任务6
快速排序算法被誉为 20 世纪科学和工程领域的十大算法之一。前面的任务只是对快速排序
的初识,下面从几个方面再更深入了解它:
① 优化快速排序:当待排序的数据量小于某个阈值时将递归的快速排序调用改为直接插入
排序调用,按照这种策略的优化的快速排序算法参照任务 4 的要求进行测试,并与任务4 中没有优化的快速排序算法的执行时间进行对比;
② 在实际应用中经常会出现含有大量重复元素的数组,例如可能需要将大量人员资料按照
生日排序,或者按照性别排序。给出使用①中完成的快速排序在数据规模为 2的16次方的情况下,数据的重复率分别为 50%、60%、80%和 100%的运行时间的变化趋势图。结合①中的运行数据,给出观察结果;
③ 当遇到②中的重复性很高的数据序列时,快速排序还有很大的改进空间,方法是改进快
速排序的划分方法,即将原有的二路划分(划分为比轴值大和不小于轴值)变成三路划分(划分为比轴值小,等于轴值和比轴值大)。三路划分的思路来自于经典的荷兰国旗问题。现要求自行查找三路划分的逻辑并实现之(高效的三路划分算法可以参考 J.Bentley 和 D.Mcllroy 的实现)。另外,用新的划分算法实现的快速排序重新对②完成实验并比较。
④ 在N个数据中找第k小元素(1≤k≤N)的问题可以有若干方法,请给出你能想到的方法,
并简要分析每个方法的时间复杂度。在若干方法中,可以利用快速排序思想高效实现,
请尽量独立思考,并最终给出设计思想、具体实现、测试以及时间复杂度分析。
①优化快速排序:定义一个private final int NUMBER 作为阈值,当待排序的数据量小于该值时,将递归的快速排序调用改为直接插入排序调用。
public void sort(Comparable[] objs, int left, int right) {
if (right - left + 1 <= NUMBER) {
// 如果待排序部分长度小于等于阈值,则调用插入排序
insertionSort(objs, left, right);
} else{
while (left < right) {
int pivotIndex = partition(objs, left, right);
if (pivotIndex - left < right - pivotIndex) {
// 左侧较短
sort(objs, left, pivotIndex - 1);
left = pivotIndex + 1;
} else {
// 右侧较短
sort(objs, pivotIndex + 1, right);
right = pivotIndex - 1;
}
}
}
}
② 给出使用①中完成的快速排序在数据规模为 2的16次方的情况下,数据的重复率分别为 50%、60%、80%和 100%的运行时间的变化趋势图。结合①中的运行数据,给出观察结果;
生成重复数的方法如下:
先得到一个0-1的有序数组,然后随机选择有序数组中的一个值,重复percent * N遍,再打乱。
public static Double[] getRepetitiveData(double percent,int N) {
int x = (int) (percent * N);
System.out.println(x);
Double[] numbers = getSortedData(N);
Random r = new Random();
int RepetitiveIndex = r.nextInt(N);
double RepetitiveNumber = numbers[RepetitiveIndex];
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
numbers[i] = RepetitiveNumber;
}
shuffle(numbers, 0, numbers.length);
return numbers;
}
③三路划分:
public class betterQuick extends SortAlgorithm {
private final int NUMBER = 60;
@Override
public void sort(Comparable[] objs) {
sort(objs, 0, objs.length - 1);
}
public void sort(Comparable[] objs, int left, int right) {
if (right - left + 1 <= NUMBER) {
insertionSort(objs, left, right);
} else {
while (left < right) {
int pivotIndex = partition3(objs, left, right);
if (pivotIndex - left < right - pivotIndex) {
sort(objs, left, pivotIndex - 1);
left = pivotIndex + 1;
} else {
sort(objs, pivotIndex + 1, right);
right = pivotIndex - 1;
}
}
}
}
private int partition3(Comparable[] objs, int left, int right) {
if (left < 0 || right >= objs.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid indices: left = " + left + ", right = " + right);
}
int lt = left;
int i = left + 1;
int gt = right;
Comparable pivot = objs[left];
while (i <= gt) {
int cmp = pivot.compareTo(objs[i]);
if (cmp < 0) {
exchange(objs, i, gt);
gt--;
} else if (cmp > 0) {
exchange(objs, i, lt);
lt++;
i++;
} else {
i++;
}
}
sort(objs, left, lt - 1);
sort(objs, gt + 1, right);
return lt;
}
public void insertionSort(Comparable[] objs, int left, int right) {
for (int i = left + 1; i <= right; i++) {
for (int j = i; j > left && less(objs[j], objs[j - 1]); j--) {
exchange(objs, j, j - 1);
}
}
}
}
这个新的partition3方法使用了三个指针:lt、i和gt。这三个指针将数组划分为四个部分:小于轴点的元素(left...lt-1)、等于轴点的元素(lt...i-1)、待扫描的元素(i...gt)、大于轴点的元素(gt+1...right)。
当objs[i]小于轴点时,交换objs[i]和objs[lt],然后增加lt和i。
当objs[i]大于轴点时,交换objs[i]和objs[gt],然后减小gt。这里不需要增加i,因为交换过来的元素还没有被比较。
当objs[i]等于轴点时,什么都不做,只需要增加i。
最后,将轴点元素放到正确的位置上(即lt的位置),然后返回这个位置。
④在N个数据中找第k小元素:
设计思想:
基于快速排序的分治思想,通过每次选择一个基准元素并进行划分,将比基准元素小的元素放在左边,比基准元素大的元素放在右边。通过划分过程,确定基准元素的位置,然后根据基准元素的位置和k的大小关系,继续在左边或右边的子数组中寻找第k小元素。
具体实现:
选择一个基准元素pivot。
对数组进行划分,将比pivot小的元素放在左边,比pivot大的元素放在右边。
如果pivot的位置等于k-1,则返回pivot作为第k小元素。
如果pivot的位置大于k-1,则在左边的子数组中继续寻找第k小元素。
如果pivot的位置小于k-1,则在右边的子数组中继续寻找第k-k'小元素,其中k' = pivot的位置 + 1。
public static Comparable findKthSmallest(Comparable[] objs, int k) {
if (k < 1 || k > objs.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid k value");
}
return quickSelect(objs, 0, objs.length - 1, k - 1);
}
private static Comparable quickSelect(Comparable[] objs, int left, int right, int k) {
while (left < right) {
int pivotIndex = partition(objs, left, right);
if (pivotIndex == k) {
return objs[k];
} else if (pivotIndex > k) {
right = pivotIndex - 1;
} else {
left = pivotIndex + 1;
}
}
return objs[k];
}
private static int partition(Comparable[] objs, int left, int right) {
int i = left, j = right;
Comparable pivot = objs[left];
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && objs[j].compareTo(pivot) >= 0)
j--;
if (i < j)
objs[i++] = objs[j];
while (i < j && objs[i].compareTo(pivot) <= 0)
i++;
if (i < j)
objs[j--] = objs[i];
}
objs[i] = pivot;
return i;
}
测试:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Comparable[] objs = {3, 2, 1, 5, 6, 4,9,7,6,21,7,64,5,0};
int k = 4;
Comparable kthSmallest = findKthSmallest(objs, k);
System.out.println("第" + k + "小的元素是" + kthSmallest);
}
![]()
进行了多次测试,均没有错误。
时间复杂度分析:
平均情况下,快速选择算法的时间复杂度为O(N),其中N是数组的大小。这是因为每次划分都会将数组的规模减半。
最坏情况下,快速选择算法的时间复杂度为O(N^2),出现在每次划分都选择到了最大或最小的元素作为基准元素的情况。
①优化快速排序:
Random:
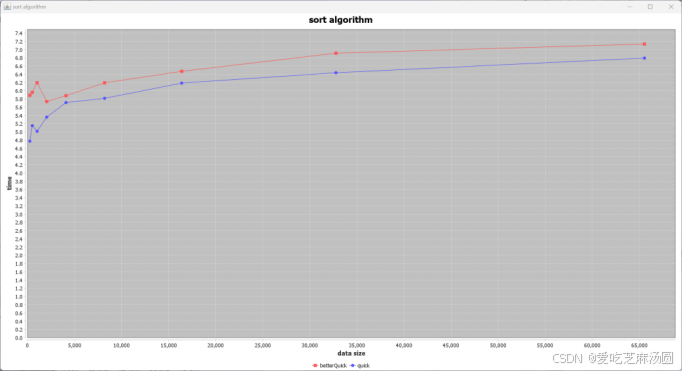
Sorted:
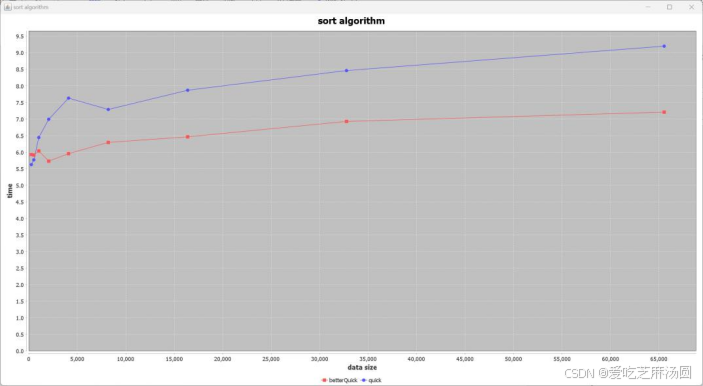
Invested:
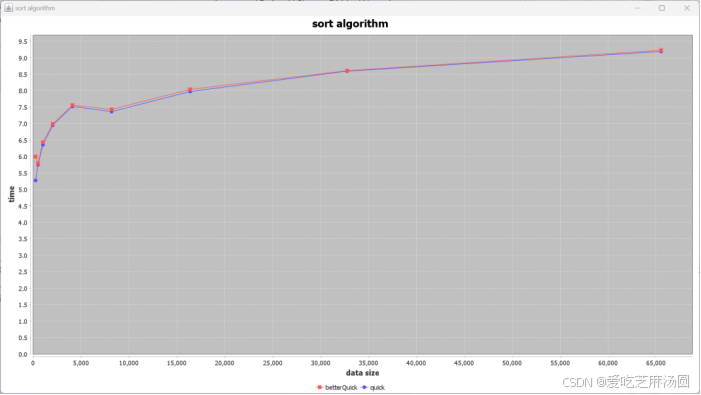
Uneven:
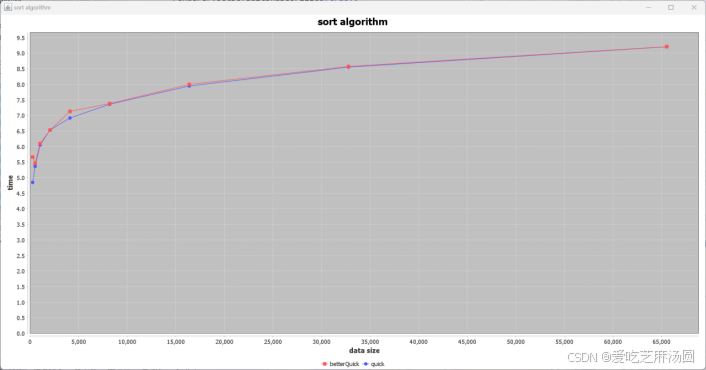
分析可知,经过优化,对于random和sorted两种数据,优化后明显加快速度,对于uneven和inverted两种数据则没有显著区别。
②重复数据:
使用插入排序优化后的quick:
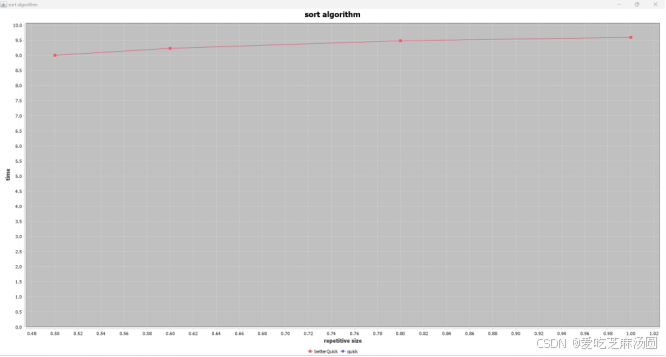
使用插入排序优化前的quick:
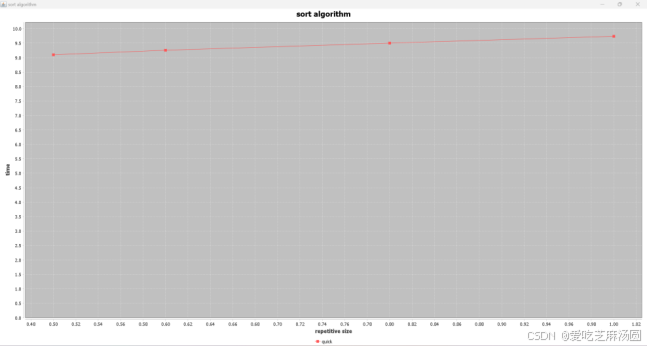
二者差异不大,并且随着数据重复量的增加,所消耗的时间会增加。
③三路划分。
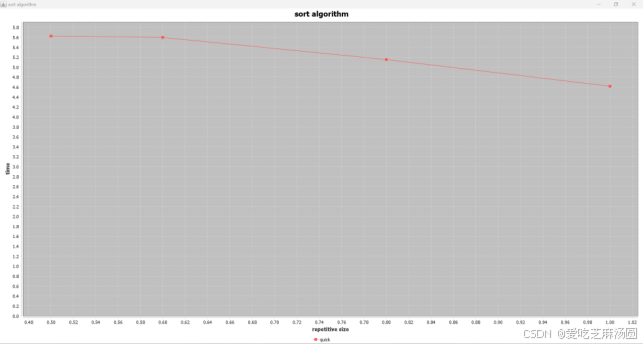
根据观察,可以得出以下结论:
随着重复率的增加,快速排序的运行时间逐渐增加。当重复率较低时,快速排序的性能较好,运行时间较短。然而,随着重复率的增加,快速排序的性能下降,运行时间增加。
当重复率接近100%时,即数组中的所有元素都相同,快速排序的性能最差。这是因为在这种情况下,快速排序的划分操作将数组分成了一个较小的部分和一个较大的部分,导致递归深度增加,从而增加了运行时间。
对于重复率较高的数据序列,三路划分的快速排序算法可以提供更好的性能。三路划分将数组划分为小于、等于和大于基准元素的三个部分,可以有效地减少划分操作的次数,从而改善性能。
因此,对于具有较高重复率的数据序列,使用三路划分的快速排序算法可能会比二路划分的算法更快。
④ 在N个数据中找第k小元素(1≤k≤N)
设计思想、具体实现、测试以及时间复杂度分析都在前面。
了解了三路划分并进行了具体实现,也学会了如何在N个数据中找第k小元素,提高了算法渐进分析的能力,收获很多。
附录:
- 任务6
1使用插入排序的快速排序:
- public void sort(Comparable[] objs, int left, int right) {
- if (right - left + 1 <= NUMBER) {
- // 如果待排序部分长度小于等于阈值,则调用插入排序
- insertionSort(objs, left, right);
- } else{
- while (left < right) {
- int pivotIndex = partition(objs, left, right);
- if (pivotIndex - left < right - pivotIndex) {
- // 左侧较短
- sort(objs, left, pivotIndex - 1);
- left = pivotIndex + 1;
- } else {
- // 右侧较短
- sort(objs, pivotIndex + 1, right);
- right = pivotIndex - 1;
- }
- }
- }
- }
② 生成重复数据的方法:
- public static Double[] getRepetitiveData(double percent,int N) {
- int x = (int) (percent * N);
- System.out.println(x);
- Double[] numbers = getSortedData(N);
- Random r = new Random();
- int RepetitiveIndex = r.nextInt(N);
- double RepetitiveNumber = numbers[RepetitiveIndex];
- for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
- numbers[i] = RepetitiveNumber;
- }
- shuffle(numbers, 0, numbers.length);
- return numbers;
- }
③三路划分:
- public class betterQuick extends SortAlgorithm {
- private final int NUMBER = 60;
- @Override
- public void sort(Comparable[] objs) {
- sort(objs, 0, objs.length - 1);
- }
- public void sort(Comparable[] objs, int left, int right) {
- if (right - left + 1 <= NUMBER) {
- insertionSort(objs, left, right);
- } else {
- while (left < right) {
- int pivotIndex = partition3(objs, left, right);
- if (pivotIndex - left < right - pivotIndex) {
- sort(objs, left, pivotIndex - 1);
- left = pivotIndex + 1;
- } else {
- sort(objs, pivotIndex + 1, right);
- right = pivotIndex - 1;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- private int partition3(Comparable[] objs, int left, int right) {
- if (left < 0 || right >= objs.length) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid indices: left = " + left + ", right = " + right);
- }
- int lt = left;
- int i = left + 1;
- int gt = right;
- Comparable pivot = objs[left];
- while (i <= gt) {
- int cmp = pivot.compareTo(objs[i]);
- if (cmp < 0) {
- exchange(objs, i, gt);
- gt--;
- } else if (cmp > 0) {
- exchange(objs, i, lt);
- lt++;
- i++;
- } else {
- i++;
- }
- }
- sort(objs, left, lt - 1);
- sort(objs, gt + 1, right);
- return lt;
- }
- public void insertionSort(Comparable[] objs, int left, int right) {
- for (int i = left + 1; i <= right; i++) {
- for (int j = i; j > left && less(objs[j], objs[j - 1]); j--) {
- exchange(objs, j, j - 1);
- }
- }
- }
- }
④ 在N个数据中找第k小元素(1≤k≤N)
- public class QuickSelect {
- public static Comparable findKthSmallest(Comparable[] objs, int k) {
- if (k < 1 || k > objs.length) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid k value");
- }
- return quickSelect(objs, 0, objs.length - 1, k - 1);
- }
- private static Comparable quickSelect(Comparable[] objs, int left, int right, int k) {
- while (left < right) {
- int pivotIndex = partition(objs, left, right);
- if (pivotIndex == k) {
- return objs[k];
- } else if (pivotIndex > k) {
- right = pivotIndex - 1;
- } else {
- left = pivotIndex + 1;
- }
- }
- return objs[k];
- }
- private static int partition(Comparable[] objs, int left, int right) {
- int i = left, j = right;
- Comparable pivot = objs[left];
- while (i < j) {
- while (i < j && objs[j].compareTo(pivot) >= 0)
- j--;
- if (i < j)
- objs[i++] = objs[j];
- while (i < j && objs[i].compareTo(pivot) <= 0)
- i++;
- if (i < j)
- objs[j--] = objs[i];
- }
- objs[i] = pivot;
- return i;
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Comparable[] objs = {3, 2, 1, 5, 6, 4,9,7,6,21,7,64,5,0};
- int k = 4;
- Comparable kthSmallest = findKthSmallest(objs, k);
- System.out.println("第" + k + "小的元素是" + kthSmallest);
- }
- }






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








