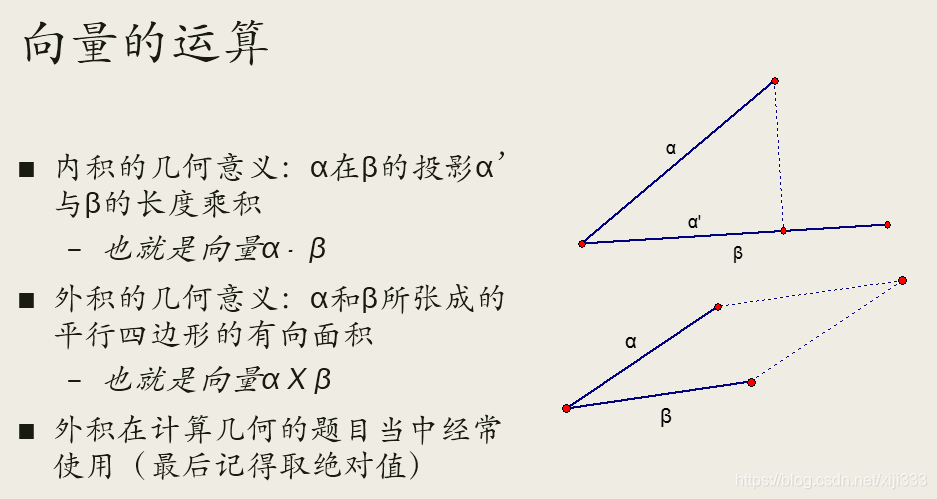
叉积的方向通过右手定则来判断,
a
⃗
×
b
⃗
\vec{a}\times\vec{b}
a×b的方向
=
=
=我们用右手从
a
ˉ
\bar{a}
aˉ扫到
b
ˉ
\bar{b}
bˉ时(不超过180°)大拇指所指向的方向。因此可以用叉积判断一个点是在一条线段的左侧还是右侧。
inline double dot(point a,point b)//点积
{
return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y;
}
inline double cross(point a,point b)//叉积
{
return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x;
}
inline double dist(point a,point b)//两点间距离
{
return (a-b).norm();
}
点的模板整合:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const double pi=acos(-1);//弧度pi
const double eps=1e-8;//精度
inline int sgn(double x)
{
if(fabs(x)<eps)
return 0;
if(x>0)
return 1;
return -1;
}
struct point
{
double x,y;
point(double a=0,double b=0)
{
x=a,y=b;
}
friend point operator * (point a,double b)
{
return point(a.x*b,a.y*b);
}
friend point operator * (double a,point b)
{
return point(b.x*a,b.y*a);
}
point operator - (const point &b)const
{
return point(x-b.x,y-b.y);
}
point operator + (const point &b)const
{
return point(x+b.x,y+b.y);
}
point operator / (const double b)const
{
return point(x/b,y/b);
}
bool operator < (const point &b)const//按坐标排序
{
if(fabs(x-b.x)<eps)
return y<b.y-eps;
return x<b.x-eps;
}
bool operator == (const point &b)const
{
return sgn(x-b.x)==0&&sgn(y-b.y)==0;
}
void transxy(double sinb,double cosb)//逆时针旋转b弧度
{ //若顺时针 在传入的sinb前加个-即可
double tx=x,ty=y;
x=tx*cosb-ty*sinb;
y=tx*sinb+ty*cosb;
}
void transxy(double b)//逆时针旋转b弧度
{ //若顺时针传入-b即可
double tx=x,ty=y;
x=tx*cos(b)-ty*sin(b);
y=tx*sin(b)+ty*cos(b);
}
double norm()
{
return sqrt(x*x+y*y);
}
};
inline double dot(point a,point b)//点积
{
return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y;
}
inline double cross(point a,point b)//叉积
{
return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x;
}
inline double dist(point a,point b)//两点间距离
{
return (a-b).norm();
}
typedef point Vector;
直线、线段的定义:
struct line
{
point s,e;
line(){}
line(point _s,point _e)
{
s=_s,e=_e;
}
};
double xmult(point p1,point p2,point p3)//p1p2 X p1p3
{
return cross(p2-p1,p3-p1);
}
bool seg_inter_line(line l1,line l2)//判断直线l1 与 线段l2 是否相交
{
return sgn(xmult(l2.s,l1.s,l1.e))*sgn(xmult(l2.e,l1.s,l1.e))<=0;
}
inline double dis_point_seg(point p,line l)//计算点到线段距离
{
if(sgn(dot(p-l.s,l.e-l.s))<0)//不存在 返回点到线段端点的距离
return (p-l.s).norm();
if(sgn(dot(p-l.e,l.s-l.e))<0)//不存在 返回点到线段端点的距离
return (p-l.e).norm();
return fabs(cross(l.s-p,l.e-p))/dist(l.s,l.e);//|叉积|=2*S△
}
void popint_proj_line(point p,point s,point t,point &cp)//计算点p到线段st的垂足 保存在cp中
{
double r=dot(t-s,p-s)/dot(t-s,t-s);
cp=s+r*(t-s);
}
bool point_on_seg(point p,point s,point t)//判断点p 是否在线段st上 包括端点
{
return sgn(cross(p-s,t-s))==0&&sgn(dot(p-s,p-t))<=0;
}
bool parallel(line a,line b)//判断a b 是否平行
{
return !sgn(cross(a.s-a.e,b.s-b.e));
}
bool line_make_point(line a,line b,point &res)//判断直线a b是否相交 若相交则返回true并把交点存在res中
{
if(parallel(a,b))
return 0;
double s1=cross(a.s-b.s,b.e-b.s);
double s2=cross(a.e-b.s,b.e-b.s);
res=(s1*a.e-s2*a.s)/(s1-s2);
return 1;
}
line move_d(line a,double len)//将直线a沿法向量方法平移len
{
point d=a.e-a.s;
d=d/d.norm();
d.transxy(pi/2);
return line(a.s+d*len,a.e+d*len);
}
注:请结合点的模板一起食用。
注:判断两线段是否相交,
S
e
g
_
i
n
t
e
r
_
l
i
n
e
Seg\_inter\_line
Seg_inter_line函数要调用两次。比如说判断线段
A
B
AB
AB与线段
C
D
CD
CD相交,首先判断直线
A
B
AB
AB与线段
C
D
CD
CD是否相交,再判断线段
A
B
AB
AB与直线
C
D
CD
CD是否相交,若两者同时成立则线段
A
B
AB
AB与线段
C
D
CD
CD相交。
注:算点到直线距离,利用叉积即可。已知点
P
P
P,在直线上任取两点
A
、
B
A、B
A、B,那么
∣
P
A
⃗
×
P
B
⃗
∣
=
2
∗
S
△
P
A
B
|\vec{PA}\ \times\vec{PB}|=2*S\bigtriangleup_{PAB}
∣PA ×PB∣=2∗S△PAB,从而得到
h
=
∣
P
A
⃗
×
P
B
⃗
∣
÷
∣
A
B
∣
h=|\vec{PA}\ \times\vec{PB}|\div|AB|
h=∣PA ×PB∣÷∣AB∣。
多边形:
struct point
{
double x,y;
point(double a=0,double b=0)
{
x=a,y=b;
}
friend point operator * (point a,double b)
{
return point(a.x*b,a.y*b);
}
friend point operator * (double a,point b)
{
return point(b.x*a,b.y*a);
}
point operator - (const point &b)const
{
return point(x-b.x,y-b.y);
}
point operator + (const point &b)const
{
return point(x+b.x,y+b.y);
}
point operator / (const double b)const
{
return point(x/b,y/b);
}
bool operator < (const point &b)const//按坐标排序
{
if(fabs(x-b.x)<eps)
return y<b.y-eps;
return x<b.x-eps;
}
void transxy(double sinb,double cosb)//逆时针旋转b弧度
{ //若顺时针 在传入的sinb前加个-即可
double tx=x,ty=y;
x=tx*cosb-ty*sinb;
y=tx*sinb+ty*cosb;
}
void transxy(double b)//逆时针旋转b弧度
{ //若顺时针传入-b即可
double tx=x,ty=y;
x=tx*cos(b)-ty*sin(b);
y=tx*sin(b)+ty*cos(b);
}
double norm()
{
return sqrt(x*x+y*y);
}
};
inline double dot(point a,point b)//点积
{
return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y;
}
inline double cross(point a,point b)//叉积
{
return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x;
}
inline double dist(point a,point b)//两点间距离
{
return (a-b).norm();
}
inline int sgn(double x)
{
if(fabs(x)<eps)
return 0;
if(x>0)
return 1;
return -1;
}
int gcd(int a,int b)
{
return b==0?a:gcd(b,a%b);
}
bool point_on_seg(point p,point s,point t)//判断点p 是否在线段st上 包括端点
{
return sgn(cross(p-s,t-s))==0&&sgn(dot(p-s,p-t))<=0;
}
typedef point Vector;
const int maxn=105;
struct polygon
{
int n;//多边形顶点数
point a[maxn];//0 到 n-1 顺时针顺序
polygon() {}
double perimeter()//计算多边形周长
{
double sum=0;
a[n]=a[0];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
sum+=(a[i+1]-a[i]).norm();
return sum;
}
double area()//计算多边形有向面积
{
double sum=0;
a[n]=a[0];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
sum+=cross(a[i+1],a[i]);
return sum/2;
}
double final_area()//多边形面积 即一定为正数
{
return fabs(area());
}
int point_in(point t)//t在多边形外返回0 t在多边形内返回1 t在多边形边界上返回2
{
int num=0,d1,d2,k;
a[n]=a[0];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(point_on_seg(t,a[i],a[i+1]))
return 2;
k=sgn(cross(a[i+1]-a[i],t-a[i]));
d1=sgn(a[i].y-t.y);
d2=sgn(a[i+1].y-t.y);
if(k>0&&d1<=0&&d2>0)
++num;
if(k<0&&d2<=0&&d1>0)
--num;
}
return num!=0;
}
point mass_center()//求多边形的重心坐标
{
point ans=point(0,0);
if(sgn(area())==0)
return ans;//多边形面积为0时重心没有定义 特判
a[n]=a[0];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
ans=ans+(a[i]+a[i+1])*cross(a[i+1],a[i]);
return ans/area()/6;
}
int border_int_point_num()
{
int num=0;
a[n]=a[0];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
num+=gcd(abs(int(a[i+1].x-a[i].x)),abs(int(a[i+1].y-a[i].y)));
return num;
}
int inside_int_point_num()
{
return int(final_area())+1-border_int_point_num()/2;
}
bool is_convex()//判断该多边形是否为凸包
{
a[n]=a[0],a[n+1]=a[1];
double tag=0,tmp;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
tmp=cross(a[i+1]-a[i],a[i+2]-a[i+1]);
if(tag==0)
tag=tmp;
else if(tag*tmp<0)//方向不同
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
};
注:因为要用到点类的相关函数,所以就把点类全搬过来了。
注:不用考虑输入点是顺时针还是逆时针,若要得到多边形的面积请用
f
i
n
a
l
_
a
r
e
a
final\_area
final_area函数。
凸包:
凸包是指对于平面上给定的一些点,选取一个最小的凸多边形使得这些点或者在其内部,或者在其边上。
凸包的求法:

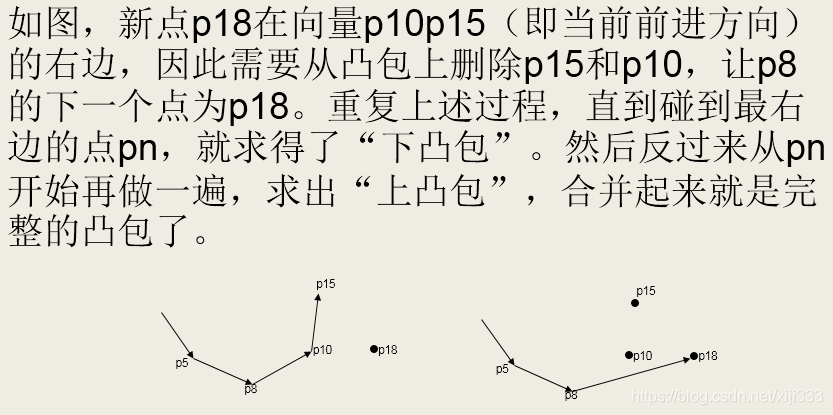
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const double pi=acos(-1);//弧度pi
const double eps=1e-8;//精度
inline int sgn(double x)
{
if(fabs(x)<eps)
return 0;
if(x>0)
return 1;
return -1;
}
struct point
{
double x,y;
point(double a=0,double b=0)
{
x=a,y=b;
}
friend point operator * (point a,double b)
{
return point(a.x*b,a.y*b);
}
friend point operator * (double a,point b)
{
return point(b.x*a,b.y*a);
}
point operator - (const point &b)const
{
return point(x-b.x,y-b.y);
}
point operator + (const point &b)const
{
return point(x+b.x,y+b.y);
}
point operator / (const double b)const
{
return point(x/b,y/b);
}
bool operator < (const point &b)const//按坐标排序
{
if(fabs(x-b.x)<eps)
return y<b.y-eps;
return x<b.x-eps;
}
bool operator == (const point &b)const
{
return sgn(x-b.x)==0&&sgn(y-b.y)==0;
}
void transxy(double sinb,double cosb)//逆时针旋转b弧度
{ //若顺时针 在传入的sinb前加个-即可
double tx=x,ty=y;
x=tx*cosb-ty*sinb;
y=tx*sinb+ty*cosb;
}
void transxy(double b)//逆时针旋转b弧度
{ //若顺时针传入-b即可
double tx=x,ty=y;
x=tx*cos(b)-ty*sin(b);
y=tx*sin(b)+ty*cos(b);
}
double norm()
{
return sqrt(x*x+y*y);
}
};
inline double dot(point a,point b)//点积
{
return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y;
}
inline double cross(point a,point b)//叉积
{
return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x;
}
inline double dist(point a,point b)//两点间距离
{
return (a-b).norm();
}
typedef point Vector;
vector<point> a;
struct polygon_convex//凸包
{
vector<point> p;
polygon_convex(int siz=0)
{
p.resize(siz);
}
double perimeter()//计算多边形周长
{
double sum=0;
int len=p.size();
for(int i=0;i<len-1;i++)
sum+=(p[i+1]-p[i]).norm();
sum+=(p[0]-p[len-1]).norm();
return sum;
}
double area()//计算多边形有向面积
{
double sum=0;
int len=p.size();
for(int i=0;i<len-1;i++)
sum+=cross(p[i+1],p[i]);
sum+=cross(p[0],p[len-1]);
return sum/2;
}
double final_area()//多边形面积 即一定为正数
{
return fabs(area());
}
int contain(const point b)//lgn的复杂度下判断点b是否在凸包内 true表示在凸包内(或边界上)
{
int n=p.size();
point g=(p[0]+p[n/3]+p[2*n/3])/3.0;
int l=0,r=n,mid;//二分凸包
while(l+1<r)
{
mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(sgn(cross(p[l]-g,p[mid]-g))>0)
{
if(sgn(cross(p[l]-g,b-g))>=0&&sgn(cross(p[mid]-g,b-g))<0)
r=mid;
else
l=mid;
}
else
{
if(sgn(cross(p[l]-g,b-g))<0&&sgn(cross(p[mid]-g,b-g))>=0)
l=mid;
else
r=mid;
}
}
r%=n;
int z=sgn(cross(p[r]-b,p[l]-b));
return z;//-1 内部 0 边界 1 外部
}
};
polygon_convex convex_hull()//用a中的点求解出凸包
{
polygon_convex res(2*a.size()+5);
sort(a.begin(),a.end());//按照横坐标排序
a.erase(unique(a.begin(),a.end()),a.end());//去重
int m=0;
int len=a.size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)//求下凸包
{
while(m>1&&sgn(cross(res.p[m-1]-res.p[m-2],a[i]-res.p[m-2]))<=0)//不包括共线点 如果包括共线点请修改此处的<=为<
--m;
res.p[m++]=a[i];
}
int k=m;
for(int i=len-2;i>=0;i--)//求上凸包
{
while(m>k&&sgn(cross(res.p[m-1]-res.p[m-2],a[i]-res.p[m-2]))<=0)//不包括共线点 如果包括共线点请修改此处的<=为<
--m;
res.p[m++]=a[i];
}
res.p.resize(m);
if(len>1)//去重
res.p.resize(m-1);
return res;
}
double convex_diameter(polygon_convex &a,int &First,int &Second)//旋转卡壳 返回最远距离 First Second 存储最远点的编号
{
vector<point> &p=a.p;
int n=p.size();
double maxd=0.0;
if(n==1)
{
First=Second=0;
return maxd;
}
p.push_back(p[0]);
for(int i=0,j=1;i<n;i++)
{
while(sgn(cross(p[i+1]-p[i],p[j]-p[i])-cross(p[i+1]-p[i],p[j+1]-p[i]))<0)
{
++j;
if(j==n)
j=0;
}
double d=dist(p[i],p[j]);
if(d>maxd)
maxd=d,First=i,Second=j;
d=dist(p[i+1],p[j+1]);
if(d>maxd)
maxd=d,First=i+1,Second=j+1;
}
if(First==n)
First=0;
if(Second==n)
Second=0;
p.pop_back();
return maxd;
}
稳定凸包:当凸包上存在一条边上的点只有端点两个点的时候,这个凸包不是稳定的,因为它可以在这条边外再引入一个点,构成一个新的凸包。但一旦一条边上存在三个点,那么不可能再找到一个点使它扩展成一个新的凸包,这样的凸包就叫稳定凸包。
注:多边形的函数完全可以移植到凸包这里,根据要求更改即可。





















 823
823

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








