膨胀卷积
介绍
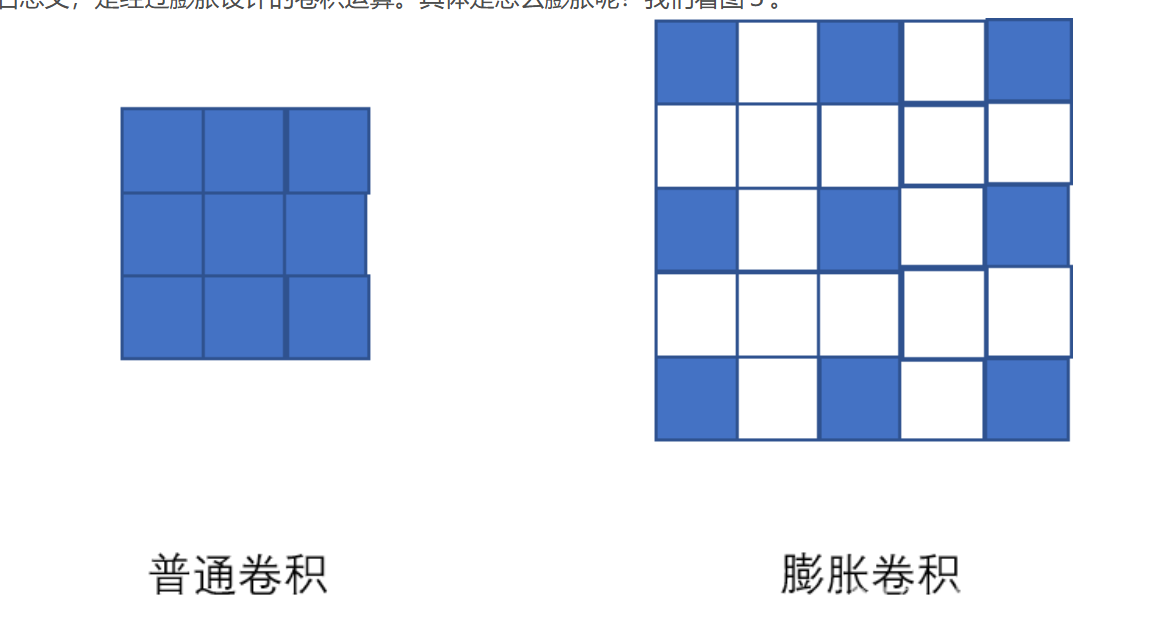
膨胀卷积又叫空洞卷积,最初的提出是为了解决图像分割的问题,常见的图像分割算法通常使用池化层和卷积层来增加感受野(Receptive Filed),同时也缩小了特征图尺寸,然后再利用上采样来还原图像尺寸,特征图缩小再放大的过程造成了精度上的损失,因此需要一种操作可以再增加感受野的同时保持特征图的尺寸不变,从而代替下采样和上采样操作。
英文: Dilated convolution (Atrous convolution)
作用
-
增大感受野
-
保持原输入特征图W、H
计算过程
kernel_size = 3, dilation=2
在卷积核每行每列之间插入dilation-1的间隔,这些间隔在实际做卷积时不纳入运算。
dilation=1时为普通卷积
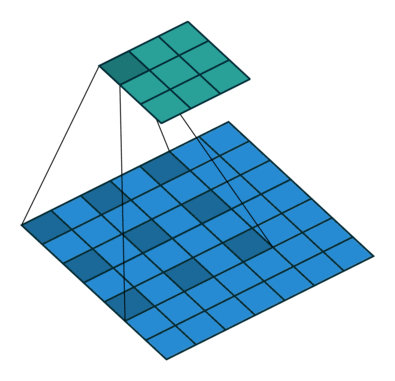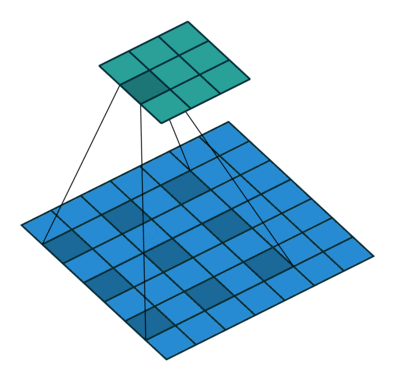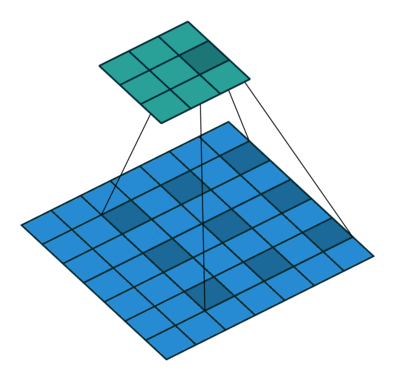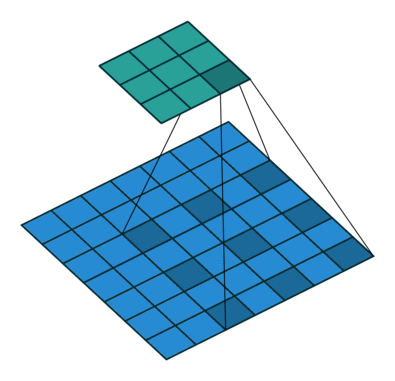
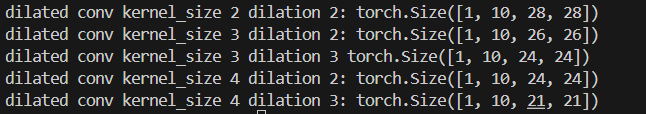
Pytorch代码使用
# Dilated Conv
conv5 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=10, kernel_size=2, dilation=2)
input = torch.randn(1, 3, 30, 30)
output = conv5(input)
print("dilated conv kernel_size 2 dilation 2:", output.shape)
# Dilated Conv
conv6 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=10, kernel_size=3, dilation=2)
input = torch.randn(1, 3, 30, 30)
output = conv6(input)
# (1, 10, 26, 26)
print("dilated conv kernel_size 3 dilation 2:", output.shape)
# Dilated Conv
conv7 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=10, kernel_size=3, dilation=3)
input = torch.randn(1, 3, 30, 30)
output = conv7(input)
# (1, 10, 4, 24)
print("dilated conv kernel_size 3 dilation 3", output.shape)
# Dilated Conv
conv8 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=10, kernel_size=4, dilation=2)
input = torch.randn(1, 3, 30, 30)
output = conv8(input)
# (1, 10, 24, 24)
print("dilated conv kernel_size 4 dilation 2:", output.shape)
# Dilated Conv
conv9 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=10, kernel_size=4, dilation=3)
input = torch.randn(1, 3, 30, 30)
output = conv9(input)
# (1, 10, 21, 21)
print("dilated conv kernel_size 4 dilation 3:", output.shape)
结果显示
使用过程
使用过程会造成 gridding effect 的问题
假设连续使用三个膨胀卷积,使用kernel_size=3, 膨胀系数为2的卷积层
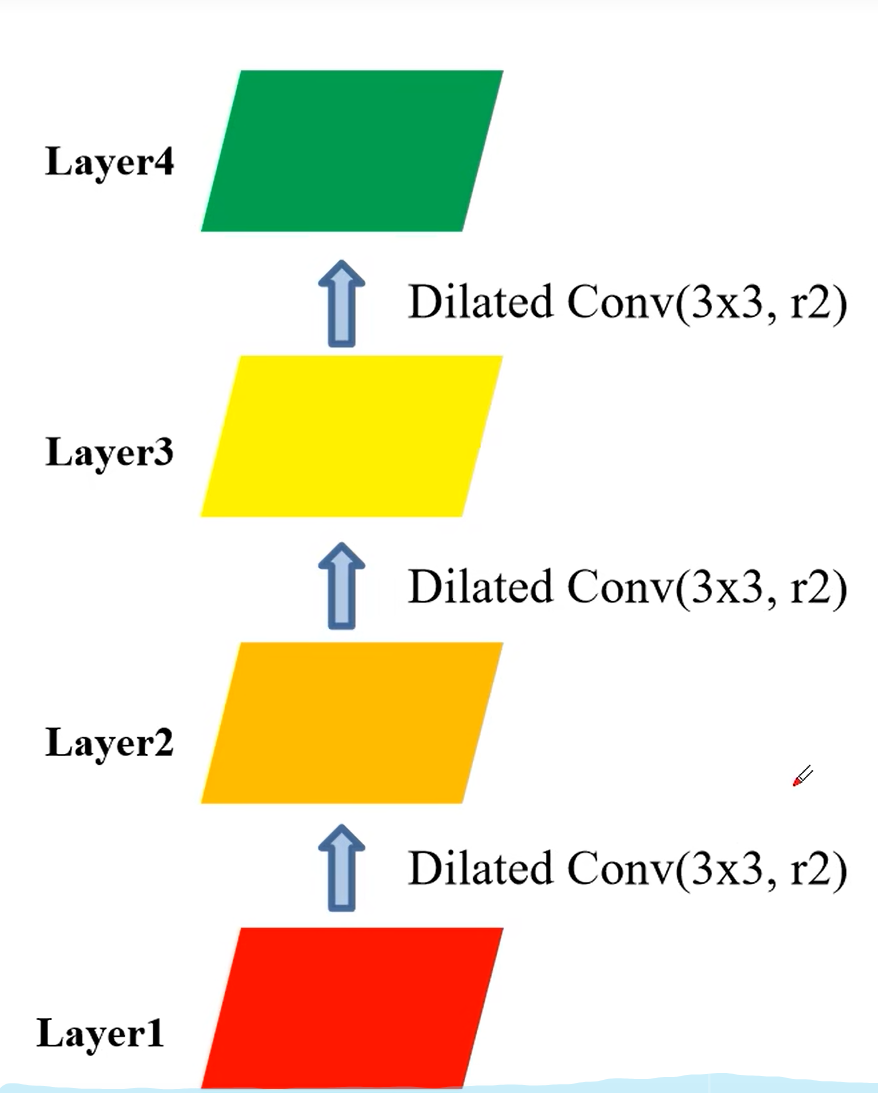
Layer2的一个pixel对应的Layer1信息
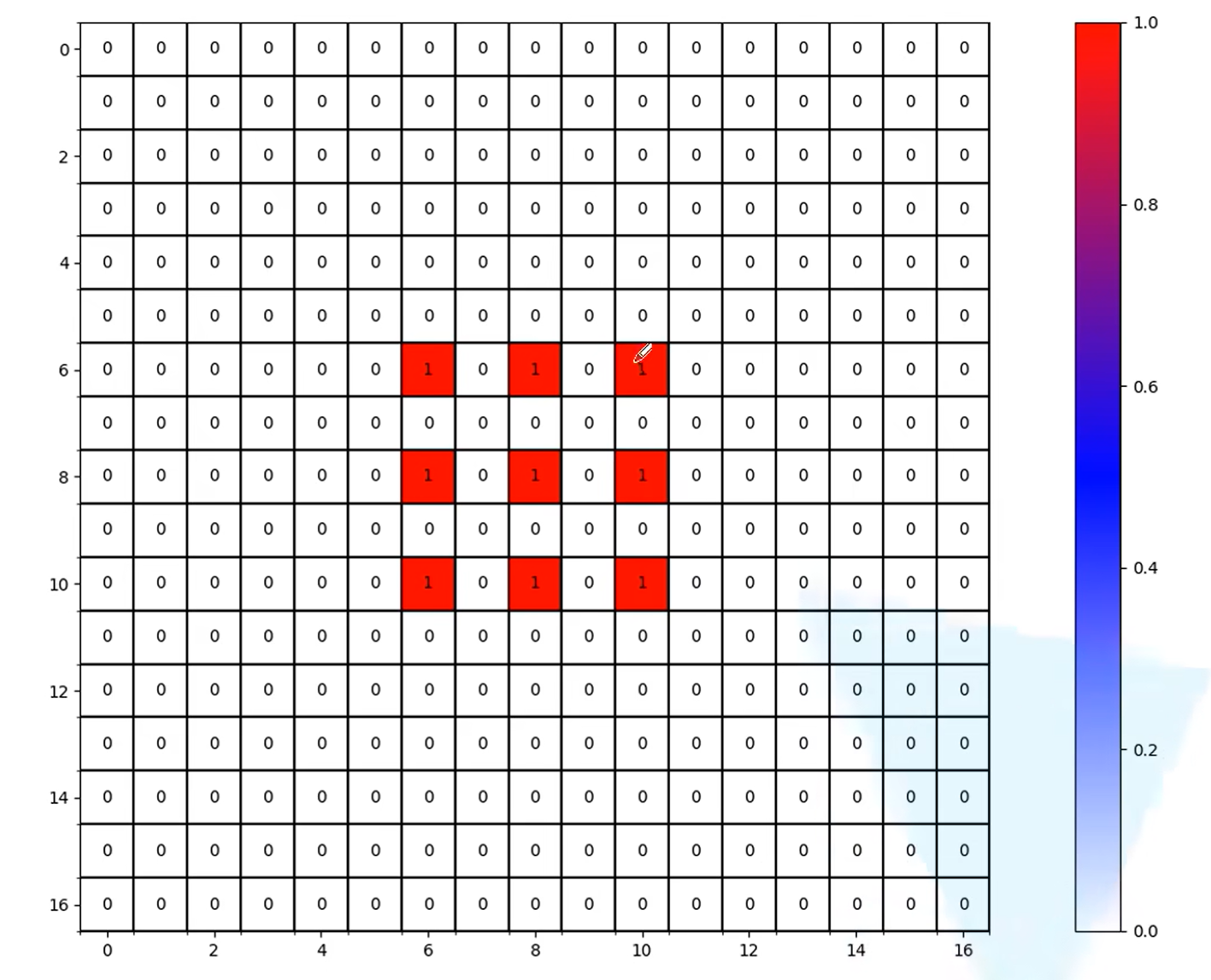
Layer3的一个pixel对应的Layer1的信息
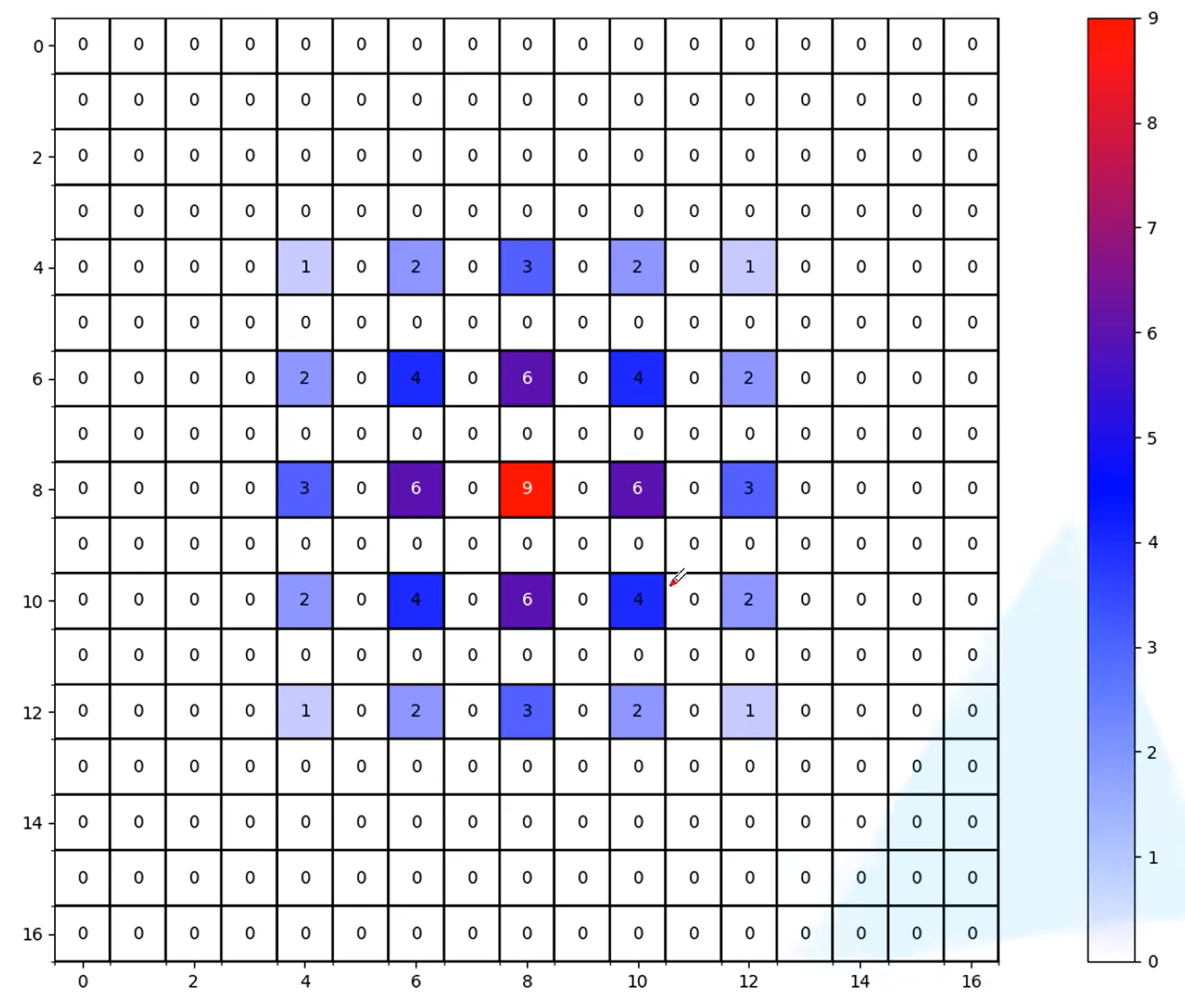
Layer4 一个pixel对应Layer1的信息
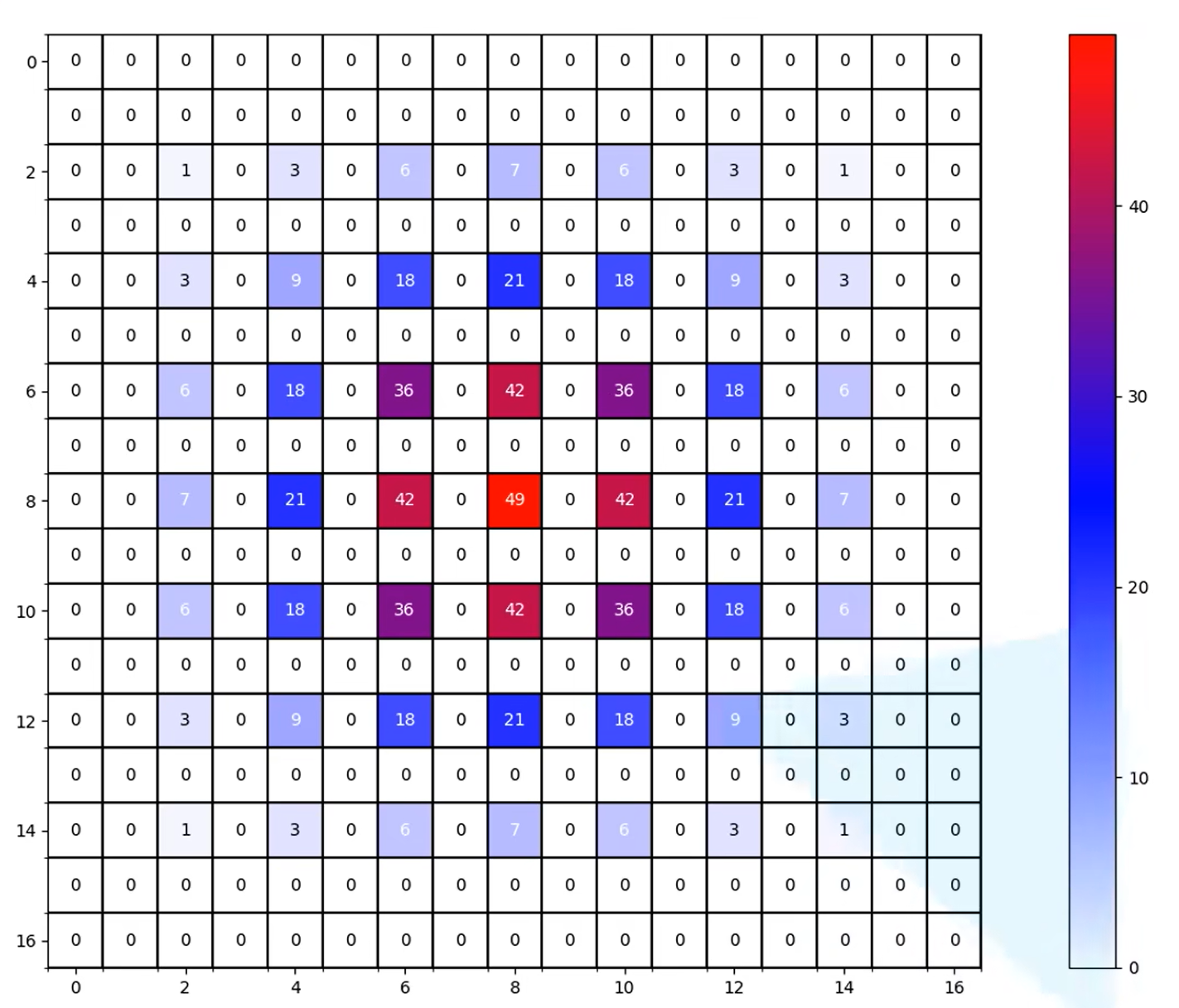
从这里发现Layer4的一个pixel信息对应Layer1的信息不是连续的,这样就造成这个gridding effect的问题。
假设现在将膨胀系数依次改成1、2、3
Layer2的一个pixel信息
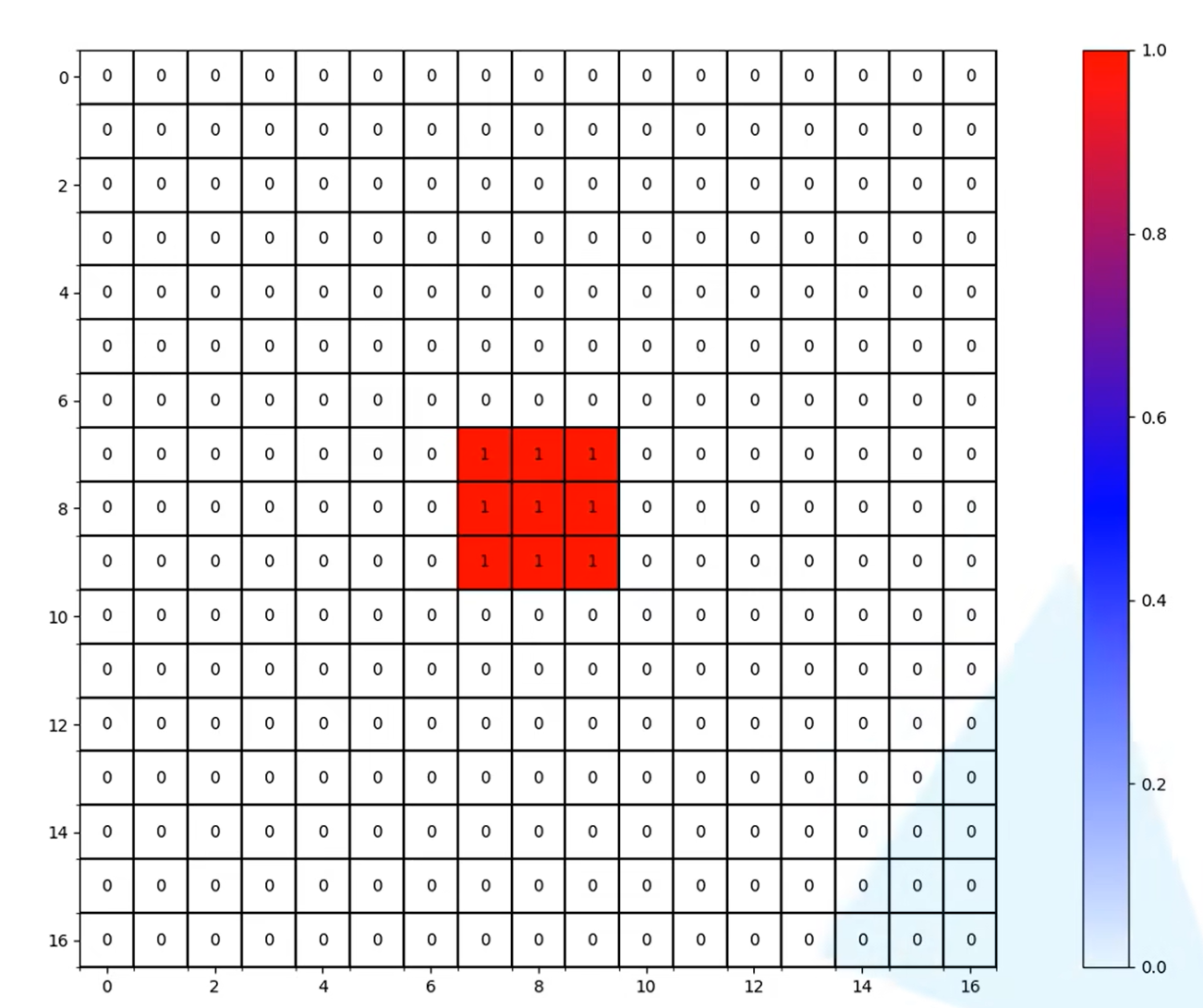
Layer3 一个pixel的信息
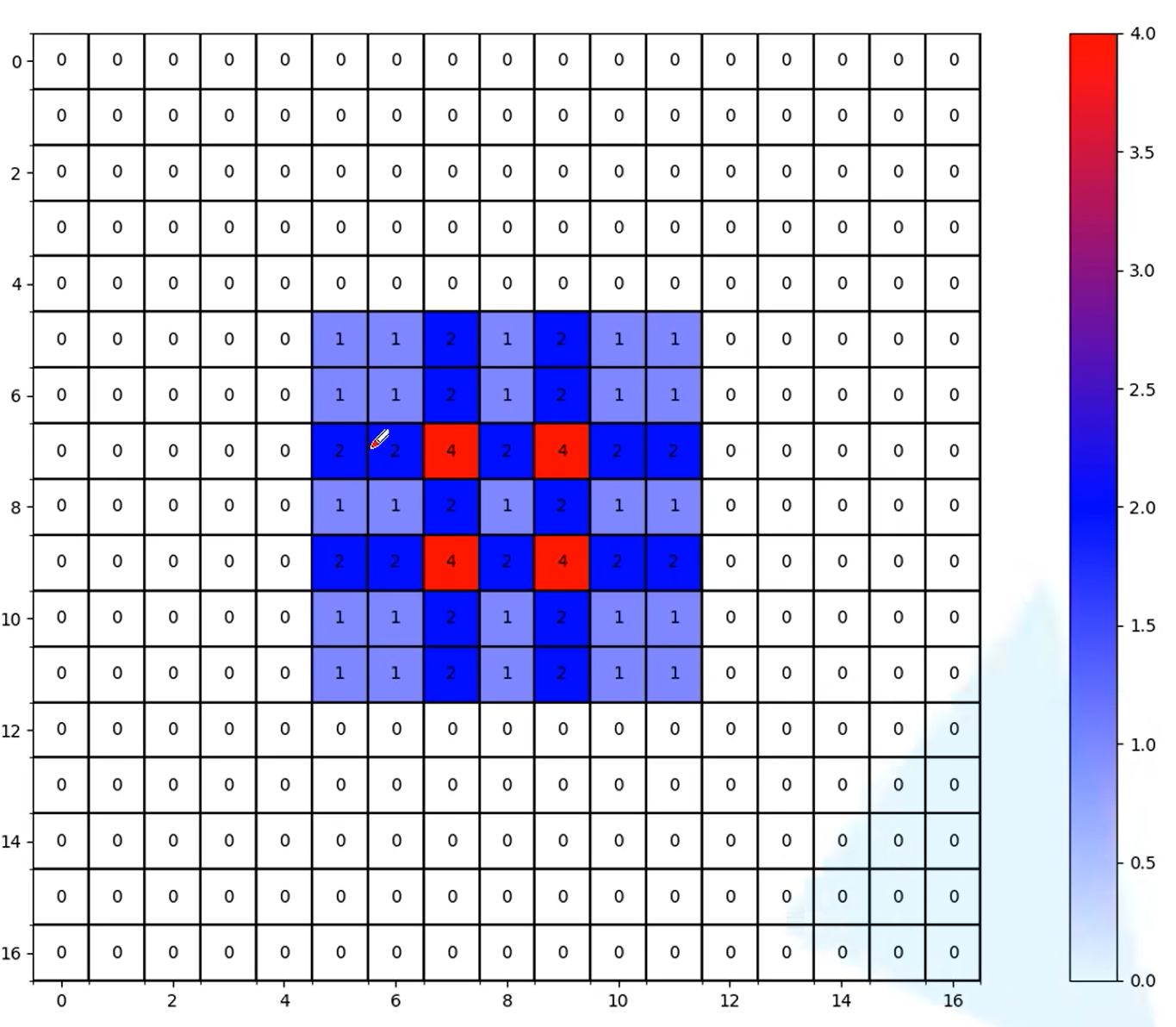
Layer4一个pixel的信息
对比可以看出,膨胀系数不同,看到信息的连续性也会不同,实际使用时,更倾向于第二种的膨胀卷积
再对比一下,使用相同系数的普通卷积的效果
普通卷积的感受野也会小一点,可以看出在使用相同参数数量的卷积核时,膨胀卷积能看到的信息会多一点。
如何设计膨胀系数
如何设计
Hybrid Dilated Convolution(HDC)准则
如何设计系数呢,使得最后一层出来的信息都是连续的且之间没有间隙
这里看出一个公式

M(i): 代表第i层的像素之间的距离(如果两个像素在附近则为1,如果两个像素之间间隔一个像素则为2,以此类推)
r(i): 代表第i层的膨胀系数,r=1为普通卷积
K: Kernel_Size的大小
已知: M(n) = r(n)
要使得, M(2) <= K
公式:
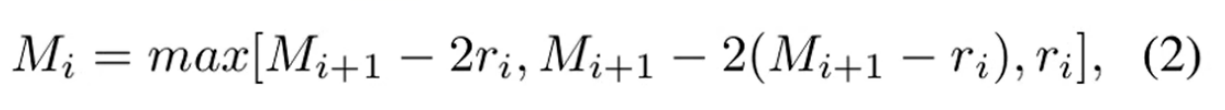
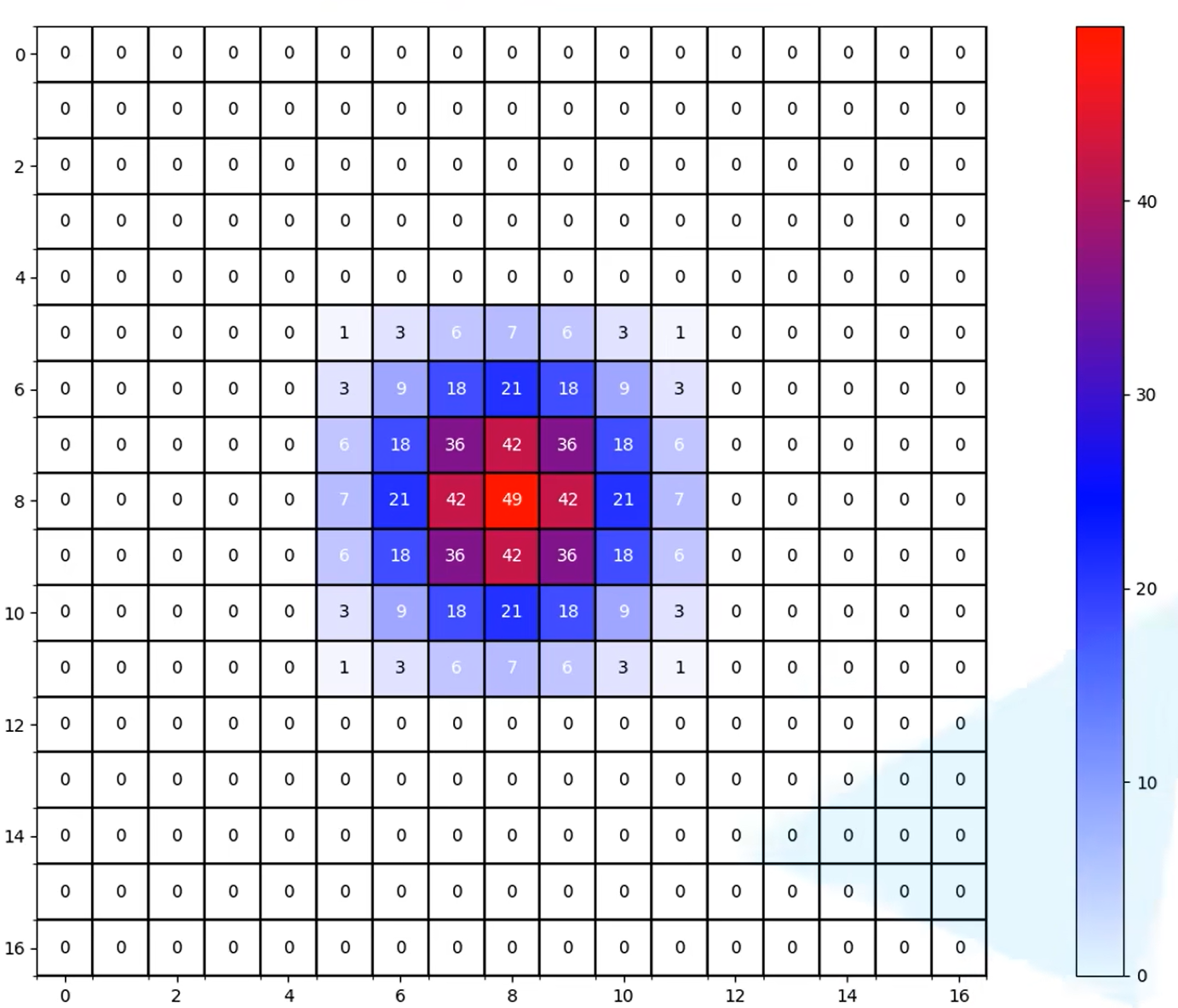
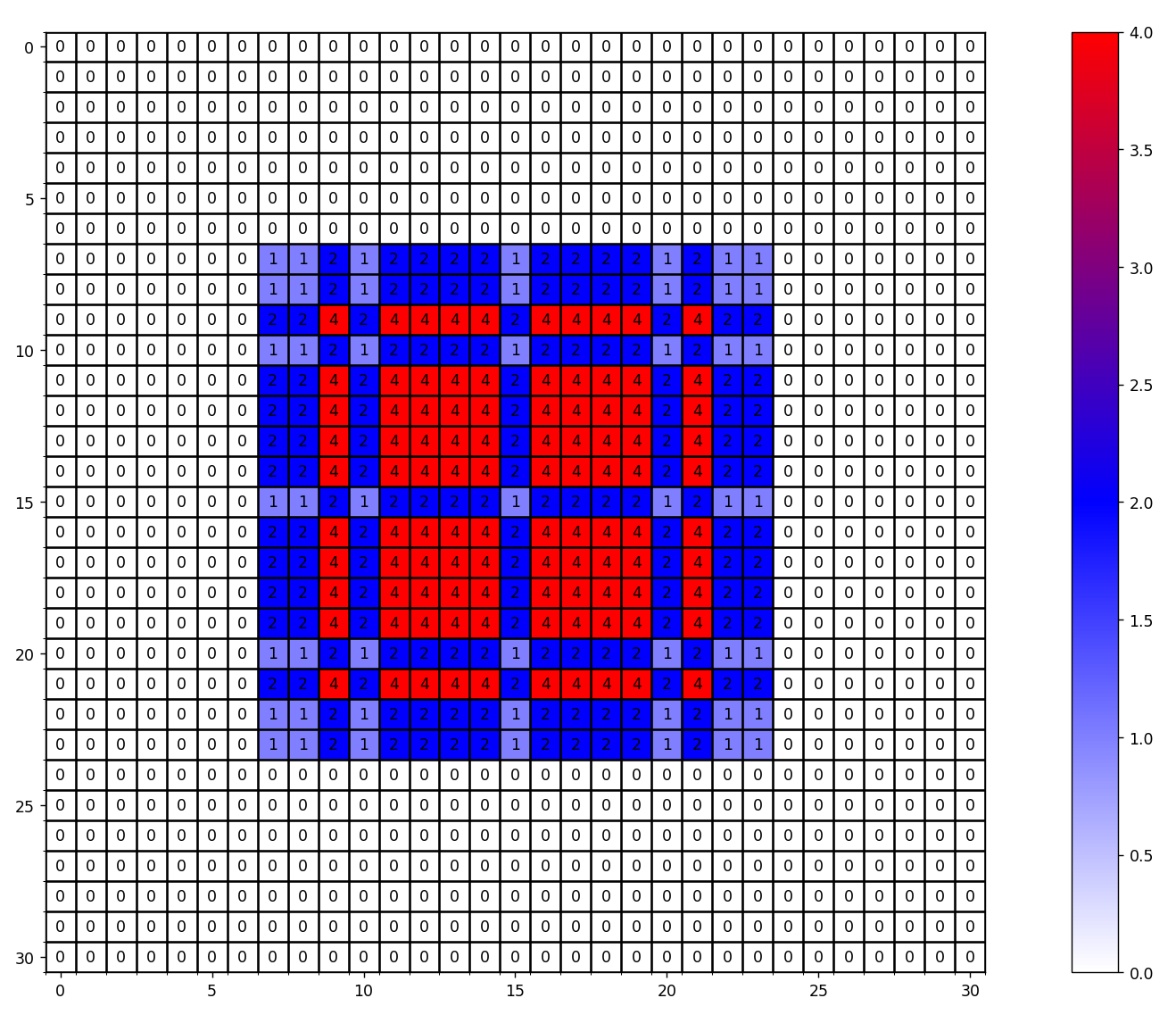
例子1:
K=3, r=[1,2,5]
根据公式:
M(3) = 5
M(2) = max[M3-2r2, M3-2(M3-r2),r2]
= max(5-4, 5-2*(5-2),2)
= max(1, -1, 2)
= 2 <= 3
符合条件
实际效果展示:
代码
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.colors import LinearSegmentedColormap def dilated_conv_one_pixel(center: (int, int), feature_map: np.ndarray, k: int = 3, r: int = 1, v: int = 1): """ 膨胀卷积核中心在指定坐标center处时,统计哪些像素被利用到, 并在利用到的像素位置处加上增量v Args: center: 膨胀卷积核中心的坐标 feature_map: 记录每个像素使用次数的特征图 k: 膨胀卷积核的kernel大小 r: 膨胀卷积的dilation rate v: 使用次数增量 """ assert divmod(3, 2)[1] == 1 # left-top: (x, y) left_top = (center[0] - ((k - 1) // 2) * r, center[1] - ((k - 1) // 2) * r) for i in range(k): for j in range(k): feature_map[left_top[1] + i * r][left_top[0] + j * r] += v def dilated_conv_all_map(dilated_map: np.ndarray, k: int = 3, r: int = 1): """ 根据输出特征矩阵中哪些像素被使用以及使用次数, 配合膨胀卷积k和r计算输入特征矩阵哪些像素被使用以及使用次数 Args: dilated_map: 记录输出特征矩阵中每个像素被使用次数的特征图 k: 膨胀卷积核的kernel大小 r: 膨胀卷积的dilation rate """ new_map = np.zeros_like(dilated_map) for i in range(dilated_map.shape[0]): for j in range(dilated_map.shape[1]): if dilated_map[i][j] > 0: dilated_conv_one_pixel((j, i), new_map, k=k, r=r, v=dilated_map[i][j]) return new_map def plot_map(matrix: np.ndarray): plt.figure() c_list = ['white', 'blue', 'red'] new_cmp = LinearSegmentedColormap.from_list('chaos', c_list) plt.imshow(matrix, cmap=new_cmp) ax = plt.gca() ax.set_xticks(np.arange(-0.5, matrix.shape[1], 1), minor=True) ax.set_yticks(np.arange(-0.5, matrix.shape[0], 1), minor=True) # 显示color bar plt.colorbar() # 在图中标注数量 thresh = 5 for x in range(matrix.shape[1]): for y in range(matrix.shape[0]): # 注意这里的matrix[y, x]不是matrix[x, y] info = int(matrix[y, x]) ax.text(x, y, info, verticalalignment='center', horizontalalignment='center', color="white" if info > thresh else "black") ax.grid(which='minor', color='black', linestyle='-', linewidth=1.5) plt.show() plt.close() def main(): # bottom to top dilated_rates = [1, 2, 5] # init feature map size = 31 m = np.zeros(shape=(size, size), dtype=np.int32) center = size // 2 m[center][center] = 1 # print(m) # plot_map(m) for index, dilated_r in enumerate(dilated_rates[::-1]): new_map = dilated_conv_all_map(m, r=dilated_r) m = new_map print(m) plot_map(m) if __name__ == '__main__': main()结果
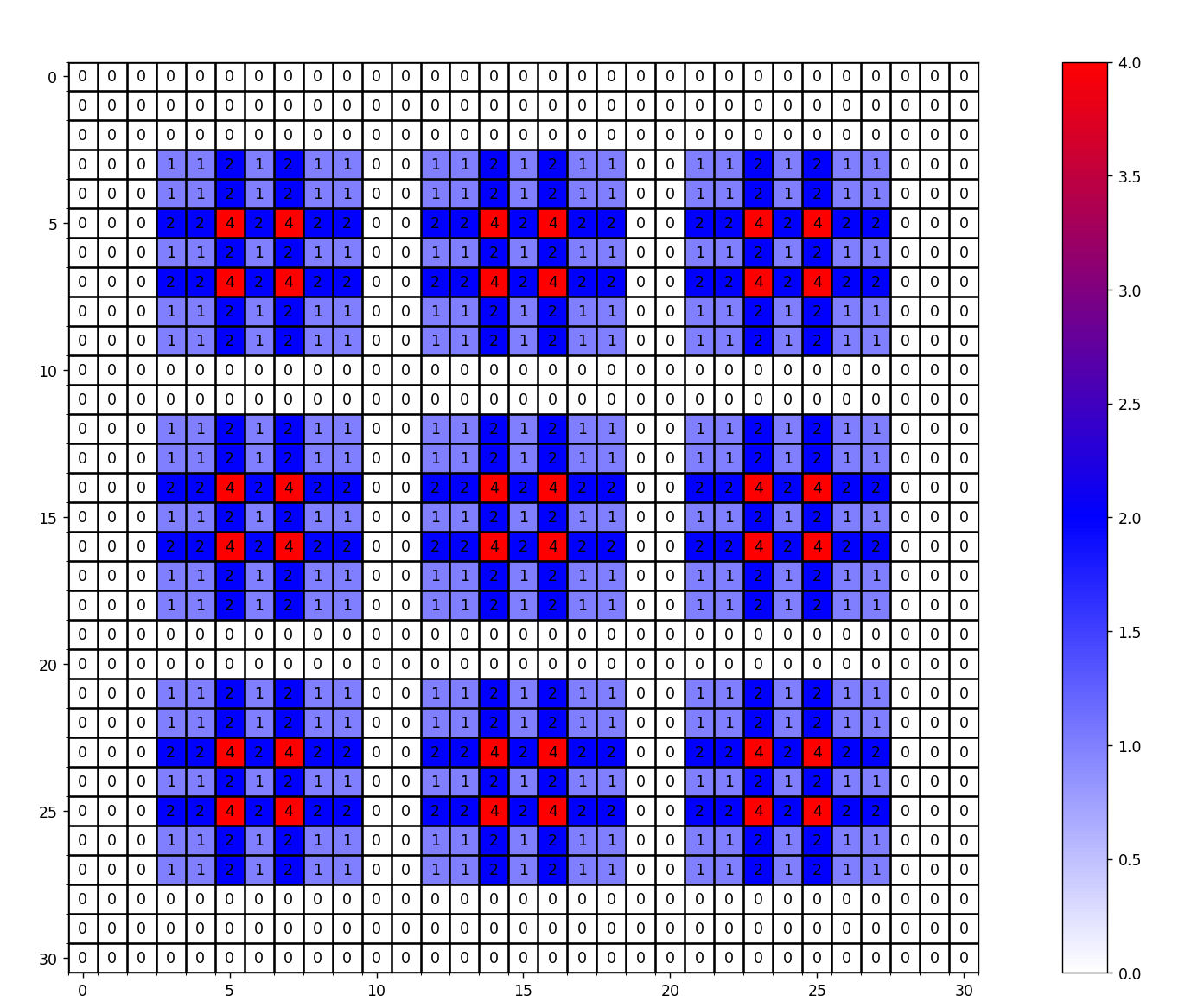
例子2:
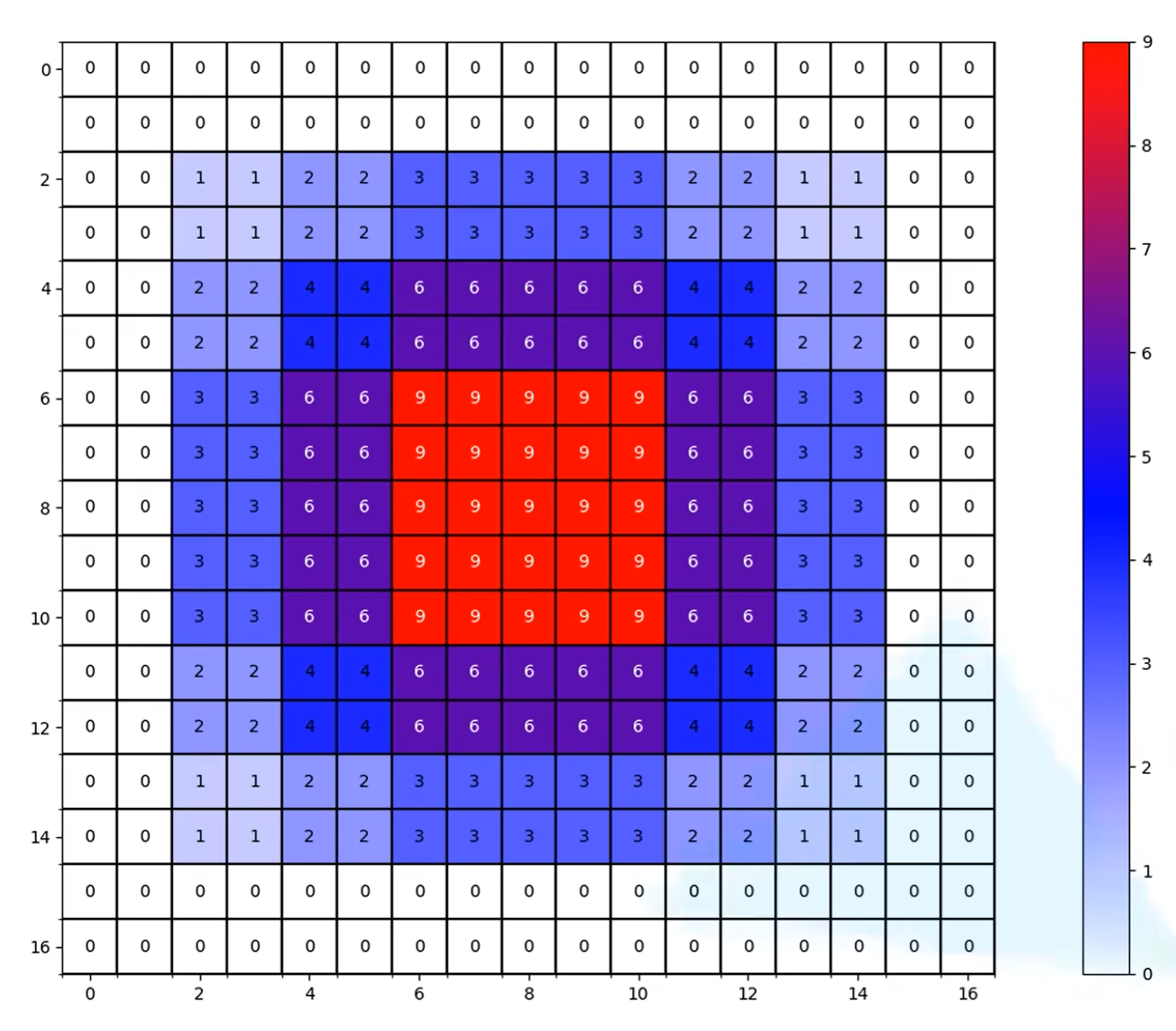
K=3, r=[1,2,9]
根据公式:
M(3) = 9
M(2) = max[M3-2r2, M3-2(M3-r2),r2]
= max(9-4, 9-2*(9-2),2)
= max(5, -5, 2)
= 5 > 3 M(1) = 3, 实际显示两个非零元素之间间隔为2
不符合条件
实际效果展示:
代码
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.colors import LinearSegmentedColormap def dilated_conv_one_pixel(center: (int, int), feature_map: np.ndarray, k: int = 3, r: int = 1, v: int = 1): """ 膨胀卷积核中心在指定坐标center处时,统计哪些像素被利用到, 并在利用到的像素位置处加上增量v Args: center: 膨胀卷积核中心的坐标 feature_map: 记录每个像素使用次数的特征图 k: 膨胀卷积核的kernel大小 r: 膨胀卷积的dilation rate v: 使用次数增量 """ assert divmod(3, 2)[1] == 1 # left-top: (x, y) left_top = (center[0] - ((k - 1) // 2) * r, center[1] - ((k - 1) // 2) * r) for i in range(k): for j in range(k): feature_map[left_top[1] + i * r][left_top[0] + j * r] += v def dilated_conv_all_map(dilated_map: np.ndarray, k: int = 3, r: int = 1): """ 根据输出特征矩阵中哪些像素被使用以及使用次数, 配合膨胀卷积k和r计算输入特征矩阵哪些像素被使用以及使用次数 Args: dilated_map: 记录输出特征矩阵中每个像素被使用次数的特征图 k: 膨胀卷积核的kernel大小 r: 膨胀卷积的dilation rate """ new_map = np.zeros_like(dilated_map) for i in range(dilated_map.shape[0]): for j in range(dilated_map.shape[1]): if dilated_map[i][j] > 0: dilated_conv_one_pixel((j, i), new_map, k=k, r=r, v=dilated_map[i][j]) return new_map def plot_map(matrix: np.ndarray): plt.figure() c_list = ['white', 'blue', 'red'] new_cmp = LinearSegmentedColormap.from_list('chaos', c_list) plt.imshow(matrix, cmap=new_cmp) ax = plt.gca() ax.set_xticks(np.arange(-0.5, matrix.shape[1], 1), minor=True) ax.set_yticks(np.arange(-0.5, matrix.shape[0], 1), minor=True) # 显示color bar plt.colorbar() # 在图中标注数量 thresh = 5 for x in range(matrix.shape[1]): for y in range(matrix.shape[0]): # 注意这里的matrix[y, x]不是matrix[x, y] info = int(matrix[y, x]) ax.text(x, y, info, verticalalignment='center', horizontalalignment='center', color="white" if info > thresh else "black") ax.grid(which='minor', color='black', linestyle='-', linewidth=1.5) plt.show() plt.close() def main(): # bottom to top dilated_rates = [1, 2, 9] # init feature map size = 31 m = np.zeros(shape=(size, size), dtype=np.int32) center = size // 2 m[center][center] = 1 # print(m) # plot_map(m) for index, dilated_r in enumerate(dilated_rates[::-1]): new_map = dilated_conv_all_map(m, r=dilated_r) m = new_map print(m) plot_map(m) if __name__ == '__main__': main()结果
通过以上发现,第一层系数都为1,通过公式可以发现,M1=max(..., r1), 如何希望M1=1的话,r1必须为1,所以第一层要从1开始
设计建议
-
-
公约数不能大于1























 2457
2457

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








