游戏简介
本游戏是基于Processing的一款融入了动画技术的交互应用,游戏操作简单,界面简洁直观,易上手,可玩性高。
创意来源
游戏思路是来源于是一个检测飞行员反应能力的小游戏,但是其模式单一,目的知识检测反应能力。所以在此之上,我想制作一个游戏既能够提高反应能力,又能够加入自己的想法实现一些创作;即使当游戏结束时也能在游戏中看到自己创作的乐趣。
玩法介绍
当玩家点击开始界面的小圆球时即开始游戏,首先,你得保证自己的小球不会越出界限,并不会被敌人追上;其次敌人会留下色彩的痕迹,你可以在躲避之余进行创作。
游戏演示效果
游戏动图

主要技术说明
- 主函数
主函数:建立画布,布置初始画面和一些其他情况的画面,创建玩家与敌人,增加死亡和开始游戏的判定,确定暂停,死亡等多种情况。
主函数源代码
void setup() {
size(800, 800);
a = new player();
v = new Vehicle(width/2, height/2);
ps = new ParticleSystem(new PVector(-500,-500),5);
frameRate(100);
}
void draw() {
background(255);
PVector mouse = new PVector(mouseX, mouseY);
a.drag();
a.hover(mouseX,mouseY);
a.display();
// Draw an ellipse at the mouse position
stroke(175);
noFill();
rectMode(CENTER);
rect(width/2, height/2, width-d*2, height-d*2);
ps.origin.set(mouseX,mouseY,0);
ps.addParticle(5);
if(v.isdie==true){
textSize(100);
text(t, width/2, height/2);
}
// Call the appropriate steering behaviors for our agents
if(!mousePressed)
{
if(v.isdie==false){
if(isfirst==true){
v.display();
textSize(15);
text("click the circle to begin", width/2-80, height/2+350);
textSize(80);
text("survive?", width/2-300, height/2-250);
text("create?", width/2+50, height/2-50);
text("or", width/2-50, height/2-150);
}
if(isfirst==false){
textSize(20);
v.display();
text("click the circle to continue", width/2, height/2+350);}
}
if(v.isdie==true){
v.display();
textSize(30);
text("Restart the game", width/2, height/2+350);}
}
if(mousePressed)
{
v.seek(mouse);
v.arrive(mouse);
v.update();
v.display();
v.boundaries(mouse);
v.maxforce+=0.0005;
v.maxspeed+=0.005;
textSize(64);
textAlign(CENTER);
if(v.isdie==false){
int a = frameCount / 100;
text(a, width/2, height/2);
t=a;
isfirst=false;
}
}
}
void mousePressed() {
a.clicked(mouseX,mouseY);
}
void mouseReleased() {
a.stopDragging();
}
- 玩家设定
1.模型设定:玩家是一个圆形图案,当鼠标在其上方会有颜色改变示意;
2.操作设定:给玩家加了鼠标点击移动的功能,当首次点击后开始游戏,断开点击相当于暂停,重新点击继续游戏;
player类的源代码:
class player {
float mass; // Mass, tied to size
float G; // Gravitational Constant
PVector position; // position
boolean dragging = false; // Is the object being dragged?
boolean rollover = false; // Is the mouse over the ellipse?
PVector dragOffset; // holds the offset for when object is clicked on
player() {
position = new PVector(width/2,height/2+300);
mass = 15;
G = 1;
dragOffset = new PVector(0.0,0.0);
}
// Method to display
void display() {
ellipseMode(CENTER);
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(0);
if (dragging) fill (50);
else if (rollover) fill(100);
else fill(175,200);
ellipse(position.x,position.y,mass*2,mass*2);
}
// The methods below are for mouse interaction
void clicked(int mx, int my) {
float d = dist(mx,my,position.x,position.y);
if (d < mass) {
dragging = true;
dragOffset.x = position.x-mx;
dragOffset.y = position.y-my;
}
}
void hover(int mx, int my) {
float d = dist(mx,my,position.x,position.y);
if (d < mass) {
rollover = true;
}
else {
rollover = false;
}
}
void stopDragging() {
dragging = false;
}
void drag() {
if (dragging) {
position.x = mouseX + dragOffset.x;
position.y = mouseY + dragOffset.y;
}
}
}
- 敌人设定
1.追踪玩家:敌人会有一个初始的转向力和一个初始速度,并向玩家的位置靠拢,在时间增加的过程中,速度和转向力匀速增加,并在追上玩家的时候停止;
2.路径画笔:通过列表将以前走过的点保存在数组并按照其位置绘制不同的颜色,产生的以往路径就会颜色鲜艳而渐变;
3.判定玩家死亡:当追上玩家时,玩家出界是判定出玩家死亡,此时触发爆炸的粒子效果;
4.游戏边界:当敌人判定出界,则会赋予很大的转向力转向;若为玩家出界则直接判定死亡。
Vehicle类源代码:
class Vehicle {
ArrayList<PVector> history = new ArrayList<PVector>();
PVector position;
PVector velocity;
PVector acceleration;
float r;
float maxforce; // Maximum steering force
float maxspeed; // Maximum speed
int ispstime=100;
int isout=5;
int m=24;
boolean isdie = false;
Vehicle(float x, float y) {
acceleration = new PVector(0,0);
velocity = new PVector(0,-2);
position = new PVector(x,y);
r = 6;
maxspeed = 4;
maxforce = 0.1;
}
void boundaries(PVector mouse) {
PVector desired = null;
if (position.x < d) {
desired = new PVector(maxspeed, velocity.y);
}
else if (position.x > width -d) {
desired = new PVector(-maxspeed, velocity.y);
}
if (position.y < d) {
desired = new PVector(velocity.x, maxspeed);
}
else if (position.y > height-d) {
desired = new PVector(velocity.x, -maxspeed);
}
if (desired != null) {
desired.normalize();
desired.mult(maxspeed);
PVector steer = PVector.sub(desired, velocity);
steer.limit(maxforce);
applyForce(steer);
}
if(isout>0){
if (mouse.x < d) {
isout-=1;
}
else if (mouse.x > width -d) {
isout-=1;
}
if (mouse.y < d) {
isout-=1;
}
else if (mouse.y > height-d) {
isout-=1;
}
}
if(isout<=0){die();}
}
// Method to update position
void update() {
// Update velocity
velocity.add(acceleration);
// Limit speed
velocity.limit(maxspeed);
position.add(velocity);
// Reset accelerationelertion to 0 each cycle
acceleration.mult(0);
history.add(position.get());
//if (history.size() > 150) {
// history.remove(0);
//}
}
void applyForce(PVector force) {
// We could add mass here if we want A = F / M
acceleration.add(force);
}
// A method that calculates a steering force towards a target
// STEER = DESIRED MINUS VELOCITY
void seek(PVector target) {
PVector desired = PVector.sub(target,position); // A vector pointing from the position to the target
// Normalize desired and scale to maximum speed
desired.normalize();
desired.mult(maxspeed);
// Steering = Desired minus velocity
PVector steer = PVector.sub(desired,velocity);
steer.limit(maxforce); // Limit to maximum steering force
applyForce(steer);
}
void arrive(PVector target) {
PVector desired = PVector.sub(target,position); // A vector pointing from the position to the target
float d2 = desired.mag();
// Scale with arbitrary damping within 100 pixels
if (d2 < m)
{
die();
m=500;
}else {
desired.setMag(maxspeed);
}
// Steering = Desired minus Velocity
PVector steer = PVector.sub(desired,velocity);
steer.limit(maxforce); // Limit to maximum steering force
applyForce(steer);
}
void die(){
if (ispstime>0) {
maxspeed = 0;
maxforce = 0;
ps.display();
ps.shatter();
ps.update();
ispstime -= 1;
isdie=true;}
}
void display() {
//beginShape();
//stroke(mouseY/3, 200, mouseX/3);
strokeWeight(15);
noFill();
PVector v1=new PVector(width/2, height/2);
for(PVector v: history) {
beginShape();
stroke(v.x/3+50,200, v.y/3+50);
vertex(v.x,v.y);
vertex(v1.x,v1.y);
v1=v;
endShape();
}
//endShape();
// Draw a triangle rotated in the direction of velocity
float theta = velocity.heading2D() + PI/2;
fill(127);
stroke(0);
strokeWeight(1);
pushMatrix();
translate(position.x,position.y);
rotate(theta);
beginShape();
vertex(0, -r*2);
vertex(-r, r*2);
vertex(r, r*2);
endShape(CLOSE);
popMatrix();
}
}
- 其他设定
1.粒子效果:粒子效果仅仅在玩家死亡的时候产生并显示,其产生的位置也是和走过的路径有关。每一个粒子为小正方形,散开并下落。
ParticleSystem类源代码:
class ParticleSystem {
ArrayList<Particle> particles;
PVector origin;
int rows = 5;
int cols = 5;
boolean intact = true;
ParticleSystem(PVector position, float r) {
origin = position.get();
particles = new ArrayList<Particle>();
for (int i = 0; i < rows*cols; i++) {
addParticle(position.x + (i%cols)*r, position.y + (i/rows)*r, r);
}
}
void addParticle(float r) {
particles.add(new Particle(origin,r));
}
void addParticle(float x, float y, float r) {
particles.add(new Particle(new PVector(x, y), r));
}
void display() {
for (Particle p : particles) {
p.display();
}
}
void shatter() {
intact = false;
}
void update() {
if (!intact) {
for (Particle p : particles) {
p.update();
}
}
}
}
Particle类源代码
class Particle {
PVector position;
PVector velocity;
PVector acceleration;
float lifespan;
float r;
Particle(PVector l, float r_) {
acceleration = new PVector(0,0.01);
velocity = PVector.random2D();
velocity.mult(0.5);
position =l.get();
lifespan = 10.0;
r = r_;
}
void run() {
update();
display();
}
// Method to update position
void update() {
velocity.add(acceleration);
position.add(velocity);
lifespan -= 5.0;
}
// Method to display
void display() {
stroke(0);
fill(0);
rectMode(CENTER);
rect(position.x,position.y,r,r);
}
// Is the particle still useful?
boolean isDead() {
if (lifespan < 0.0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
游戏截图
功能界面
1.开始界面

2.暂停界面
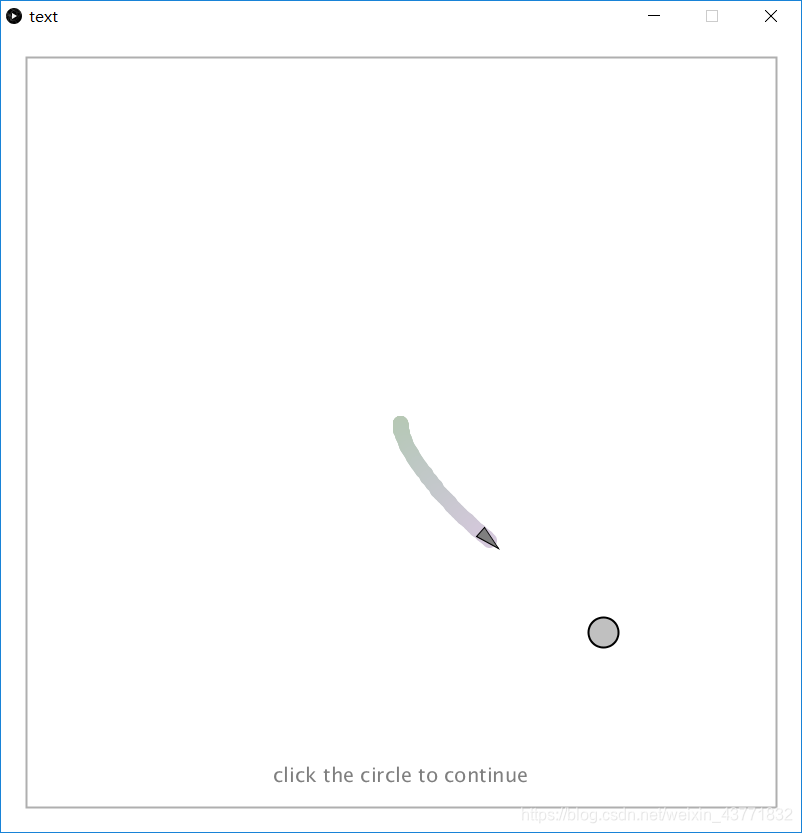
3.死亡界面
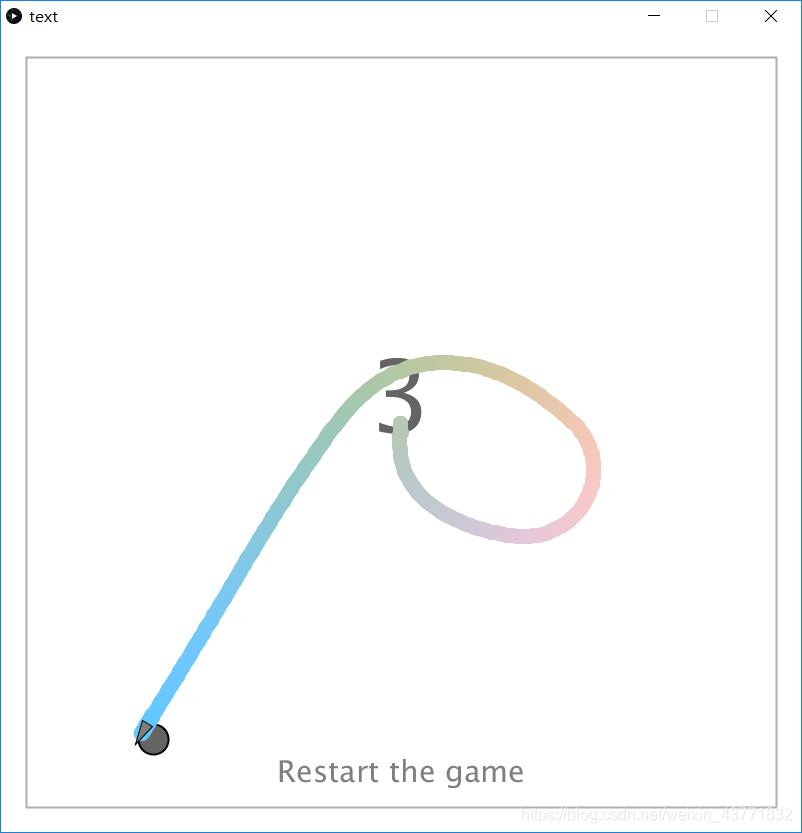
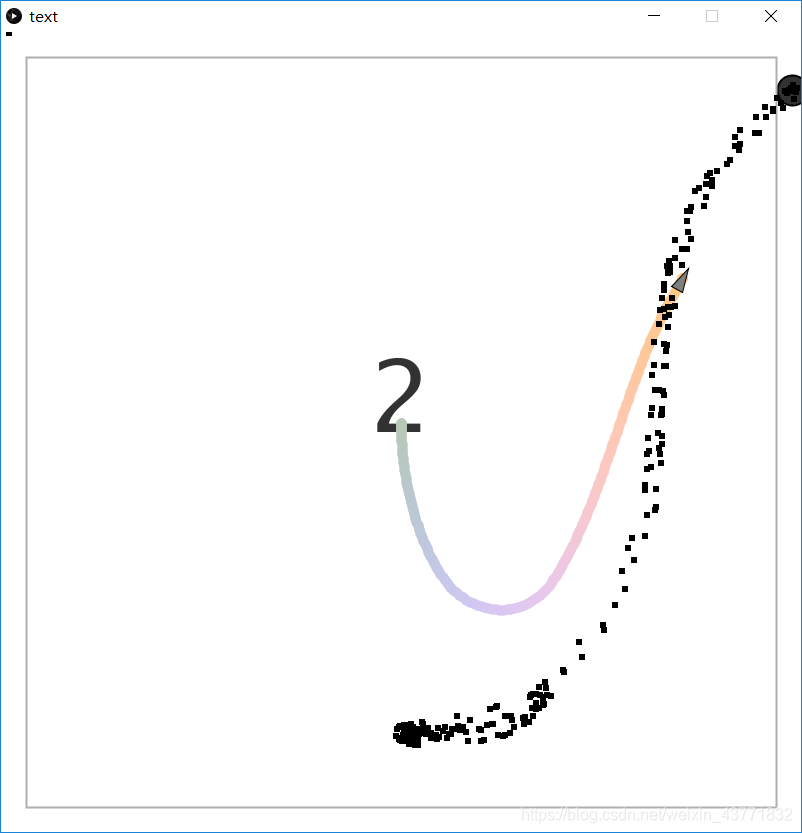
死亡画面
1.被敌人追击到死亡

2.越出游戏界限死亡
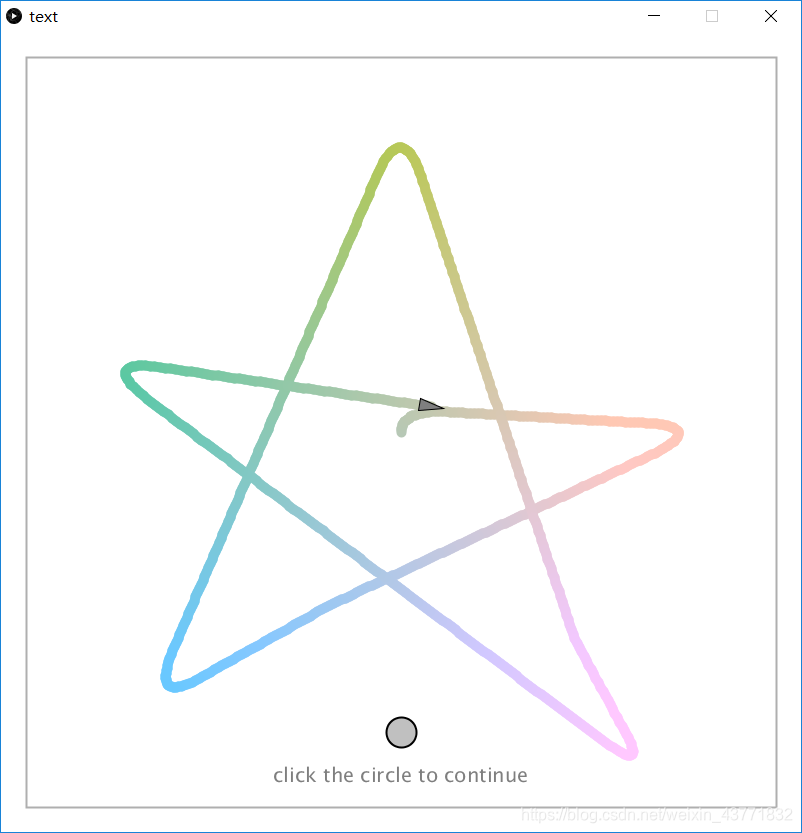
游戏作品
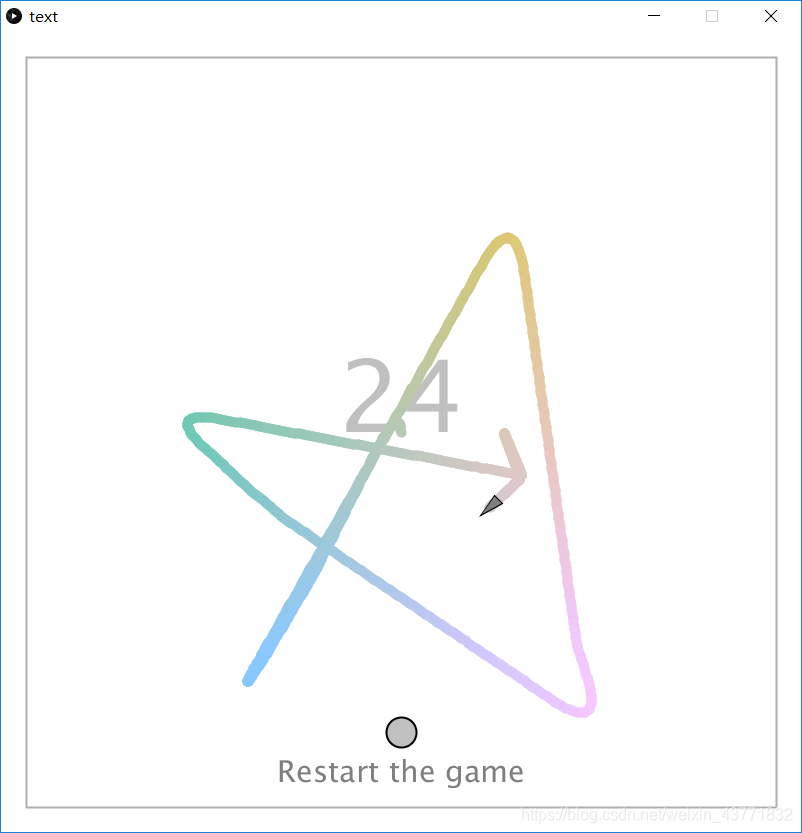
1.五角星
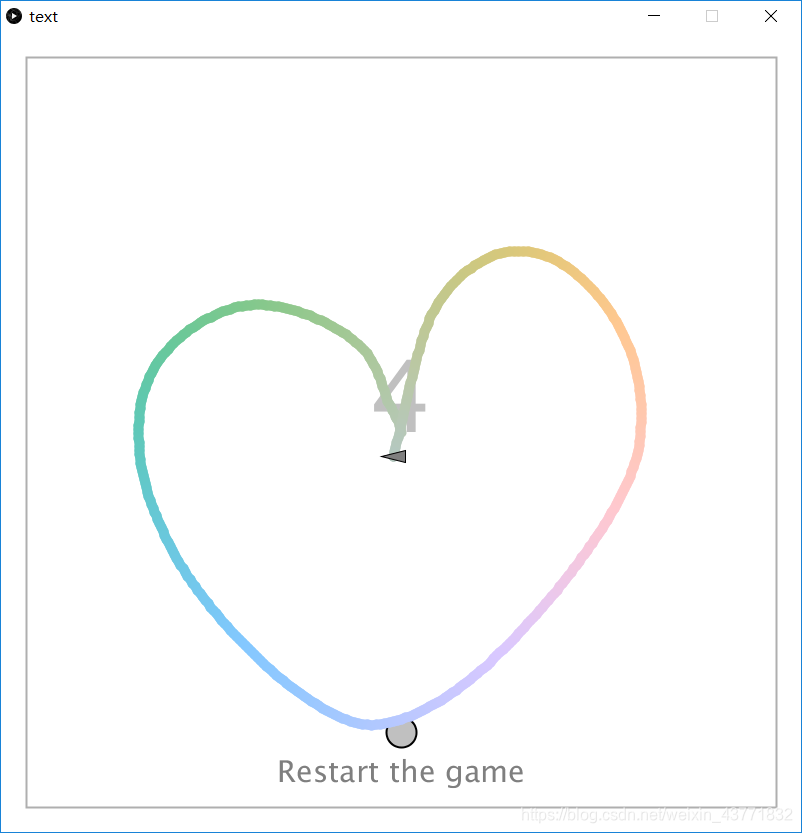
2.心形图案
3.复仇者联盟标志








 这是一款基于Processing的交互小游戏,融合动画技术,玩家需躲避敌人并利用敌人轨迹进行创作。游戏设有开始、暂停、死亡等场景,死亡时产生粒子效果。玩家死亡包括被敌人追上或出界,游戏截图展示多样创作可能。
这是一款基于Processing的交互小游戏,融合动画技术,玩家需躲避敌人并利用敌人轨迹进行创作。游戏设有开始、暂停、死亡等场景,死亡时产生粒子效果。玩家死亡包括被敌人追上或出界,游戏截图展示多样创作可能。
















 796
796

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








