运算符重载的作用:
在 C++ 中,运算符重载是指给定一个运算符,我们可以定义该运算符在自定义类对象上的行为。通过运算符重载,我们可以为自定义类对象定义特定的操作,使其支持与内置类型相似的操作。
例如 比较两个类对象时可以采用运算符重载来进行操作,运算符重载的使用相当于内置类型运算符的使用,需要考虑操作数以及返回结果。
运算符重载的定义:
类似于函数的定义,只是函数名有所不同。运算符重载的定义遵循以下一般格式:
return_type operator op (parameters) { // 实现运算符的具体操作 }
其中,operator 是关键字用于指定要重载的运算符,op 是要重载的运算符,return_type 是运算符重载函数的返回类型,parameters 是运算符重载函数的参数列表。
其中的 返回值,参数,运算符都是可以自己选择,但是 关键字 operator 一点要带上。
并且 参数个数也要和 所写的运算符的个数匹配。
注意:
若是在类中声名和定义运算符重载,此运算符重载会隐藏一个 this 指针,而这个指针会占用一个参数位置。所以要注意参数的个数。
以下是一个简单的运算符重载:
class A
{
public:
A(int val = 1, int count = 1)
{
_val = val;
_count = count;
}
bool operator==(const A& e1)
{
return _val == e1._val && _count == e1._count;
}
private:
int _val;
int _count;
};
int main()
{
A a1;
A a2(1,1);
cout << (a1 == a2) << endl;
return 0;
}
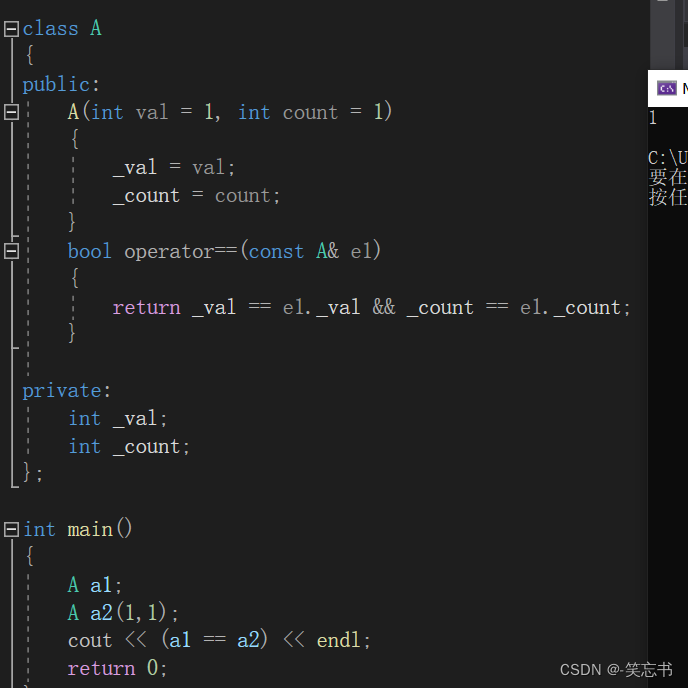
在 bool operator== 中,因为 操作符 == 所需的操作数的个数是 2个,但由于 this 指针的存在,占用了一个 参数位置,所以在传参时要注意 传入参数的数量。
实例:日期类中进行操作符重载操作:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
// 获取某年某月的天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
int arr[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if (month == 2 && year % 4 == 0 && year % 10 != 0 || year % 400 == 0)
return 29;
return arr[month];
}
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
// 拷贝构造函数
// d2(d1)
Date(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
// 赋值运算符重载
// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)
Date& operator=(const Date& d)
{
if (this != &d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
return *this;
}
// 析构函数
~Date()
{
_year = _month = _day = 0;
}
// 日期+=天数
Date& operator+=(int day)
{
_day = _day + day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_month++;
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
// 日期+天数
Date operator+(int day)
{
Date tem = *this;
//tem = tem.operator+=(day);
tem += day;
return tem;
}
// 日期-=天数
Date& operator-=(int day)
{
_day -= day;
while (_day < 1)
{
_month--;
if (_month < 1)
{
_year--;
_month = 12;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
// 日期-天数
Date operator-(int day)
{
Date tem = *this;
tem -= day;
return tem;
}
// 前置++
Date& operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置++
Date operator++(int)
{
Date tem = *this;
*this += 1;
return tem;
}
// 后置--
Date operator--(int)
{
Date tem = *this;
*this -= 1;
return tem;
}
// 前置--
Date& operator--()
{
return *this -= 1;
}
// >运算符重载
bool operator>(const Date& d)
{
if (_year > d._year)
return true;
else if (_year == d._year && _month > d._month)
return true;
else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// ==运算符重载
bool operator==(const Date& d)
{
if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._day)
return true;
return false;
}
// >=运算符重载
bool operator >= (const Date& d)
{
if (*this > d || *this == d)
return true;
return false;
}
// <运算符重载
bool operator < (const Date& d)
{
if (_year != d._year)
return _year<d._year;
if (_month != d._month)
return _month < d._month;
return _day < d._day;
}
// <=运算符重载
bool operator <= (const Date& d)
{
if (*this < d || *this == d)
return true;
return false;
}
// !=运算符重载
bool operator != (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this==d);
}
// 日期-日期 返回天数
int operator-(const Date& d)
{
int flag = 1;
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
if (*this < d)
{
flag = -1;
max = d;
min = *this;
}
int n = 0;
while (min != max)
{
++min;
++n;
}
return n * flag;
}
void Print()
{
cout << _year << "年" << _month << "月" << _day << "日" << endl;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
Date d1(1900,3,30);
Date d2(d1);
Date d3 = d1;
d3 -= 24;
cout << (d2 > d3) << endl;
cout << (d1 - d3) << endl;
return 0;
}
注意:
1.在进行前置++、前置--、后置++、后置--的操作时,由于操作数只能放在 关键字operator 的右边,所以可以 添加一个参数,构成参数重载,避免歧义。
2.在实现+和+=操作时,可以先实现+=操作,再通过 +=操作实现+操作,这样可以大大的减少代码的冗余。
3.若想使得,this指针指向的内容不变,可以加以 const 修饰 this指针,在类函数后加 上 const 即可,如下图:
![]()
但若是函数的声名和定义分离,则要在 函数的 声名 和 定义 都要加上 const 进行修饰。
总结:
在使用运算符重载时,有一些注意事项需要考虑:
-
保持运算符的语义和约定:在重载运算符时,应该尽量保持该运算符原有的语义和约定,以确保代码的可读性和可预测性。例如,重载加法运算符
+应该执行加法操作,而不是进行其他不相关的操作。 -
避免改变运算符的优先级和结合性:运算符重载只是改变了运算符在特定类对象上的行为,不应该改变运算符的优先级和结合性。例如,重载加法运算符
+不应该改变其在表达式中的优先级和结合性。 -
避免过度使用运算符重载:虽然运算符重载提供了方便的方式来定义类的行为,但过度使用运算符重载可能会导致代码难以理解和维护。应该谨慎选择需要重载的运算符,并确保重载后的行为符合直觉。
-
考虑参数类型和返回值类型:在定义运算符重载函数时,需要考虑参数的类型和返回值的类型,以确保运算符重载函数可以正确地与其他表达式结合使用。
-
避免破坏类的封装性:在定义运算符重载函数时,应该遵循类的封装性原则,不要直接访问类的私有成员,而是通过公有接口进行操作。
-
避免产生二义性:当定义多个版本的运算符重载函数时,应该避免产生二义性,确保编译器能够正确选择最合适的重载函数。
通过遵循这些注意事项,可以更好地使用运算符重载功能,提高代码的可读性和可维护性。
okok,今天任务完成,谢谢大家能看到后面,希望大家能够多多支持,多多讨论,一起共同进步!!!!























 1252
1252

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








