引言
本篇博文承接上一篇博文 https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/wenhao_ir/article/details/145176361继续完善代码,在上一篇博文的代码中,只实现了对中断的处理,并没有用户空间的事(我们并未创建内核空间与用户空间进行交互的设备文件),即处于用户空间的应用程序还无法读取按键值。
为了节约CPU的资源,读取按键值的程序显然不能一直在那里死循环读取按键的值嘛,因为大部分情况下按键都是没有值的,按键按下的时间毕竟是少数时间嘛。
在本篇博文中,我们让读取按键的程序在没有按键按下时就进入睡眠状态,但这种睡眠状态是可以被打断并唤醒的,即这种睡眠状态是可以被中断唤醒的,有按键按下的时候,这种“可中断的睡眠状态”被唤醒,然后去读取按钮值。
要特别注意的是:
虽然在本篇博文中咱们是在对中断事件的处理中唤醒处于睡眠状态的线程,但是这种“可中断的睡眠状态”并不是只能被中断事件唤醒,也能被别的事件唤醒,即wake_up_interruptible()这个函数不仅可以在中断服务程序中被运行,在别的函数中或其它地方也可以运行,千万不要认为wake_up_interruptible()这个函数只能在中断服务程序中运行。其实这里准确的称呼应该叫做“可被打断的睡眠状态(即线程能被某个事件唤醒)”
代码的修改比较简单,主要就是加入创建设备号、设备类、设备文件的代码,并运用相关的睡眠和唤醒函数。
完整代码
驱动程序gpio_key_drv.c中的代码
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
#include <linux/gpio/consumer.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/of_irq.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
struct gpio_key{
int gpio;
struct gpio_desc *gpiod;
int flag;
int irq;
} ;
static struct gpio_key *gpio_keys_100ask;
/* 主设备号 */
static int major = 0;
static struct class *gpio_key_class;
static int g_key = 0;
static DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(gpio_key_wait);
/* 实现文件操作结构体中的read函数 */
static ssize_t gpio_key_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
//printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
int err;
wait_event_interruptible(gpio_key_wait, g_key);
err = copy_to_user(buf, &g_key, 4);
g_key = 0;
// 返回值为4表明读到了4字节的数据
return 4;
}
/* 定义自己的file_operations结构体 */
static struct file_operations gpio_key_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = gpio_key_drv_read,
};
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = dev_id;
int val;
// 返回引脚电平的逻辑值,注意:如果是低电平有效,则当物理电平为低电平时,其返回值为1;则当物理电平为高电平时,其返回值为0.
// 如果要得到物理电平值,可以用函数gpiod_get_raw_value()得到
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
// 打印中断号、GPIO引脚编号和电平值
// printk("Interrupt number: %d; GPIO pin number: %d; Pin Logical value: %d\n", irq, gpio_key->gpio, val);
// g_key的高8位中存储的是GPIO口的编号,低8位中存储的是按键按下时的逻辑值
g_key = (gpio_key->gpio << 8) | val;
wake_up_interruptible(&gpio_key_wait);
return IRQ_HANDLED; // 表示中断已处理
}
/* 1. 从platform_device获得GPIO
* 2. gpio=>irq
* 3. request_irq
*/
static int gpio_key_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int err;
// 获取设备树节点指针
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
// count用于存储设备树中描述的GPIO口的数量
int count;
int i;
enum of_gpio_flags flag;
unsigned flags = GPIOF_IN;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
count = of_gpio_count(node);
if (!count)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, there isn't any gpio available\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_100ask = kzalloc(sizeof(struct gpio_key) * count, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!gpio_keys_100ask) {
printk("Memory allocation failed for gpio_keys_100ask\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
// 获取GIPO的全局编号及其标志位信息的代码
gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio = of_get_gpio_flags(node, i, &flag);
if (gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio < 0)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, of_get_gpio_flags fail\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
// 获取GPIO口的GPIO描述符的代码
gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpiod = gpio_to_desc(gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio);
if (!gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpiod) {
printk("Failed to get GPIO descriptor for GPIO %d\n", gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio);
return -EINVAL;
}
// 结构体gpio_key的成员flag用于存储对应的GPIO口是否是低电平有效,假如是低电平有效,成员flag的值为1,假如不是低电平有效,成员flag的值为0。
// 后续代码实际上并没有用到成员flag,这里出现这句代码只是考虑到代码的可扩展性,所以在这里是可以删除的。
gpio_keys_100ask[i].flag = flag & OF_GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW;
// 每次循环都重新初始化flags
flags = GPIOF_IN;
// 假如GPIO口是低电平有效,则把flags添加上低电平有效的信息
if (flag & OF_GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW)
flags |= GPIOF_ACTIVE_LOW;
// 请求一个GPIO硬件资源与设备结构体`pdev->dev`进行绑定
// 注意,这个绑定操作会在调用函数platform_driver_unregister()注销platform_driver时自动由内核解除绑定操作,所以gpio_key_remove函数中不需要显示去解除绑定
// 由`devm`开头的函数通常都会内核自动管理资源,咱们在退出函数中不用人为的去释放资源或解除绑定。
err = devm_gpio_request_one(&pdev->dev, gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio, flags, NULL);
// 获取GPIO口的中断请求号
gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq = gpio_to_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio);
}
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
char irq_name[32]; // 用于存储动态生成的中断名称
//使用snprintf()函数将动态生成的中断名称写入irq_name数组
snprintf(irq_name, sizeof(irq_name), "swh_gpio_irq_%d", i); // 根据i生成名称
//调用函数request_irq()来请求并设置一个中断
err = request_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq, gpio_key_isr, IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, irq_name, &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
}
/* 注册file_operations */
major = register_chrdev(0, "swh_read_keys_major", &gpio_key_drv);
gpio_key_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "swh_read_keys_class");
if (IS_ERR(gpio_key_class)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev(major, "swh_read_keys_major");
return PTR_ERR(gpio_key_class);
}
// 由于这里是把多个按键看成是一个设备,你可以想像一个键盘上对应多个按键,但键盘本身是一个设备,所以只有一个设备文件
device_create(gpio_key_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "read_keys0"); /* /dev/read_keys0 */
return 0;
}
static int gpio_key_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
int count;
int i;
device_destroy(gpio_key_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(gpio_key_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "swh_read_keys_major");
count = of_gpio_count(node);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
// 只有在irq有效时才释放中断资源
if (gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq >= 0) {
// 释放GPIO中断资源,下面这句代码做了下面两件事:
// 1、解除 `gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq` 中断号和 `gpio_key_isr` 中断处理函数的绑定。
// 2、解除 `gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq` 中断号和中断处理函数与 `gpio_keys_100ask[i]` 数据结构的绑定。
free_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq, &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
}
// 释放GPIO描述符
if (gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpiod) {
gpiod_put(gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpiod);
}
}
// 释放内存
kfree(gpio_keys_100ask);
return 0;
}
static const struct of_device_id irq_matach_table[] = {
{ .compatible = "swh-gpio_irq_key" },
{ },
};
/* 1. 定义platform_driver */
static struct platform_driver gpio_keys_driver = {
.probe = gpio_key_probe,
.remove = gpio_key_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "swh_irq_platform_dirver",
.of_match_table = irq_matach_table,
},
};
/* 2. 在入口函数注册platform_driver */
static int __init gpio_key_init(void)
{
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
err = platform_driver_register(&gpio_keys_driver);
return err;
}
/* 3. 有入口函数就应该有出口函数:卸载驱动程序时,就会去调用这个出口函数
* 卸载platform_driver
*/
static void __exit gpio_key_exit(void)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
platform_driver_unregister(&gpio_keys_driver);
}
/* 7. 其他完善:提供设备信息,自动创建设备节点 */
module_init(gpio_key_init);
module_exit(gpio_key_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
测试程序button_test.c中的代码
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
/*
* ./button_test /dev/100ask_button0
*
*/
// 打印线程的执行函数
void* print_while_waiting(void* arg)
{
while (1)
{
printf("I am another thread, and while the main thread is waiting for a button to be pressed, I can still run normally.\n");
sleep(10); // 每隔10秒打印一次
}
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
int val;
pthread_t print_thread;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s <dev>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 2. 打开文件 */
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("Can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
// 创建一个线程,每隔一段时间打印输出一条信息表示在等待按键期间,另外的线程在继续正常执行。
if (pthread_create(&print_thread, NULL, print_while_waiting, NULL) != 0)
{
printf("Failed to create print thread\n");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
while (1)
{
/* 3. 读文件 */
read(fd, &val, 4);
/* 提取 GPIO 编号和逻辑值 */
int gpio_number = (val >> 8) & 0xFF; // 高8位为 GPIO 编号
int gpio_value = val & 0xFF; // 低8位为逻辑值
/* 打印读到的信息 */
printf("GPIO Number: %d, Logical Value: %d\n", gpio_number, gpio_value);
}
//pthread_join的作用是使主线程等待线程print_threa结束后再继续执行剩下的代码。
//如果主线程在结束时未等待子线程完成,可能会导致未完成的资源清理或意外的程序终止。
//这里由于主线程中有个条件永远为真的while循环,实际上这句代码没有实际作用。
pthread_join(print_thread, NULL);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
关键代码的解读
关键代码如下
/* 实现文件操作结构体中的read函数 */
static ssize_t gpio_key_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
//printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
int err;
wait_event_interruptible(gpio_key_wait, g_key);
err = copy_to_user(buf, &g_key, 4);
g_key = 0;
// 返回值为4表明读到了4字节的数据
return 4;
}
......
// 中断处理函数
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = dev_id;
int val;
// 返回引脚电平的逻辑值,注意:如果是低电平有效,则当物理电平为低电平时,其返回值为1;则当物理电平为高电平时,其返回值为0.
// 如果要得到物理电平值,可以用函数gpiod_get_raw_value()得到
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
// 打印中断号、GPIO引脚编号和电平值
// printk("Interrupt number: %d; GPIO pin number: %d; Pin Logical value: %d\n", irq, gpio_key->gpio, val);
// g_key的高8位中存储的是GPIO口的编号,低8位中存储的是按键按下时的逻辑值
g_key = (gpio_key->gpio << 8) | val;
wake_up_interruptible(&gpio_key_wait);
return IRQ_HANDLED; // 表示中断已处理
}
......
关键代码解析
请以上面的代码为例,说明函数wake_up_interruptible和函数wait_event_interruptible如何互相配合实现读取按键值到用户空间的?
函数wait_event_interruptible的介绍
在Linux内核中,wait_event_interruptible 是一个常用的等待队列(wait queue)相关函数,主要用于让线程进入“可被打断的睡眠状态(即线程能被某个事件唤醒)”,直到某个特定条件变为真线程才从睡眠状态中被唤醒。
函数原型
int wait_event_interruptible(wait_queue_head_t wq, condition);
wq:类型为wait_queue_head_t,表示等待队列的头部。【关于什么叫等待队列的头部,下面有详细介绍。】condition:表示等待的条件,当其逻辑值为真时,线程将被唤醒。【具体的介绍请看下面工作原理中的“条件检查”】
返回值
- 0:表示等待成功,并且条件满足,线程被唤醒继续执行。
- -ERESTARTSYS:表示在等待期间接收到一个信号(例如,用户按下
Ctrl+C或其他信号)。
工作原理
- 可被打断的睡眠状态(即线程能被某个事件唤醒):调用
wait_event_interruptible的线程将进入可被打断的睡眠状态(即线程能被某个事件唤醒)。 - 条件检查:
- 如果调用
wait_event_interruptible时,condition已经为真,则函数立即返回。 - 如果
condition为假,则将当前线程加入到wq的等待队列中,并进入可被唤醒的睡眠状态。 - 线程进入睡眠状态后,当中断处理函数中调用函数
wake_up_interruptible()时,由wait_queue_head_t管理的等待队列中所有处于睡眠状态的线程都将被唤醒,被唤醒的线程们会分别去检查此时自己的condition是否已经为真,如果是真,则被唤醒,继续执行,否则,再次进入睡眠状态。
- 如果调用
注意事项
- 信号中断:由
wait_event_interruptible而进入睡眠状态不仅可以被函数wake_up_interruptible()和condition唤醒,也可以被信号中断(比如用户按下Ctrl+C或其他信号),在使用时最好检查返回值并处理-ERESTARTSYS错误。 - 条件保护:条件变量通常需要在临界区内被检查或更新,避免竞态条件(如通过
mutex或spinlock)。 - 避免死锁:确保在调用
wait_event_interruptible前已释放可能导致死锁的锁。
相关函数
wait_event:不可中断版本,线程进入不可被打断唤醒的睡眠状态。wait_event_timeout:带有超时时间的版本。wake_up_interruptible:唤醒wait_event_interruptible的等待线程。
等待队列的头部详解(参数 wait_queue_head_t)
函数wait_event_interruptible的第一个参数是 wait_queue_head_t,表示等待队列的头部,那么什么叫等待队列的头部?
在 Linux 内核中,等待队列的头部是用来管理一个等待队列的核心结构。等待队列是内核中用于实现任务(线程)同步的机制,当某些资源不可用或者某些条件未满足时,任务可以进入等待队列,直到条件满足或资源变得可用时被唤醒。
等待队列头部的定义
wait_queue_head_t 是一个数据结构,表示等待队列的头部,用于管理队列中的所有等待任务。它的定义如下(摘自内核代码):
typedef struct __wait_queue_head {
spinlock_t lock; // 用于保护等待队列的自旋锁
struct list_head task_list; // 等待队列中所有等待任务的链表
} wait_queue_head_t;
字段说明:
-
spinlock_t lock:- 用于保护等待队列的操作(如添加任务、唤醒任务),确保在多核环境下的并发安全。
-
struct list_head task_list:- 一个双向链表,链表中的每个节点对应一个等待的任务。
- 任务通过
wait_queue_t(或更具体的类型,如wait_queue_entry_t)结构体加入这个链表。
为什么叫头部?
等待队列实际上是一个链表,wait_queue_head_t 代表链表的头部节点,负责:
- 组织和管理整个等待队列中的任务。
- 提供对等待队列的全局访问点,方便进行任务的添加、删除和唤醒操作。
头部本身并不表示具体的任务,而是整个等待队列的入口或管理中心。
等待队列的工作机制
-
任务进入队列:
- 当任务需要等待某个条件时,它会通过函数(如
wait_event_interruptible)将自己加入到等待队列中。 - 内核会将任务标记为睡眠状态,并挂载到等待队列的链表中。
- 当任务需要等待某个条件时,它会通过函数(如
-
条件满足时唤醒任务:
- 其他任务或中断处理程序可以通过调用
wake_up_interruptible或类似函数,从等待队列的头部开始遍历任务链表,并唤醒满足条件的任务。
- 其他任务或中断处理程序可以通过调用
初始化等待队列头部
等待队列的头部需要在使用前初始化,有两种常用方法:
-
静态初始化:
使用宏DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD:DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(my_wait_queue);这会定义一个名为
my_wait_queue的等待队列头部,并自动完成初始化。 -
动态初始化:
使用函数init_waitqueue_head:wait_queue_head_t my_wait_queue; init_waitqueue_head(&my_wait_queue);
关于等待队列头部的总结
- 等待队列头部(
wait_queue_head_t)是一个管理等待队列的核心结构,负责维护队列中所有等待的任务。 - 它包含一个链表(
task_list),记录所有等待任务,以及一个锁(lock),保证对队列操作的并发安全。 - 等待队列头部是整个队列的入口,操作等待队列时,所有任务的管理都从头部开始。
关键代码的完整流程分析
/* 实现文件操作结构体中的read函数 */
static ssize_t gpio_key_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
//printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
int err;
wait_event_interruptible(gpio_key_wait, g_key);
err = copy_to_user(buf, &g_key, 4);
g_key = 0;
// 返回值为4表明读到了4字节的数据
return 4;
}
......
// 中断处理函数
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = dev_id;
int val;
// 返回引脚电平的逻辑值,注意:如果是低电平有效,则当物理电平为低电平时,其返回值为1;则当物理电平为高电平时,其返回值为0.
// 如果要得到物理电平值,可以用函数gpiod_get_raw_value()得到
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
// 打印中断号、GPIO引脚编号和电平值
// printk("Interrupt number: %d; GPIO pin number: %d; Pin Logical value: %d\n", irq, gpio_key->gpio, val);
// g_key的高8位中存储的是GPIO口的编号,低8位中存储的是按键按下时的逻辑值
g_key = (gpio_key->gpio << 8) | val;
wake_up_interruptible(&gpio_key_wait);
return IRQ_HANDLED; // 表示中断已处理
}
......
在关键代码中,wait_event_interruptible 和 wake_up_interruptible 函数通过等待队列机制互相配合,实现了从内核到用户空间的按键值传递。以下是它们的工作原理和协作流程的具体解析:
代码中的主要角色
-
wait_event_interruptible:- 让调用它的线程(即用户空间程序)进入可被打断的睡眠状态(即线程能被某个事件唤醒),直到条件满足(即按键事件发生)。
- 判断条件是int型变量
g_key的逻辑值,当其逻辑值为0时,线程进入等待队列。
-
wake_up_interruptible:- 当中断处理程序捕获到按键事件时,通过调用
wake_up_interruptible并设置g_key的值为非零值,从而唤醒等待队列中睡眠的线程。 - 这使用户空间程序能够继续执行并读取按键值。
- 当中断处理程序捕获到按键事件时,通过调用
-
gpio_key_isr:- 中断处理函数,负责处理按键中断事件。
- 通过更新全局变量
g_key来记录按键值,并通过调用wake_up_interruptible唤醒等待队列。
-
全局变量
g_key:- 用于存储按键的值,包括 GPIO 口编号和按键逻辑值,传递给用户空间。
-
gpio_key_wait:- 等待队列头部,用于管理在等待按键事件的线程。
执行流程解析
1. 等待按键事件发生
当用户空间程序调用 gpio_key_drv_read 时:
wait_event_interruptible(gpio_key_wait, g_key);
- 用户程序进入可中断的睡眠状态,前提是
g_key == 0。 - 如果
g_key == 0(没有按键事件),则当前线程会被挂载到等待队列gpio_key_wait中,并让出 CPU。 - 此时,用户程序暂停执行,直到满足
g_key的值为非零。
2. 中断触发(按键事件发生)
当按键中断发生时,内核会调用 gpio_key_isr:
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
g_key = (gpio_key->gpio << 8) | val; // 更新全局变量 g_key
wake_up_interruptible(&gpio_key_wait); // 唤醒等待队列中的线程
- 步骤 1:通过
gpiod_get_value获取按键的逻辑值,并将 GPIO 口编号和按键值合并存储到全局变量g_key中。 - 步骤 2:调用
wake_up_interruptible(&gpio_key_wait),唤醒等待队列gpio_key_wait中的所有线程。
唤醒后的线程会重新检查条件 g_key ,如果其值不为零值,则线程真正的被唤醒,从而继续执行。
3. 读取按键值
被唤醒的用户程序从睡眠中返回,继续执行 gpio_key_drv_read:
err = copy_to_user(buf, &g_key, 4); // 将按键值从内核空间复制到用户空间
g_key = 0; // 重置 g_key,表示按键值已被处理
return 4; // 返回 4 字节数据的长度
- 使用
copy_to_user将g_key的值传递到用户空间的缓冲区buf。 - 重置
g_key为 0,表示已经处理完当前的按键事件,为下一次按键事件做好准备。 - 返回值
4表示用户程序成功读取了 4 字节数据。
设备树文件的修改和更新
和博文 https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/wenhao_ir/article/details/145176361 没有任何区别,所以这里略。
Makefile文件的书写
# 使用不同的Linux内核时, 一定要修改KERN_DIR,KERN_DIR代表已经配置、编译好的Linux源码的根目录
KERN_DIR = /home/book/100ask_imx6ull-sdk/Linux-4.9.88
all:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules
$(CROSS_COMPILE)gcc -o button_test_01 button_test.c
clean:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` clean
rm -rf modules.order
obj-m += gpio_key_drv.o
交叉编译出驱动模块和测试程序
源码复制到Ubuntu中。
make
将交叉编译出的gpio_key_drv.ko和button_test_01复制到NFS文件目录中,备用。
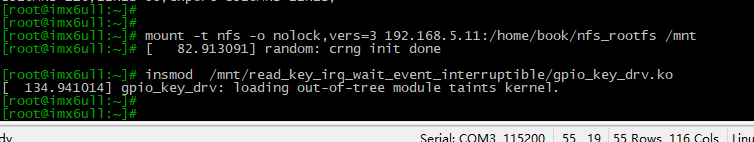
加载模块
打开串口终端→打开开发板→挂载网络文件系统
mount -t nfs -o nolock,vers=3 192.168.5.11:/home/book/nfs_rootfs /mnt
insmod /mnt/read_key_irq_wait_event_interruptible/gpio_key_drv.ko
检查设备文件生成没有
ls /dev/
有了:

运行测试程序
cd /mnt/read_key_irq_wait_event_interruptible
./button_test_01 /dev/read_keys0
先按下按键KEY1
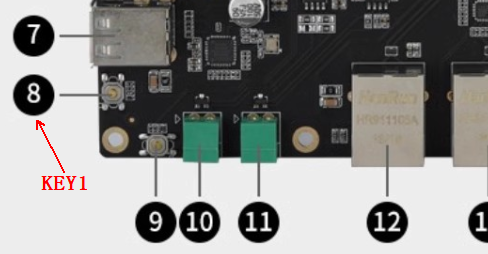
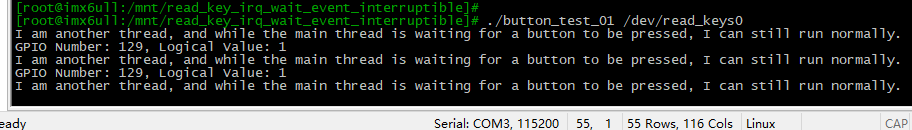
I am another thread, and while the main thread is waiting for a button to be pressed, I can still run normally.
GPIO Number: 129, Logical Value: 1
I am another thread, and while the main thread is waiting for a button to be pressed, I can still run normally.
GPIO Number: 129, Logical Value: 1
I am another thread, and while the main thread is waiting for a button to be pressed, I can still run normally.
可见达到了我们想要的效果,读取按键的主线程在执行中时,另外的线程仍仍可以正常运行。并且当按钮按下时打印出了相应的值。这里按键按下时其实物理电平为低电平,但因为这里设置了低电平有效,所以逻辑值为1。
再按下按键KEY2:
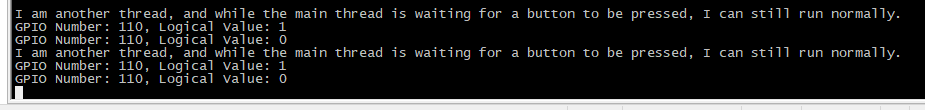
I am another thread, and while the main thread is waiting for a button to be pressed, I can still run normally.
GPIO Number: 110, Logical Value: 1
GPIO Number: 110, Logical Value: 0
I am another thread, and while the main thread is waiting for a button to be pressed, I can still run normally.
GPIO Number: 110, Logical Value: 1
GPIO Number: 110, Logical Value: 0
I am another thread, and while the main thread is waiting for a button to be pressed, I can still run normally.
可见达到了我们想要的效果,读取按键的主线程在执行中时,另外的线程仍仍可以正常运行。并且当按钮按下时打印出了相应的值。这里按键按下时其实物理电平为低电平,但因为这里设置了低电平有效,所以逻辑值为1。但是这里还是存在和上篇博文中的问题,存在机械按键抖动的问题,这导致了按一次有多次下降沿,但因为电平值的波动,导致第二次触发的逻辑值为0,对应于物理电平的高电平。
卸载驱动程序模块
rmmod gpio_key_drv.ko
查看下设备文件件/dev/read_keys0还在不在
ls /dev/
可见,设备文件/dev/read_keys0已经不在了。
查看下设备类swh_read_keys_class的目录还在不在
ls /sys/class/
看下驱动程序swh_read_keys_major还在不在
cat /proc/devices
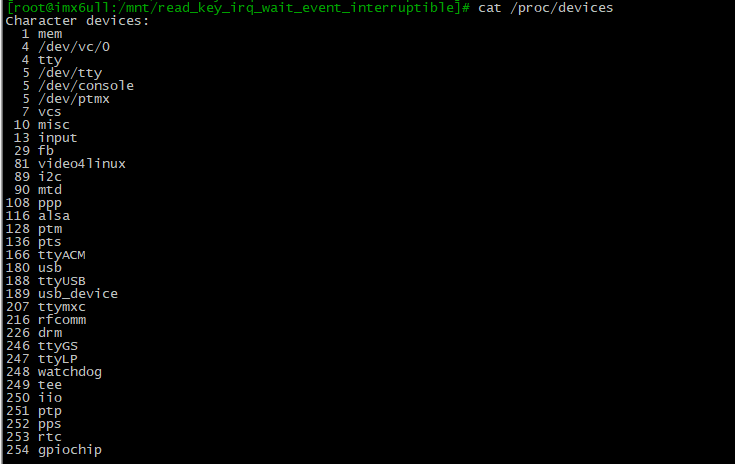
可见不在了。
说明卸载模块的程序部分是没问题了。
附完整工程文件
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1X0TtqSkRTN2ZGCN462C-Zw?pwd=xpd5
程序存在的问题及改进
按键速度过快时,后面的按键值会覆盖前面的按键值,具体的原因分析见 https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/wenhao_ir/article/details/145228617
所以需要对程序进行改进,具体的改进见:
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/wenhao_ir/article/details/145228617






















 680
680

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










