第P3周:Pytorch实现天气识别
- 🍨 本文为🔗365天深度学习训练营 中的学习记录博客
- 🍖 原作者:K同学啊
要求:
- 本地读取并加载数据。
- 测试集accuracy到达93%
🍻拔高:
- 测试集accuracy到达95% (尝试将卷积核,padding更改,效果不理想)
- 调用模型识别一张本地图片 (已实现)
见代码:
1。设置GPU
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
import os,PIL,pathlib,random
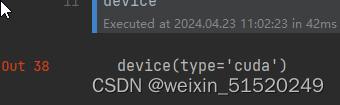
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
device
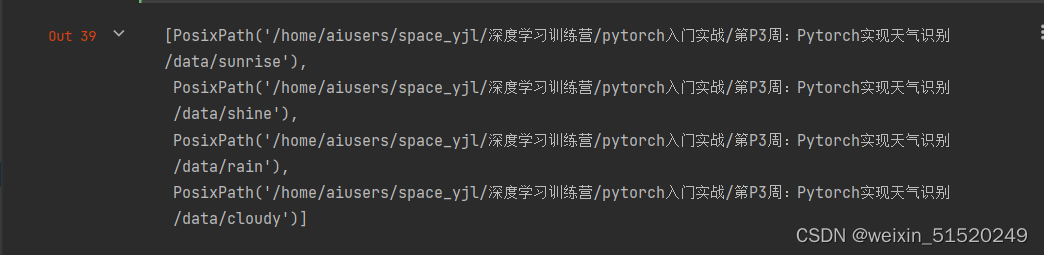
data_dir = r'/home/aiusers/space_yjl/深度学习训练营/pytorch入门实战/第P3周:Pytorch实现天气识别/data'
data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir)
data_paths = list(data_dir.glob('*'))#data_dir.glob('*')会返回data_dir目录下所有的文件和子目录的路径
data_paths
# classeNames = [str(path).split("\\")[1] for path in data_paths]
# classeNames = [str(path).split("/")[8] for path in data_paths]
# classeNames
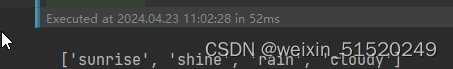
classeNames = [str(path).split("/")[8] for path in data_paths]
classeNames
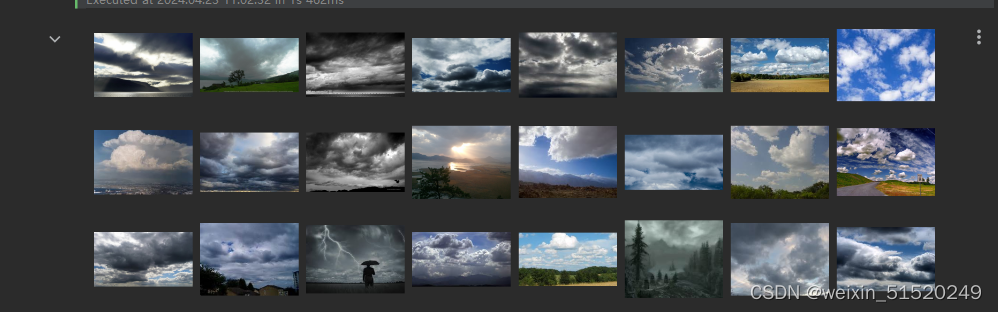
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
# 指定图像文件夹路径
image_folder = r'/home/aiusers/space_yjl/深度学习训练营/pytorch入门实战/第P3周:Pytorch实现天气识别/data/cloudy'
# 获取文件夹中的所有图像文件
image_files = [f for f in os.listdir(image_folder) if f.endswith((".jpg", ".png", ".jpeg"))]
# 创建Matplotlib图像
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 8, figsize=(16, 6))
# 使用列表推导式加载和显示图像
for ax, img_file in zip(axes.flat, image_files):
img_path = os.path.join(image_folder, img_file)
img = Image.open(img_path)
ax.imshow(img)
ax.axis('off')
# 显示图像
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
total_datadir =r'/home/aiusers/space_yjl/深度学习训练营/pytorch入门实战/第P3周:Pytorch实现天气识别/data'
# 关于transforms.Compose的更多介绍可以参考:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_38251616/article/details/124878863
train_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize([224, 224]), # 将输入图片resize成统一尺寸
transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL Image或numpy.ndarray转换为tensor,并归一化到[0,1]之间
transforms.Normalize( # 标准化处理-->转换为标准正太分布(高斯分布),使模型更容易收敛
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 其中 mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406]与std=[0.229,0.224,0.225] 从数据集中随机抽样计算得到的。
])
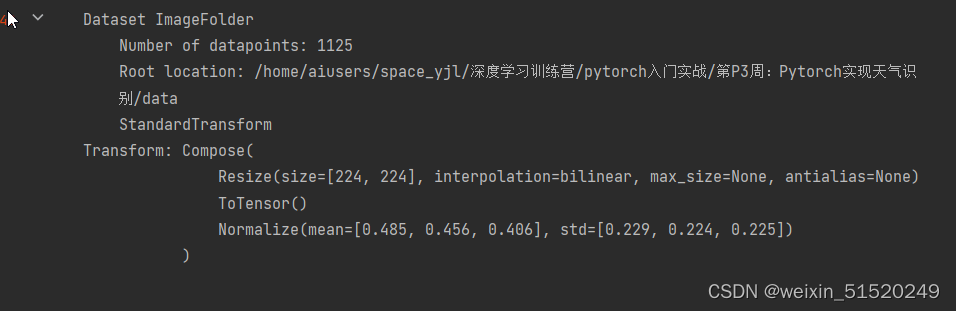
total_data = datasets.ImageFolder(total_datadir,transform=train_transforms)
total_data
划分数据集
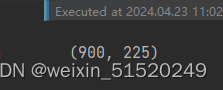
train_size = int(0.8 * len(total_data))
test_size = len(total_data) - train_size
train_dataset, test_dataset = torch.utils.data.random_split(total_data, [train_size, test_size])
train_dataset, test_dataset
train_size,test_size
batch_size = 32
train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=1)
test_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=1)
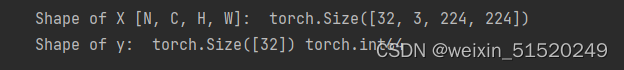
for X, y in test_dl:
print("Shape of X [N, C, H, W]: ", X.shape)
print("Shape of y: ", y.shape, y.dtype)
break
构建简单的神经网络
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Network_bn(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Network_bn, self).__init__()
"""
nn.Conv2d()函数:
第一个参数(in_channels)是输入的channel数量
第二个参数(out_channels)是输出的channel数量
第三个参数(kernel_size)是卷积核大小
第四个参数(stride)是步长,默认为1
第五个参数(padding)是填充大小,默认为0
"""
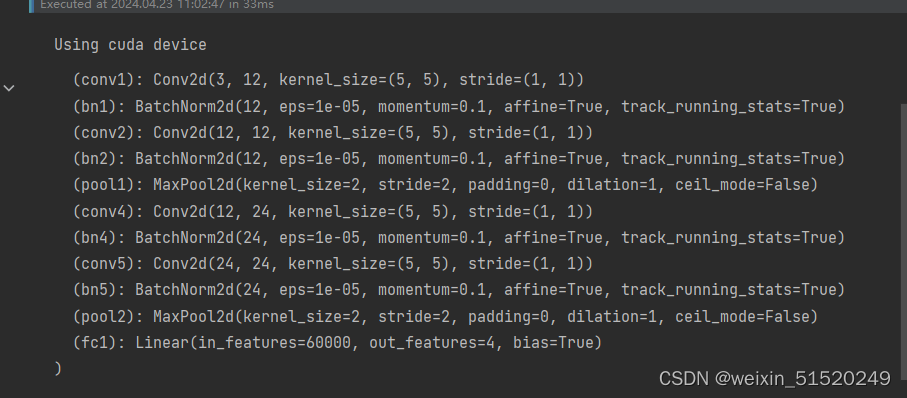
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=12, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=0)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(12)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=12, out_channels=12, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=0)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(12)
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(2,2)
self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=12, out_channels=24, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=0)
self.bn4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(24)
self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=24, out_channels=24, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=0)
self.bn5 = nn.BatchNorm2d(24)
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(2,2)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(24*50*50, len(classeNames))
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x)))
x = self.pool1(x)
x = F.relu(self.bn4(self.conv4(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn5(self.conv5(x)))
x = self.pool2(x)
x = x.view(-1, 24*50*50)
x = self.fc1(x)
return x
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print("Using {} device".format(device))
model = Network_bn().to(device)
model
训练模型
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 创建损失函数
learn_rate = 1e-4 # 学习率
opt = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=learn_rate)
# 训练循环
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 训练集的大小,一共60000张图片
num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目,1875(60000/32)
train_loss, train_acc = 0, 0 # 初始化训练损失和正确率
for X, y in dataloader: # 获取图片及其标签
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
# 计算预测误差
pred = model(X) # 网络输出
loss = loss_fn(pred, y) # 计算网络输出和真实值之间的差距,targets为真实值,计算二者差值即为损失
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad() # grad属性归零
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 每一步自动更新
# 记录acc与loss
train_acc += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
train_loss += loss.item()
train_acc /= size
train_loss /= num_batches
return train_acc, train_loss
def test (dataloader, model, loss_fn):
size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 测试集的大小,一共10000张图片
num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目,313(10000/32=312.5,向上取整)
test_loss, test_acc = 0, 0
# 当不进行训练时,停止梯度更新,节省计算内存消耗
with torch.no_grad():
for imgs, target in dataloader:
imgs, target = imgs.to(device), target.to(device)
# 计算loss
target_pred = model(imgs)
loss = loss_fn(target_pred, target)
test_loss += loss.item()
test_acc += (target_pred.argmax(1) == target).type(torch.float).sum().item()
test_acc /= size
test_loss /= num_batches
return test_acc, test_loss
正式训练
epochs = 20
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_loss = []
test_acc = []
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss = train(train_dl, model, loss_fn, opt)
model.eval()
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, model, loss_fn)
train_acc.append(epoch_train_acc)
train_loss.append(epoch_train_loss)
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
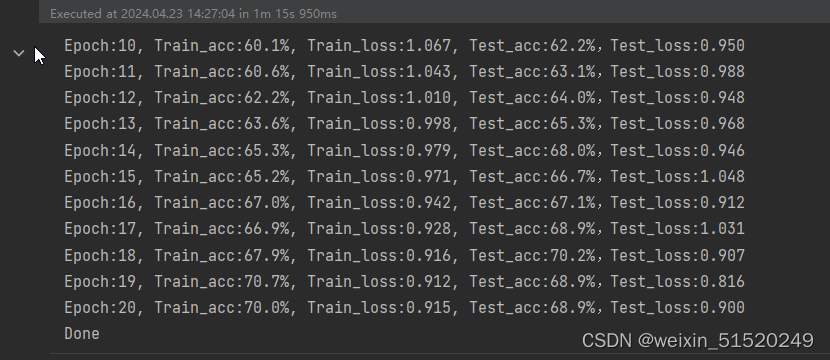
template = ('Epoch:{:2d}, Train_acc:{:.1f}%, Train_loss:{:.3f}, Test_acc:{:.1f}%,Test_loss:{:.3f}')
print(template.format(epoch+1, epoch_train_acc*100, epoch_train_loss, epoch_test_acc*100, epoch_test_loss))
# 在训练循环中的合适位置保存模型权重
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model_weights.pth')
print('Done')
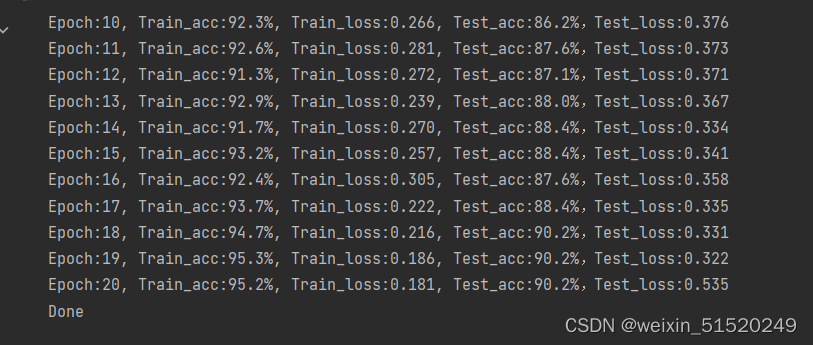
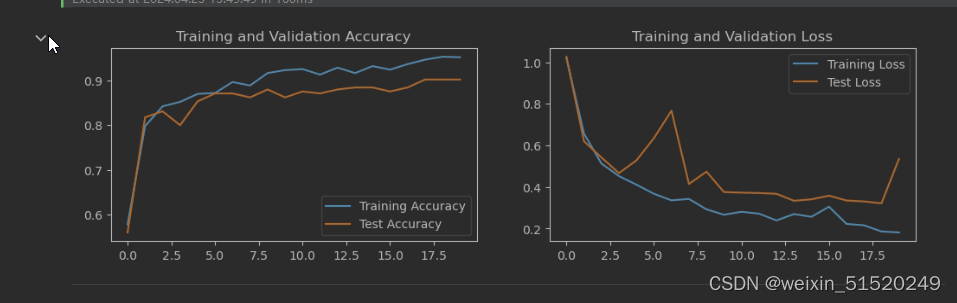
结果可视化
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#隐藏警告
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") #忽略警告信息
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 100 #分辨率
epochs_range = range(epochs)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 3))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(epochs_range, train_acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(epochs_range, test_acc, label='Test Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(epochs_range, train_loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(epochs_range, test_loss, label='Test Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.show()
拔高部分:加载模型进行预测
import torch
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from PIL import Image
# 定义预处理函数
def preprocess_image(image_path):
preprocess = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize([224, 224]),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
image = Image.open(image_path)
image_tensor = preprocess(image).unsqueeze(0)
return image_tensor
# 加载已训练好的模型
model = Network_bn()
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('/home/aiusers/space_yjl/深度学习训练营/pytorch入门实战/第P3周:Pytorch实现天气识别/model_weights.pth'))
model.eval()
# 加载并预处理待预测的图像
image_path = "/home/aiusers/space_yjl/深度学习训练营/pytorch入门实战/第P3周:Pytorch实现天气识别/feiji.jpg"
image_tensor = preprocess_image(image_path)
# 将图像传递给模型进行预测
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(image_tensor)
# 处理模型输出
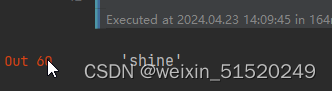
predicted_class = torch.argmax(output, dim=1).item()
# 创建一个字典来映射类别索引到类别名字
class_names = {
0: "cloudy",
1: "rain",
2: "shine",
3: "sunrise"
}
# 使用字典将类别索引转换为类别名字
predicted_class_name = class_names[predicted_class]
predicted_class_name
拔高部分:更改网络架构–效果不好
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class Network_bn(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Network_bn, self).__init__()
"""
nn.Conv2d()函数:
第一个参数(in_channels)是输入的channel数量
第二个参数(out_channels)是输出的channel数量
第三个参数(kernel_size)是卷积核大小
第四个参数(stride)是步长,默认为1
第五个参数(padding)是填充大小,默认为0
"""
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=12, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(12)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=12, out_channels=12, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(12)
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(2,2)
self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=12, out_channels=24, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0)
self.bn4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(24)
self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=24, out_channels=24, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0)
self.bn5 = nn.BatchNorm2d(24)
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(2,2)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(24*3*3, 4)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x)))
x = self.pool1(x)
x = F.relu(self.bn4(self.conv4(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn5(self.conv5(x)))
x = self.pool2(x)
x = x.view(-1, 24*3*3)
x = self.fc1(x)
return x
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print("Using {} device".format(device))
model = Network_bn().to(device)
model
个人总结:
1.使用了imagefolder可以加载自己的数据集
2.学会了搭建简单的神经网络
3.也可以在训练的时候,调用训练好的模型权重,去直接进行预测




















 815
815










