前言:
1.使用matlab读取图片,将RGB图片转换为YUV型,对Y分量进行sobel增强。
2.使用verilog读取图片,完成对Y分量sobel增强的过程。
matlab部分:
%%
%-----------------------------------------------显示原始图像------------------------------
clear all;
load('Y_verilog.mat');
load('Y_verilog_fpga.mat');
filename = 'testpic.bmp';
rgbImage = imread(filename);
figure;
subplot(1, 4, 1); imshow(rgbImage); title('原始RGB图像');
disp(['最小值: ', num2str(min(rgbImage(:)))]);
disp(['最大值: ', num2str(max(rgbImage(:)))]); %这里显示输出范围在0~255
R_component = rgbImage(:,:,1);
G_component = rgbImage(:,:,2);
B_component = rgbImage(:,:,3);
R_component = double(R_component);
G_component = double(G_component);
B_component = double(B_component);
%%
%--------------------------------------------RGB转YUV------------------------------------------------------
% RGB 到 YUV 转换矩阵
M = [0.299, 0.587, 0.114; -0.169, -0.331, 0.500; 0.500, -0.419, -0.081];
Y_component = 0.299 * R_component + 0.587 * G_component + 0.114 * B_component;
U_component = -0.1684 * R_component - 0.3316 * G_component + 0.500 * B_component + 128;
V_component = 0.500 * R_component - 0.4187 * G_component - 0.083 * B_component + 128;
% Y*256 = 0.299 * 256R + 0.587 * 256G + 0.114 * 256B
% U*256 = -0.169 * 256R - 0.331 * 256G + 0.500 * 256B + 128*256
% V*256 = 0.500 * 256R - 0.419 * 256G - 0.081 * 256B + 128*256
%进行转换后:
% 256Y = 77R + 150G + 29B
% 256U = -43R - 85G + 128B + 32768
% 256V = 128R -107G - 21B + 32768
yuvImage_reBuilt = cat(3, uint8(Y_component), uint8(U_component), uint8(V_component));
subplot(1, 4, 2); imshow(yuvImage_reBuilt); title('重建YUV图像');
%%
%---------------------------------------------sobel算子进行梯度运算-----------------------
%定义sobel算子
Sobel_x = [ 1, 0, -1; 2, 0, -2; 1, 0, -1 ]; %水平分量
Sobel_y = [ 1, 2, 1; 0, 0, 0; -1,-2,-1 ]; %竖直分量
% [ROW , COL , DIM] = size(y);
% sobel_img = zeros(ROW , COL);
% sobel_img = uint8(sobel_img);
% Gy = y_new(1,1) + 2*y_new(1,2) + y_new(1,3) - y_new(3,1) - 2*y_new(3,2) - y_new(3,3);
% for r = 2:ROW-1
% for c = 2:COL-1
% Gx = y(r-1,c-1) + 2*y(r,c-1) + y(r+1,c-1) - y(r-1,c+1) - 2*y(r,c+1) - y(r+1,c+1);
% Gy = y(r-1,c-1) + 2*y(r-1,c) + y(r-1,c+1) - y(r+1,c-1) - 2*y(r+1,c) - y(r+1,c+1);
% G = abs(Gx) + abs(Gy);
%
% % if(G > 255)
% % sobel_img( r , c ) = 255;
% % else
% sobel_img( r , c ) = G;
% % end
% end
% end
% 应用Sobel算子
Ix = imfilter(Y_component, Sobel_x,'replicate'); % 水平梯度replicate
Iy = imfilter(Y_component, Sobel_y,'replicate'); % 垂直梯度
% 计算梯度幅值
Y_component_enhance = abs(Ix) + abs(Iy);
% Y_component_enhance = sqrt(dIx.^2 + dIy.^2);
% Y_component_enhance_double = Y_component_enhance + Y_component;
% Y_component_enhance_double = Y_verilog + Y_component;
Y_component_enhance_double = Y_verilog_fpga + Y_component;
yuvImage_enhance = cat(3, uint8(Y_component_enhance_double), uint8(U_component), uint8(V_component));
subplot(1, 4, 3); imshow(yuvImage_enhance); title('增强后YUV图像');
%%
%-------------------------------------------YUV转RGB-------------------------------------
%将重建后的YUV图像叠加后 转换回去
% R = Y + 1.403 * (V - 128);
% G = Y - 0.343 * (U - 128) - 0.714 * (V - 128);
% B = Y + 1.770 * (U - 128);
R = Y_component_enhance_double + 1.403 * (V_component - 128);
G = Y_component_enhance_double - 0.343 * (U_component - 128) - 0.714 * (V_component - 128);
B = Y_component_enhance_double + 1.770 * (U_component - 128);
RGB_Image_reBuilt = cat(3, uint8(R), uint8(G), uint8(B));
subplot(1, 4, 4); imshow( RGB_Image_reBuilt); title('增强后RGB图像');
figure; imshow(uint8(Y_component_enhance)); title('Y_component');
%figure; imshow(uint8(Y_verilog)); title('Y_component_Verilog');
%figure; imshow(uint8(Y_verilog_fpga)); title('Y_component_Verilog_fpga');
%生成bmp文件
% filename = 'output_image.bmp';
% imwrite(RGB_Image_reBuilt, filename);
%
% filename = 'output_image_verilog.bmp';
% imwrite(RGB_Image_reBuilt, filename);
%filename = 'output_image_verilog_fpga.bmp';
%imwrite(RGB_Image_reBuilt, filename);
verilog部分:
这里读取的是一张480*640大小的图片,图像作为二维数据,不能一次性读取到fpga中,因此采用行缓存的办法,用3个fifo连续读取三行数据,随后用sobel算子同时对三行数据进行卷积处理。这里采用的全填充类型,因此输入的顺序应为line0、line0、line1、line2、line3......line479、line480、line480。整个工程基本能实现图像增强的功能,但在精度上或许达不到matlab处理的程度。
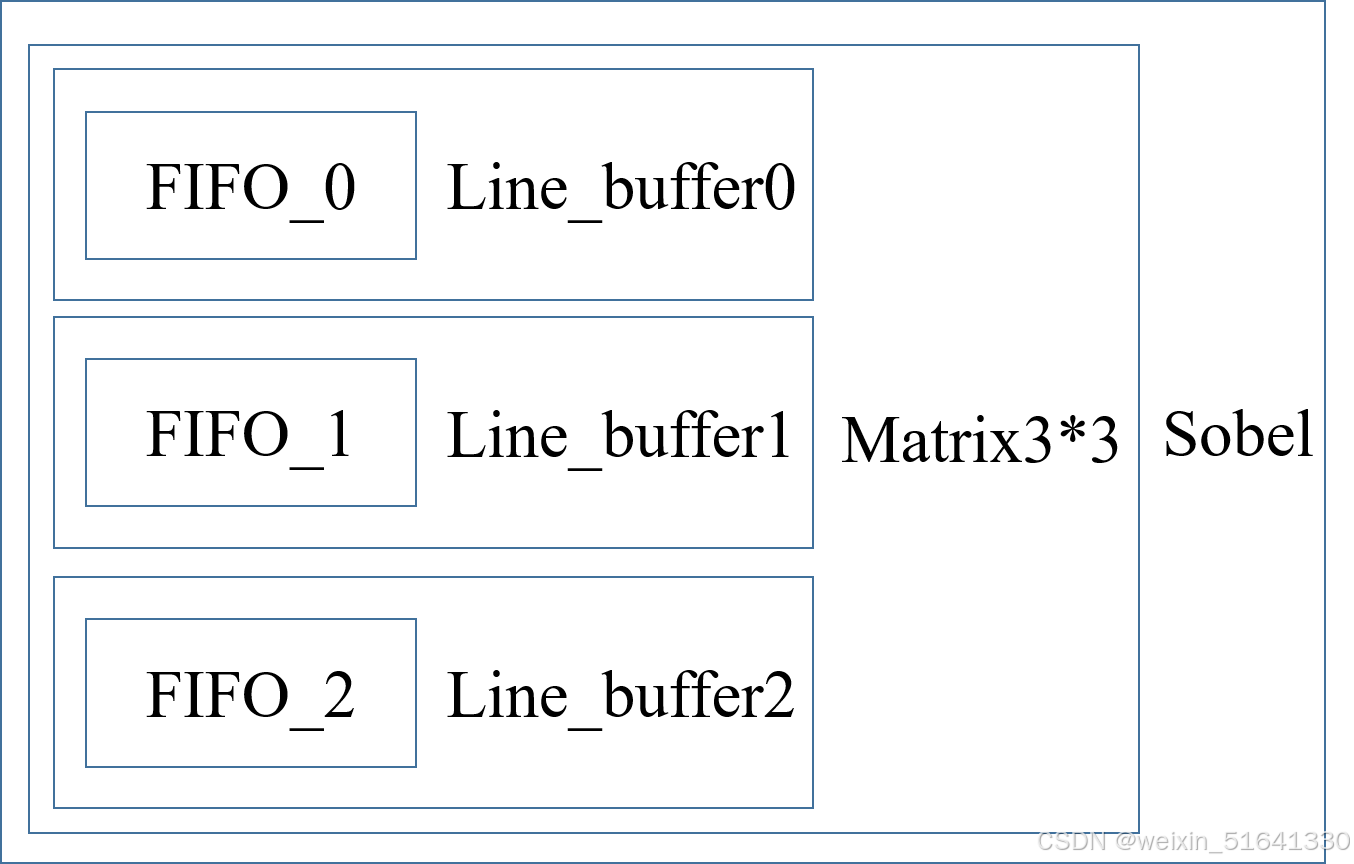
Line_buffer.v:
//例化一个fifo,用来缓存一行数据
module line_buffer (
rst_n,
clk,
din,
dout,
valid_in,
valid_out
);
parameter WIDTH = 8; //数据位宽
parameter IMG_WIDTH = 640; //图像宽度
input rst_n;
input clk;
input [WIDTH-1:0] din;
output [WIDTH-1:0] dout;
input valid_in;//输入数据有效,写使能
output valid_out;//输出给下一级的valid_in,也即上一级开始读的同时下一级就可以开始写入
wire rd_en;//读使能
reg [9:0] cnt;//这里的宽度注意要根据IMG_WIDTH的值来设置,需要满足cnt的范围≥图像宽度
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n)
cnt <= {9{1'b0}};
else if(valid_in)
if(cnt == IMG_WIDTH)
cnt <= IMG_WIDTH;
else
cnt <= cnt +1'b1;
else
cnt <= cnt;
end
//一行数据写完之后,该级fifo就可以开始读出,下一级也可以开始写入了
assign rd_en = ((cnt == IMG_WIDTH) && (valid_in)) ? 1'b1:1'b0;
assign valid_out = rd_en;
line_fifo u_line_fifo(
.clk (clk),
.srst (!rst_n),
.din (din),
.wr_en (valid_in),
.rd_en (rd_en),
.dout(dout),
.empty(),
.full()
);
endmodule
Matrix3_3
//连续取三个fifo,生成3*3矩阵,对行列数据进行逻辑描述
module matrix_3x3 (
clk,
rst_n,
valid_in, //输入数据有效信号
din, //输入的图像数据,将一帧的数据从左到右,然后从上到下依次输入
dout_r0, //第一行的输出数据
dout_r1, //第二行的输出数据
dout_r2, //第三行的输出数据
dout, //最后一行的输出数据
column_cnt,
mat_flag //当第四行数据到来,前三行数据才开始同时输出,此时该信号拉高
);
parameter WIDTH = 8 ; //数据位宽
parameter COL_NUM = 640 ;
parameter ROW_NUM = 480 ;
parameter LINE_NUM = 3 ; //行缓存的行数
input clk;
input rst_n;
input valid_in;
input [WIDTH-1:0] din;
output[WIDTH-1:0] dout;
output[WIDTH-1:0] dout_r0;
output[WIDTH-1:0] dout_r1;
output[WIDTH-1:0] dout_r2;
output[9:0] column_cnt;
output mat_flag;
reg [WIDTH-1:0] line[2:0];//保存每个line_buffer的输入数据
reg valid_in_r [2:0];
wire valid_out_r [2:0];
wire [WIDTH-1:0] dout_r[2:0];//保存每个line_buffer的输出数据
reg [WIDTH-1:0] ch_data[2:0];
assign dout_r0 = ch_data[0];
assign dout_r1 = ch_data[1];
assign dout_r2 = ch_data[2];
assign dout = ch_data[2];
assign column_cnt = col_cnt;
genvar i;
generate
begin:HDL1
for (i = 0;i < LINE_NUM;i = i +1)
begin : buffer_inst
// line 0
if( i==0 ) begin: MAPO
always @(*)begin
line[i]<=din;
valid_in_r[i]<= valid_in;//第一个line_fifo的din和valid_in由顶层直接提供
end
end
// line 1 2 ...
if( i) begin: MAP1
always @(*) begin
//将上一个line_fifo的输出连接到下一个line_fifo的输入
line[i] <= dout_r[i-1];
//当上一个line_fifo写入480个数据之后拉高rd_en,表示开始读出数据;
//valid_out和rd_en同步,valid_out赋值给下一个line_fifo的
//valid_in,表示可以开始写入了
valid_in_r[i] <= valid_out_r[i-1];
end
end
line_buffer #(WIDTH,COL_NUM)
line_buffer_inst(
.rst_n (rst_n),
.clk (clk),
.din (line[i]),
.dout (dout_r[i]),
.valid_in(valid_in_r[i]),
.valid_out (valid_out_r[i])
);
end
end
endgenerate
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(rst_n == 1'b0)
begin
ch_data[0] <= 0;
ch_data[1] <= 0;
ch_data[2] <= 0;
end
else if (valid_in)
begin
if ((row_cnt == 2 ) || (row_cnt == 1 )) //输入为第一行数据
begin
ch_data[2] <= dout_r[1];
ch_data[1] <= dout_r[1];
ch_data[0] <= dout_r[0];
end
else if (row_cnt == ROW_NUM + 1 ) // 当输入最后一行数据
begin
ch_data[2] <= dout_r[2];
ch_data[1] <= dout_r[1];
ch_data[0] <= dout_r[1];
end
else
begin
ch_data[2] <= dout_r[2];
ch_data[1] <= dout_r[1];
ch_data[0] <= dout_r[0];
end
end
end
reg [9:0] col_cnt ;
reg [8:0] row_cnt ;
assign mat_flag = row_cnt >= 11'd2 ? valid_in : 1'b0; //输出标志位
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(rst_n == 1'b0)
col_cnt <= 11'd0;
else if(col_cnt == COL_NUM && valid_in == 1'b1)
col_cnt <= 11'd1;
else if(valid_in == 1'b1)
col_cnt <= col_cnt + 1'b1;
else
col_cnt <= col_cnt;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(rst_n == 1'b0)
row_cnt <= 11'd0;
else if((row_cnt == ROW_NUM + 1) && col_cnt == COL_NUM && valid_in == 1'b1)
row_cnt <= 11'd0;
else if(col_cnt == COL_NUM && valid_in == 1'b1)
row_cnt <= row_cnt + 1'b1;
endmodule
sobel.v
//对每一个3*3矩阵进行sobel处理并输出
module sobel(
input clk ,
input rst_n ,
input [7:0] data_in , //连接din
input data_in_en , //输入有效位 ,连接valid_in
input [9:0] column_cnt ,
output reg [7:0] data_out ,
output reg data_out_en
);
//------------------------------------
// 三行像素缓存
//------------------------------------
wire [7:0] line0;
wire [7:0] line1;
wire [7:0] line2;
//-----------------------------------------
//3x3 像素矩阵中9个像素点
//-----------------------------------------
reg [7:0] line0_data0;
reg [7:0] line0_data1;
reg [7:0] line0_data2;
reg [7:0] line1_data0;
reg [7:0] line1_data1;
reg [7:0] line1_data2;
reg [7:0] line2_data0;
reg [7:0] line2_data1;
reg [7:0] line2_data2;
//-----------------------------------------
//定义gx和gy的正负项中间变量
//-----------------------------------------
reg [9:0] sum0_gx;
reg [9:0] sum1_gx;
reg [9:0] sum0_gy;
reg [9:0] sum1_gy;
wire [9:0] sobel_gx;
wire [9:0] sobel_gy;
wire [9:0] sobel_g;
wire mat_flag;
reg mat_flag_1;
reg mat_flag_2;
reg mat_flag_3;
reg mat_flag_4;
reg mat_flag_5; //这里假设开方用的SQRT IP核输出和输入的延迟是一个clk
always @(posedge clk)
begin
mat_flag_1 <= mat_flag;
mat_flag_2 <= mat_flag_1;
mat_flag_3 <= mat_flag_2;
mat_flag_4 <= mat_flag_3;
mat_flag_5 <= mat_flag_4;
end
//---------------------------------------------
// 获取3*3的图像矩阵
//---------------------------------------------
matrix_3x3 matrix_3x3_inst(
.clk (clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.din (data_in),
.valid_in(data_in_en),
.dout(),
.dout_r0(line0),
.dout_r1(line1),
.dout_r2(line2),
.column_cnt(column_cnt),
.mat_flag(mat_flag)
);
//--------------------------------------------------
// 3*3数据矩阵
//--------------------------------------------------
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
begin
line0_data0 <= 8'b0;
line0_data1 <= 8'b0;
line0_data2 <= 8'b0;
line1_data0 <= 8'b0;
line1_data1 <= 8'b0;
line1_data2 <= 8'b0;
line2_data0 <= 8'b0;
line2_data1 <= 8'b0;
line2_data2 <= 8'b0;
end
else if(data_in_en)
begin //像素有效信号
line0_data0 <= line0;
line0_data1 <= line0_data0;
line0_data2 <= line0_data1;
line1_data0 <= line1;
line1_data1 <= line1_data0;
line1_data2 <= line1_data1;
line2_data0 <= line2;
line2_data1 <= line2_data0;
line2_data2 <= line2_data1;
end
end
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 计算gx,gy
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
begin
sum0_gx <= 10'b0;
sum1_gx <= 10'b0;
sum0_gy <= 10'b0;
sum1_gy <= 10'b0;
end
else if(data_in_en)
begin
//这里数据从左到右流进来,所以在3*3的像素矩阵中左右两侧像素是反的
//sum0计算的是正权重部分,sum1计算的是负权重部分
sum0_gx <= line0_data0 + line1_data0*2 + line2_data0;
sum1_gx <= line0_data2 + line1_data2*2 + line2_data2;
sum0_gy <= line0_data0 + line0_data1*2 + line0_data2;
sum1_gy <= line2_data2 + line2_data1*2 + line2_data0;
end
end
//这里得到真实值的相反数,但不影响计算,只要绝对值相同即可
assign sobel_gx = (sum0_gx>=sum1_gx)?(sum0_gx-sum1_gx):(sum1_gx-sum0_gx);
assign sobel_gy = (sum0_gy>=sum1_gy)?(sum0_gy-sum1_gy):(sum1_gy-sum0_gy);
// 得到G,这里开方近似取绝对值之和
assign sobel_g = sobel_gx + sobel_gy ;
// 阈值比较
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
data_out <= 8'b0;
else if( data_in_en && (column_cnt != 4) && (column_cnt != 5) ) //卷积过程中,每行的最后两个数据总会和下一行的第一和第二个数据发生多余运算,产生多余的运算结果
data_out <= (sobel_g >= 8'hff) ? 8'hff : sobel_g; //这个结果会在cnt=4和5时,被计算出来并输出
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
data_out_en <= 1'b0;
else if(mat_flag_3 == 1'b1 && mat_flag_5 == 1'b1)
data_out_en <= 1'b1; //处理结束标志位
else
data_out_en <= 1'b0;
end
endmodule
TB_sobel.v:
module tb_sobel;
reg clk ;
reg rst_n ;
reg [7:0] data_in ;
reg data_in_en ;
wire [7:0] data_out ;
wire data_out_en ;
sobel sim_sobel(
.clk ( clk ),
.rst_n ( rst_n ),
.data_in ( data_in ),
.data_in_en ( data_in_en ),
.data_out ( data_out ),
.data_out_en ( data_out_en )
);
reg [24:0] input_cnt;
reg [24:0] output_cnt;
reg [7:0] input_mem[0:310000];
reg [7:0] out_mem[0:307200] ;
//------------------------------------------从文件向input_mem读数据------------------------------------------------//
integer i;
integer file_r;
initial
begin
file_r = $fopen("F:/xilinx/code/sobel/project_2/data.txt", "r"); // 打开文件读数据
if (file_r == 0) begin
$display("Error: Unable to open file data.txt");
$finish;
end
for (i = 0; i < 307300; i = i + 1)
begin
if ($fscanf(file_r, "%d", input_mem[i]) != 1)
$display("Error: Failed to read data from file at index %d", i);
end
$fclose(file_r);
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) //从mem中写数据
begin
if(!rst_n)
begin
data_in <= 'b0;
input_cnt <= 'b0;
end
else if(data_in_en)
begin
data_in <= input_mem[input_cnt];
input_cnt <= input_cnt + 1;
end
end
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------//
//----------------------------------------------从out_mem向文件写数据----------------------------------------------//
integer j,m;
integer file_w;
initial
begin
#12895 //延时
file_w = $fopen("F:/xilinx/code/sobel/project_2/data_out.txt", "w");
if (file_w == 0)
begin
$display("Unable to open file data_out.txt.");
$finish;
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) //向out_mem中写数据
begin
if(!rst_n)
begin
output_cnt <= 'b0;
end
else if(data_out_en)
begin
$fwrite(file_w , "%d " , out_mem[output_cnt - 1]);
end
end
initial
begin
#3084900
$fclose(file_w); //等待一段时间关闭文件
$finish;
end
//-----------------------------------------从data_out向out_mem写数据----------------------------------------------------//
initial
begin
for (m = 0; m < 307200; m = m + 1) //对out_mem进行初始化
begin
out_mem[m] = 'b0;
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) //向out_mem中写数据
begin
if(!rst_n)
begin
output_cnt <= 'b0;
end
else if(data_out_en)
begin
out_mem[output_cnt] <= data_out;
output_cnt <= output_cnt + 1;
$display("At time %t, data_out = %d, out_mem[%d] = %d", $time, data_out, output_cnt, out_mem[output_cnt - 1]);
end
end
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------//
initial
begin
clk = 0;
rst_n = 1;
#10 rst_n = 0;
#20 rst_n = 1;
end
always #5 clk = ~clk;
initial
begin
data_in_en = 0;
#30 data_in_en = 1;
end
endmodule
仿真结果:
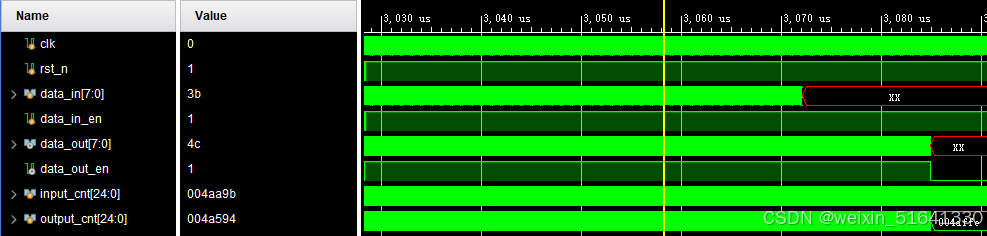
结果对比:
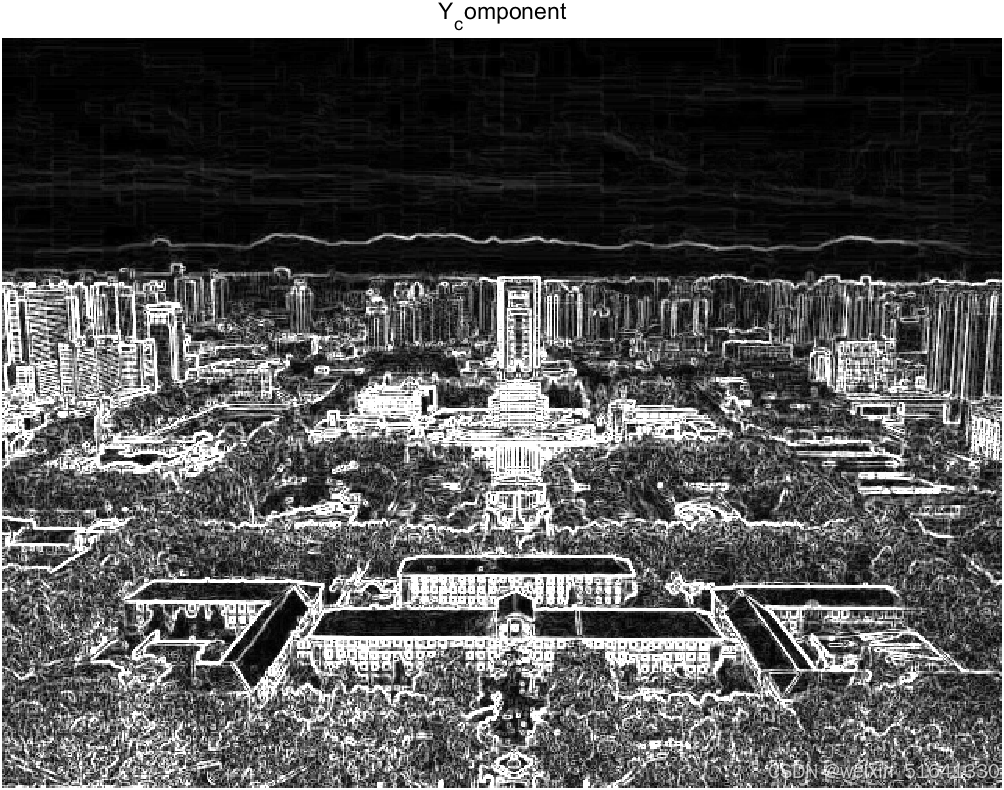


左图是matlab处理的结果,右图是verilog处理的结果,区别不大,打开像素点发现会有一些区别,总结一下就是,matlab这里用的浮点数处理,verilog用的定点数处理,并且verilog在开方的地方用加法代替。
 Matlab与Verilog实现图像Sobel增强对比
Matlab与Verilog实现图像Sobel增强对比




















 6357
6357










