Python实现Bag of Features图像检索
Bag of Features基本原理
此算法的思想是在我们先做一个数据集,然后找到图像中的关键词,这些关键词必须具备较高的区分度,最主要的操作就是提取sift特征,然后对这些特征点进行聚类算法,然后得到聚类中心,聚类中心就具有很高的代表性,这些聚类中心形成字典,然后自取一张图片,进行sift特征提取,就可以在字典里找到最相似的聚类中心,统计这些聚类中心出现的次数,然后就直方图表示出来,对于不同类别的图片,就可以训练处一些分类模型,然后就可以进行图片分类。
关于Bag of Words
对于了解「Bag of Feature」来说,了解「Bag of Words」原理是非常重要的。
「Bag of Words」 是文本分类中一种通俗易懂的策略。一般来讲,如果我们要了解一段文本的主要内容,最行之有效的策略是抓取文本中的关键词,根据关键词出现的频率确定这段文本的中心思想。
「Bag of words」中的 words ,它们是区分度较高的单词。根据这些 words ,我们就可以快速识别出文章内容,并对文章进行分类。
而「Bag of Feature」算法与其大同小异,只是我们抽出的“关键词word”是图像中的关键特征。
Bag of Features算法步骤
首先我们要找到图像中的关键词,而且这些关键词必须具备较高的区分度。实际过程中,通常会采用SIFT特征。
特征提取:

特征聚类:
提取完特征后,我们会采用一些聚类算法对这些特征向量进行聚类。最常用的聚类算法是 k-means。至于 k-means 中的 k 如何取,要根据具体情况来确定。另外,由于特征的数量可能非常庞大,这个聚类的过程也会非常漫长。
聚类完成后,我们就得到了这 k 个向量组成的视觉词典。

转化直方图:
上一步训练得到的字典,是为了这一步对图像特征进行量化。对于一幅图像而言,我们可以提取出大量的SIFT特征点,但这些特征点仍然缺乏代表性。因此,这一步的目标,是根据字典重新提取图像的高层特征。
具体做法是,对于图像中的每一个SIFT特征,都可以在字典中找到一个最相似的 ,这样,我们可以统计一个 k 维的直方图,代表该图像的SIFT特征在字典中的相似度频率。
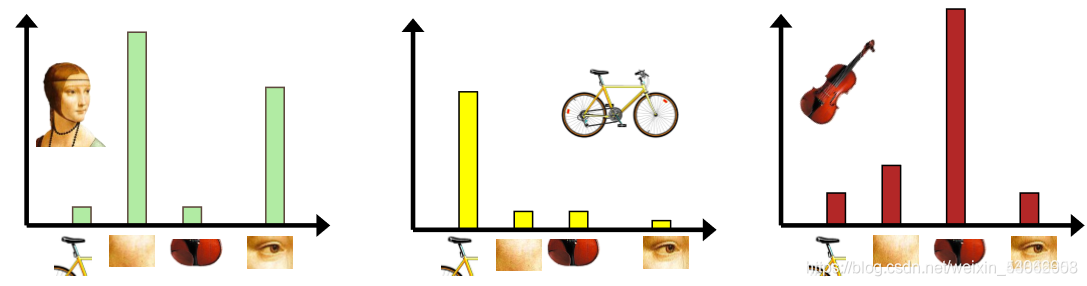
总结步骤:
1.首先,我们用sift算法生成图像库中每幅图的特征点及描述符。
2.再用k-means算法对图像库中的特征点进行聚类,得到一部视觉词典。
3.针对输入特征集,根据视觉词典进行量化
4.把输入图像转化成视觉单词(visual words) 的频率直方图
5.构造特征到图像的倒排表,通过倒排表快速 索引相关图像
6.根据索引结果进行直方图匹配
代码实现
1.读取图片,提取特征,建立字典
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pickle
from PCV.imagesearch import vocabulary
from PCV.tools.imtools import get_imlist
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
#获取图像列表
#imlist = get_imlist('E:/Python37_course/test7/first1000/')
imlist = get_imlist('C:/Users/Administrator/PycharmProjects/pythonProject/VC/BagOfFeature/datasets/')
nbr_images = len(imlist)
#获取特征列表
featlist = [imlist[i][:-3]+'sift' for i in range(nbr_images)]
#提取文件夹下图像的sift特征
for i in range(nbr_images):
sift.process_image(imlist[i], featlist[i])
#生成词汇
#voc = vocabulary.Vocabulary('ukbenchtest')
#voc.train(featlist, 1000, 10)
voc = vocabulary.Vocabulary('test77_test')
voc.train(featlist, 122, 10)
#保存词汇
# saving vocabulary
'''with open('C:/Users/Administrator/PycharmProjects/pythonProject/VC/BagOfFeature/BOW/vocabulary.pkl', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(voc, f)'''
with open('C:/Users/Administrator/PycharmProjects/pythonProject/VC/BagOfFeature/BOW/vocabulary.pkl', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(voc, f)
print ('vocabulary is:', voc.name, voc.nbr_words)
2.遍历图像,将它们的特征投影到词汇并提交到数据库
import pickle
from PCV.imagesearch import vocabulary
from PCV.tools.imtools import get_imlist
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.imagesearch import imagesearch
from PCV.geometry import homography
from sqlite3 import dbapi2 as sqlite # 使用sqlite作为数据库
#获取图像列表
imlist = get_imlist('C:/Users/Administrator/PycharmProjects/pythonProject/VC/BagOfFeature/datasets/')
nbr_images = len(imlist)
#获取特征列表
featlist = [imlist[i][:-3]+'sift' for i in range(nbr_images)]
# load vocabulary
#载入词汇
with open('C:/Users/Administrator/PycharmProjects/pythonProject/VC/BagOfFeature/BOW/vocabulary.pkl', 'rb') as f:
voc = pickle.load(f)
#创建索引
indx = imagesearch.Indexer('testImaAdd.db',voc) # 在Indexer这个类中创建表、索引,将图像数据写入数据库
indx.create_tables() # 创建表
# go through all images, project features on vocabulary and insert
#遍历所有的图像,并将它们的特征投影到词汇上
for i in range(nbr_images)[:888]:
locs,descr = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
indx.add_to_index(imlist[i],descr) # 使用add_to_index获取带有特征描述子的图像,投影到词汇上
# 将图像的单词直方图编码存储
# commit to database
#提交到数据库
indx.db_commit()
con = sqlite.connect('testImaAdd.db')
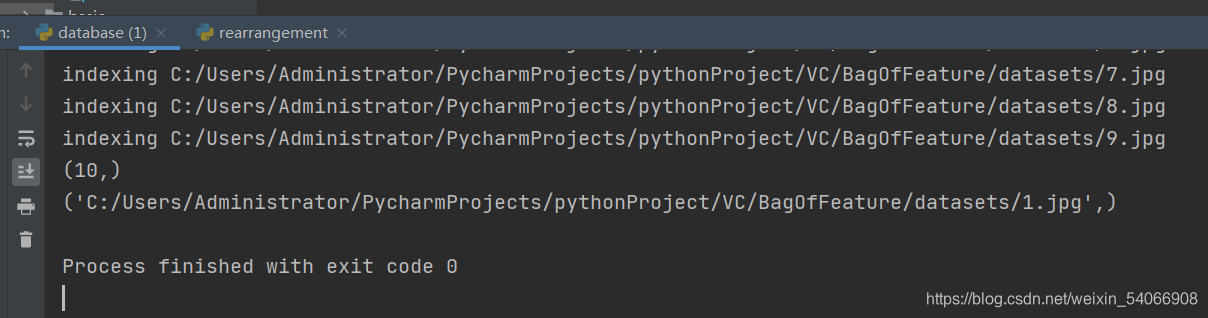
print (con.execute('select count (filename) from imlist').fetchone())
print (con.execute('select * from imlist').fetchone())
3.进行查询测试
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#使用视觉单词表示图像时不包含图像特征的位置信息
import pickle
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.imagesearch import imagesearch
from PCV.geometry import homography
from PCV.tools.imtools import get_imlist
# load image list and vocabulary
#载入图像列表
#imlist = get_imlist('E:/Python37_course/test7/first1000/')
imlist = get_imlist('C:/Users/Administrator/PycharmProjects/pythonProject/VC/BagOfFeature/datasets/')
nbr_images = len(imlist)
#载入特征列表
featlist = [imlist[i][:-3]+'sift' for i in range(nbr_images)]
#载入词汇
'''with open('C:/Users/Administrator/PycharmProjects/pythonProject/VC/BagOfFeature/BOW/vocabulary.pkl', 'rb') as f:
voc = pickle.load(f)'''
with open('C:/Users/Administrator/PycharmProjects/pythonProject/VC/BagOfFeature/BOW/vocabulary.pkl', 'rb') as f:
voc = pickle.load(f)
src = imagesearch.Searcher('testImaAdd.db',voc)# Searcher类读入图像的单词直方图执行查询
# index of query image and number of results to return
#查询图像索引和查询返回的图像数
q_ind = 3
nbr_results = 3
# regular query
# 常规查询(按欧式距离对结果排序)
res_reg = [w[1] for w in src.query(imlist[q_ind])[:nbr_results]] # 查询的结果
print ('top matches (regular):', res_reg)
# load image features for query image
#载入查询图像特征进行匹配
q_locs,q_descr = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[q_ind])
fp = homography.make_homog(q_locs[:,:2].T)
# RANSAC model for homography fitting
#用单应性进行拟合建立RANSAC模型
model = homography.RansacModel()
rank = {}
# load image features for result
#载入候选图像的特征
for ndx in res_reg[1:]:
locs,descr = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[ndx]) # because 'ndx' is a rowid of the DB that starts at 1
# get matches
matches = sift.match(q_descr,descr)
ind = matches.nonzero()[0]
ind2 = matches[ind]
tp = homography.make_homog(locs[:,:2].T)
# compute homography, count inliers. if not enough matches return empty list
# 计算单应性矩阵
try:
H,inliers = homography.H_from_ransac(fp[:,ind],tp[:,ind2],model,match_theshold=4)
except:
inliers = []
# store inlier count
rank[ndx] = len(inliers)
# sort dictionary to get the most inliers first
# 对字典进行排序,可以得到重排之后的查询结果
sorted_rank = sorted(rank.items(), key=lambda t: t[1], reverse=True)
res_geom = [res_reg[0]]+[s[0] for s in sorted_rank]
print ('top matches (homography):', res_geom)
# 显示查询结果
imagesearch.plot_results(src,res_reg[:6]) #常规查询
imagesearch.plot_results(src,res_geom[:6]) #重排后的结果
运行结果
1.读取图片,提取特征,建立字典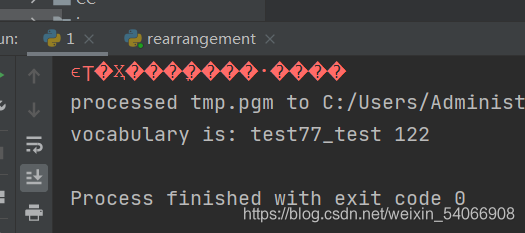
2.遍历图像,将它们的特征投影到词汇并提交到数据库
3.进行查询测试
测试图片:

测试结果:
常规查询:
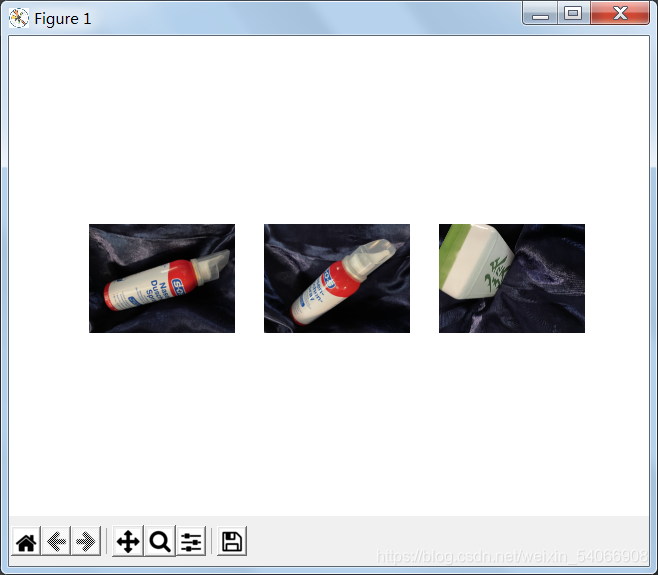
用单应性进行拟合建立RANSAC模型:
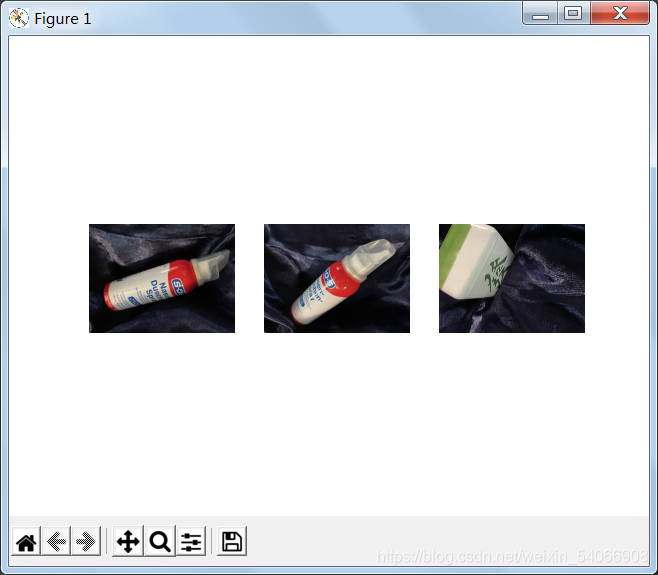
第三幅匹配出现了错误,本应该还是喷剂瓶的,却匹配成麻将了。
实验小结
当时实验中出现了%d format: a number is required, not str报错 ——在一条查询语句中,查询条件既包含了整形又包含了字符串型就会出现此错误,我把%d改成%s就能run了。
同时也有一些不太了解的问题,当我进一步增大数据集和匹配图像的数量时,出现了匹配的精确度变差许多的情况。所以最后才又选择了匹配三张top matches。还需要多努力查找资料,看懂代码找一下原因,继续努力!





















 2118
2118

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








