一、图优化简介
图优化本质上仍然是非线性优化。只不过利用图的方式表现出来,使问题可视化,然后可以根据可视化的结果来更好的调整优化过程。
图是一种数据结构。在图优化中,用节点 (vertex) 表示优化变量,用边 (edge) 表示误差项。于是,对于任意一个上述形式的非线性最小二乘问题,都可以构建一个与之对应的图。
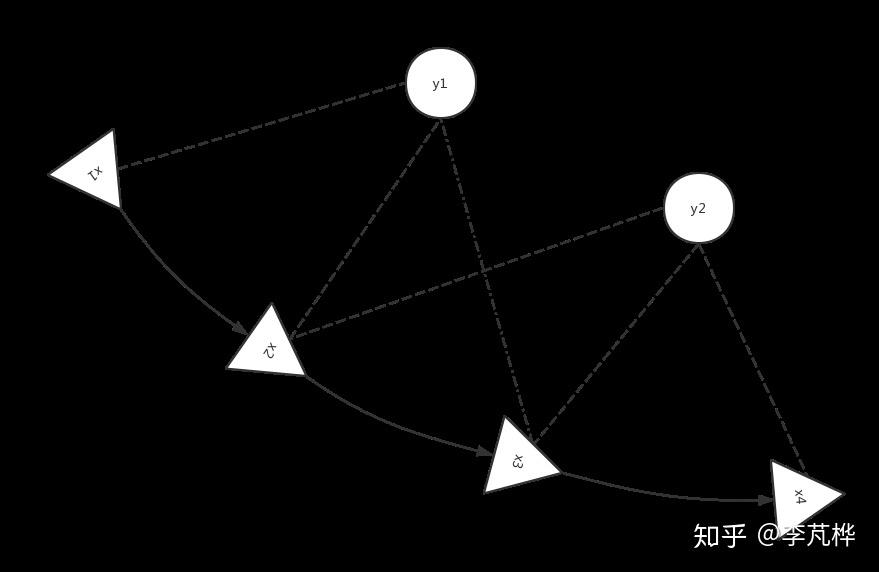
以视觉SLAM为例,用三角形表示相机,圆表示路标,它们共同构成了图优化的顶点;用实线表示相机的运动模型,用虚线表示观测模型,它们构成了图优化的边。则图就表示如下图所示:
二、g2o简介
g2o 是一个是一个图优化库,它使用一个generic hyper-graph 结构来表达一个优化问题。其内部类关系图如下图所示:
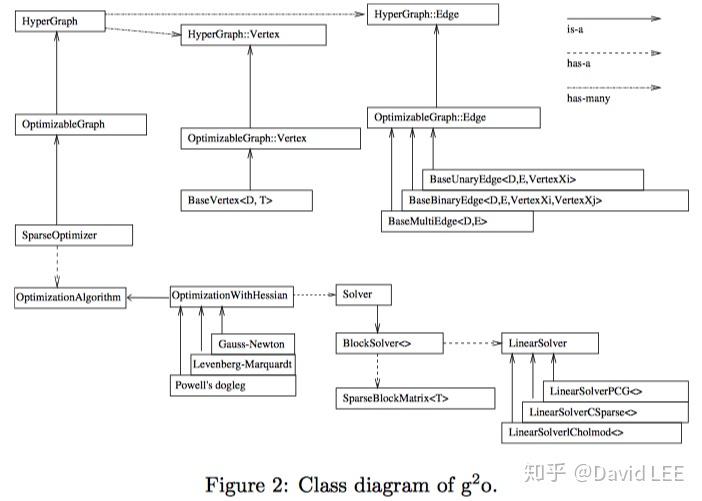
由这张图可以看出,整个g2o的架构分为了三层:
外层的图优化架构:包含了图、节点和边等等。这也是最主要的和用户进行交互的一层,用于构建整个优化问题
中间的优化算法:这是具体的最小二乘优化算法,包括了GN、LM和狗腿算法。用户一般只要选择某个优化算法即可(根据问题性质),并不用太关心内部实现。而且,在g2o中,这些优化算法只专注于本次迭代中的求解,至于说何时停止、如何更新节点都是外层的图优化来维护的
最里层的线性求解器:这是所有优化算法的核心,即如何高效求解一个大型(稀疏或稠密)的线性系统 (Hx=b),也是最复杂的。除非对效率由极致追求(必须选择最合适的计算方式),否则用户一般不关心
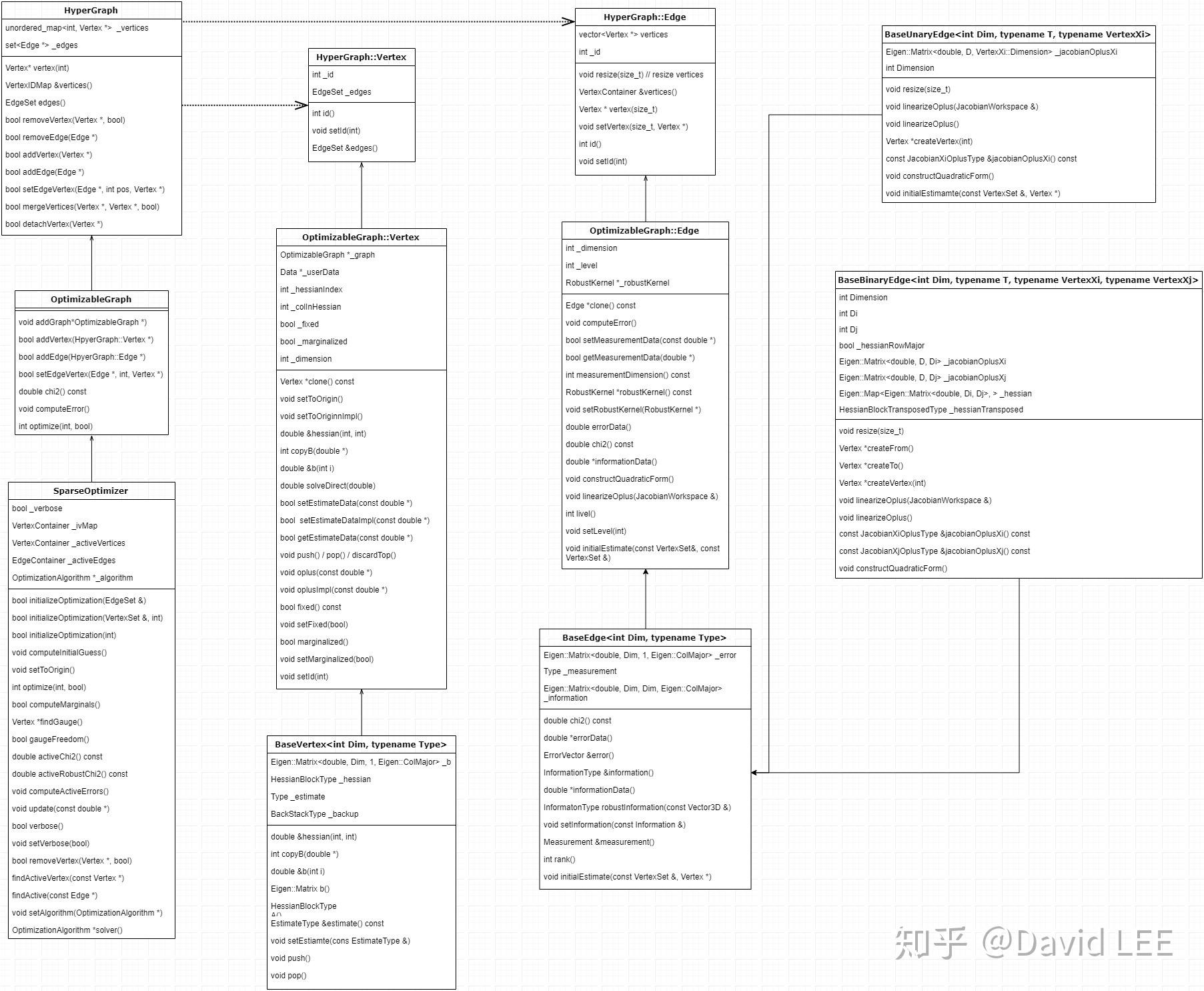
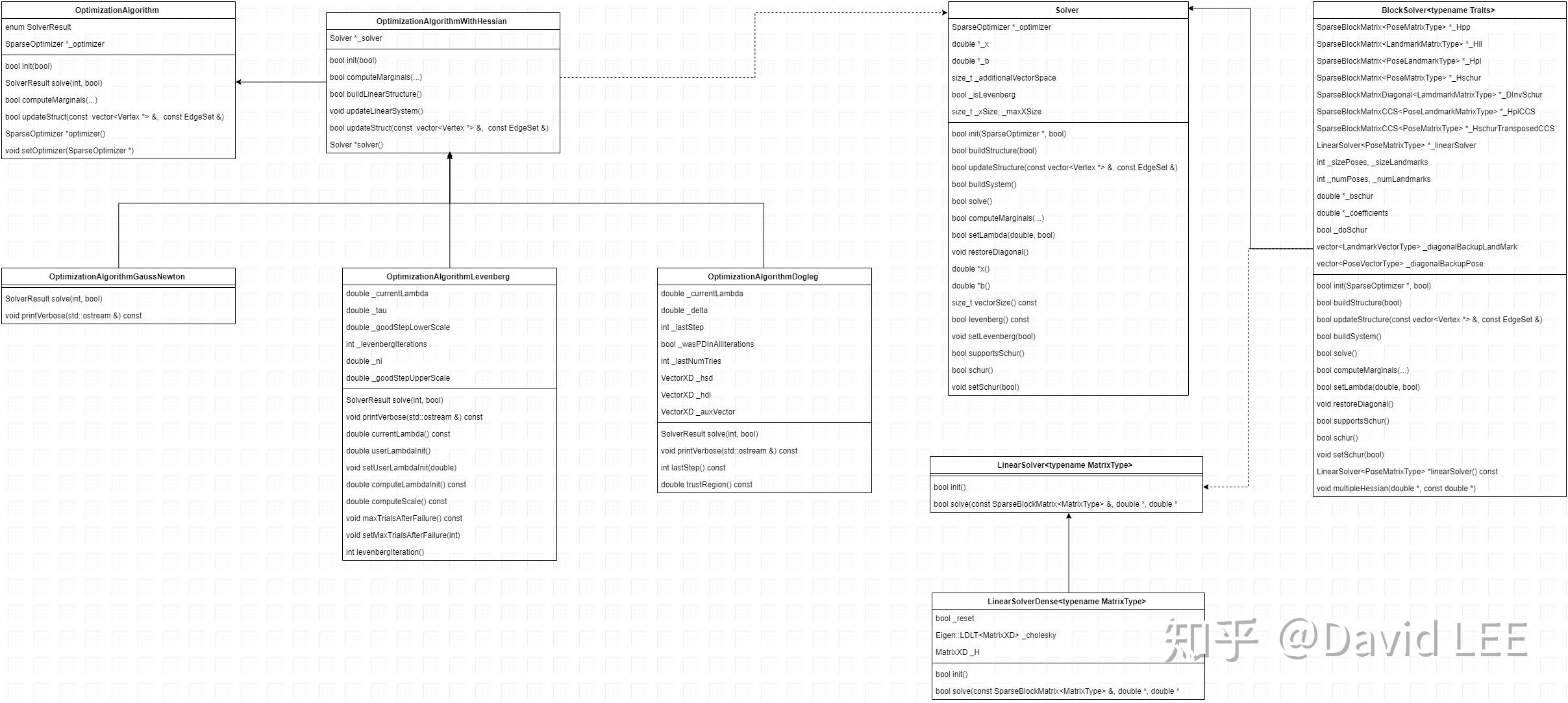
g2o中个各类的属性和方法如下图所示:
三、OptimizableGraph
类OptimizableGraph 定义在optimizable_graph.h 中。两个内部类OptimizableGraph::Vertex 和OptimizableGraph::Edge 来表示节点和超边。这两个类比较基础,所以系统也提供了一些模版类来协助扩展
1、BaseVertex
_estimate:储存节点的值
setToOriginImpl():重置节点的值
setEstimate(type):定义估计值
setId(int) :定义节点编号
oplusImpl(type):节点的更新函数
class myVertex: public g2::BaseVertex<Dim, Type>
{
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
myVertex(){}
virtual void read(std::istream& is) {}
virtual void write(std::ostream& os) const {}
virtual void setOriginImpl()
{
_estimate = Type();
}
virtual void oplusImpl(const double* update) override
{
_estimate += /*update*/;
}
}2、BaseUnaryEdge
_measurement:存储观测值
_error:存储误差
_vertices[]:存储节点
setId(int):定义边的编号
setMeasurement(type):定义观测值
setVertex(int, vertex):设置连接的节点
setInformation():设置信息矩阵(协方差矩阵之逆)
linearizeOplus():计算雅可比矩阵
computeError():计算误差
_jacobianOplusXi:雅可比矩阵,由Eigen::Matrix<观测维度,节点维度>定义而来
lass myEdge: public g2o::BaseBinaryEdge<errorDim, errorType, Vertex1Type, Vertex2Type>
{
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
myEdge(){}
virtual bool read(istream& in) {}
virtual bool write(ostream& out) const {}
virtual void computeError() override
{
// ...
_error = _measurement - Something;
}
virtual void linearizeOplus() override
{
_jacobianOplusXi(pos, pos) = something;
// ...
/*
_jocobianOplusXj(pos, pos) = something;
...
*/
}
private:
// data
}四、Solver
最小二乘中的一个问题就是求解线性系统 ,为此,g2o 提供了Solver 类。但利用Solver 类进行优化需要设置很多参数。所以g2o 提供了模版类BlockSolver<> (内置了SparseBlockMatrix<> 类)来简化流程。BlockSolver<> 可以进行Schur 消元并利用另一个模版类LinearSolver<> 来求解。g2o 提供了多种线性求解器,包括CSparse, CHOLMOD 等等。
,为此,g2o 提供了Solver 类。但利用Solver 类进行优化需要设置很多参数。所以g2o 提供了模版类BlockSolver<> (内置了SparseBlockMatrix<> 类)来简化流程。BlockSolver<> 可以进行Schur 消元并利用另一个模版类LinearSolver<> 来求解。g2o 提供了多种线性求解器,包括CSparse, CHOLMOD 等等。
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_binary_edge.h> // base_unary_edge.h
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_gauss_newton.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_dogleg.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/dense/linear_solver_dense.h>
int main(int argc char** argv)
{
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<poseDim, landmarkDim> > Block;
// 线性方程求解器
// linear solver using dense cholesky decompositio
Block::LinearSolverType* linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverDense<Block::PoseMatrixType>(); //稠密增量方程
// linear solver which uses the sparse Cholesky solver from Eigen
// Block::LinearSolverType* linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverEigen<Block::PoseMatrixType>();
// linear solver which uses CSparse
// Block::LinearSolverType* linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverCSparse<Block::PoseMatrixType>();
// basic solver for Ax = b which has to reimplemented for different linear algebra libraries
// Block::LinearSolverType* linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverCholmod<Block::PoseMatrixType>();
Block* solver_ptr = new Block(linearSolver); // 矩阵块求解器,设置线形求解器
// 梯度下降法
g2o::optimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLenvnberg(solver_ptr);
// g2o::optimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton(solver_ptr);
//g2o::optimizationAlgorithmGaussDogleg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmDogleg(solver_ptr);
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 图模型
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); // 设置求解器
// optimizer.setVerbose(true); // 打开调试输出
// vertex
g2o::VertexSE3Expmap* pose = new g2o::VeretxSE3Expmap(); // 相机位姿
pose->setId(0);
pose->setEstimate(/*something*/);
optimizer.addVertex(pose);
int index = 1;
for (const Point p : points) // 伪码
{
g2o::PointType* point = new g2o::pointType(); // 伪码
point->setId(index++);
point->setEstimate(/*something*/);
// point->setMarginalized(true); // 该点在解方程时进行Schur消元
optimizer->addVertex(point);
}
// parameter: camera intrinsics 可有可无
g2o::CameraParameters* camera = new g2o::CameraParameters(/*K*/);
camera->setId(0);
optimizer.addParameter(camera);
// edges
index = 1;
for (const Point2d p : point_2d) // 伪码
{
g2o::EdgeType* edge = new g2o::EdgeType(); // 伪码
edge->setId(index);
// huber loss, 默认为不用设置
/*
if (robustify)
{
g2o::RobustKernelHuber* rk = new g2o::RobustKernelHuber;
rk->setDelta(1.0);
edge->setRobustKernel(rk);
}
*/
edge->setVertex(0, dynamic_cast<g2o::PointType*>(optimizer.vertex(index))); // 二元边,第一个顶点为节点
edge->setVertex(1, pose); // 第二个顶点为相机
edge->setMeasurement(/*something*/);
// edge->setParameterId(0, 0);
edge->setInformation(/*Identity*/); // 协方差矩阵之逆
optimizer.addEdge(edge);
index++;
}
optimizer.setVerbose(true);
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(/*iteration times*/);
return 0;
}五、代码示例
视觉SLAM十四讲部分代码
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgcodecs/legacy/constants_c.h>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/sparse_optimizer.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_gauss_newton.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/dense/linear_solver_dense.h>
#include <sophus/se3.hpp>
#include <chrono>
class VertexPose : public g2o::BaseVertex<6, Sophus::SE3d> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate = Sophus::SE3d();
}
/// left multiplication on SE3
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> update_eigen;
update_eigen << update[0], update[1], update[2], update[3], update[4], update[5];
_estimate = Sophus::SE3d::exp(update_eigen) * _estimate;
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) override {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const override {}
};
class EdgeProjection : public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<2, Eigen::Vector2d, VertexPose> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
EdgeProjection(const Eigen::Vector3d &pos, const Eigen::Matrix3d &K) : _pos3d(pos), _K(K) {}
virtual void computeError() override {
const VertexPose *v = static_cast<VertexPose *> (_vertices[0]);
Sophus::SE3d T = v->estimate();
Eigen::Vector3d pos_pixel = _K * (T * _pos3d);
pos_pixel /= pos_pixel[2];
_error = _measurement - pos_pixel.head<2>();
}
virtual void linearizeOplus() override {
const VertexPose *v = static_cast<VertexPose *> (_vertices[0]);
Sophus::SE3d T = v->estimate();
Eigen::Vector3d pos_cam = T * _pos3d;
double fx = _K(0, 0);
double fy = _K(1, 1);
double cx = _K(0, 2);
double cy = _K(1, 2);
double X = pos_cam[0];
double Y = pos_cam[1];
double Z = pos_cam[2];
double Z2 = Z * Z;
_jacobianOplusXi
<< -fx / Z, 0, fx * X / Z2, fx * X * Y / Z2, -fx - fx * X * X / Z2, fx * Y / Z,
0, -fy / Z, fy * Y / (Z * Z), fy + fy * Y * Y / Z2, -fy * X * Y / Z2, -fy * X / Z;
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) override {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const override {}
private:
Eigen::Vector3d _pos3d;
Eigen::Matrix3d _K;
};
void bundleAdjustmentG2O(
const VecVector3d &points_3d,
const VecVector2d &points_2d,
const Mat &K,
Sophus::SE3d &pose) {
// 构建图优化,先设定g2o
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6, 3>> BlockSolverType; // pose is 6, landmark is 3
typedef g2o::LinearSolverDense<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType; // 线性求解器类型
// 梯度下降方法,可以从GN, LM, DogLeg 中选
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton(
g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 图模型
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); // 设置求解器
optimizer.setVerbose(true); // 打开调试输出
// vertex
VertexPose *vertex_pose = new VertexPose(); // camera vertex_pose
vertex_pose->setId(0);
vertex_pose->setEstimate(Sophus::SE3d());
optimizer.addVertex(vertex_pose);
// K
Eigen::Matrix3d K_eigen;
K_eigen <<
K.at<double>(0, 0), K.at<double>(0, 1), K.at<double>(0, 2),
K.at<double>(1, 0), K.at<double>(1, 1), K.at<double>(1, 2),
K.at<double>(2, 0), K.at<double>(2, 1), K.at<double>(2, 2);
// edges
int index = 1;
for (size_t i = 0; i < points_2d.size(); ++i) {
auto p2d = points_2d[i];
auto p3d = points_3d[i];
EdgeProjection *edge = new EdgeProjection(p3d, K_eigen);
edge->setId(index);
edge->setVertex(0, vertex_pose);
edge->setMeasurement(p2d);
edge->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity());
optimizer.addEdge(edge);
index++;
}
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
optimizer.setVerbose(true);
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(10);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "optimization costs time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;
cout << "pose estimated by g2o =\n" << vertex_pose->estimate().matrix() << endl;
pose = vertex_pose->estimate();
}







 文章介绍了图优化的基本概念,以非线性最小二乘问题为例,展示了如何用图结构表示优化问题。g2o是一个图优化库,采用通用超图结构处理优化问题,分为图优化架构、优化算法和线性求解器三层。OptimizableGraph类用于表示节点和边,提供基类如BaseVertex和BaseUnaryEdge用于自定义节点和边。优化过程中,使用BlockSolver和不同的线性求解器如CSparse、Cholmod等解决线性系统。最后,通过一个视觉SLAM的代码示例展示了g2o在实际问题中的应用。
文章介绍了图优化的基本概念,以非线性最小二乘问题为例,展示了如何用图结构表示优化问题。g2o是一个图优化库,采用通用超图结构处理优化问题,分为图优化架构、优化算法和线性求解器三层。OptimizableGraph类用于表示节点和边,提供基类如BaseVertex和BaseUnaryEdge用于自定义节点和边。优化过程中,使用BlockSolver和不同的线性求解器如CSparse、Cholmod等解决线性系统。最后,通过一个视觉SLAM的代码示例展示了g2o在实际问题中的应用。
















 1896
1896

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








