一、安装requests包
安装requests包:
pip install requests
查看安装的包
pip.exe list
pip.exe show requests
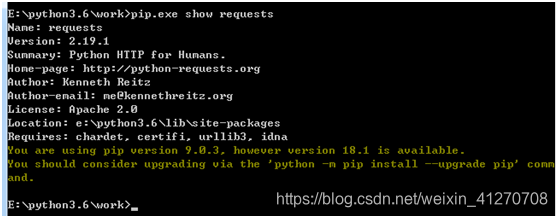
如何查看是否安装成功
import requests
http协议:
客户端(浏览器、使用cmd):发送给请求包---》网络服务器
返回给客户服务器一个响应包
请求包:
首部:header
主体:body
响应包:
首部:header
主体:body
常见的请求格式:
get、post:、delete、put、options
get请求和post请求区别:
get用于信息的获取,而且是安全和幂等的。所谓安全意味着该操作用于获取信息而非修改信息,就像数据库查询一样,不会修改,增加数据,不会影响资源的状态;幂等意味着对同一URL的多个请求应该返回同样的结果。
post请求用于修改服务器上的资源的请求。
简单总结
1 get是从服务器上获取数据,post是向服务器传送数据
2 get传送的数据量较小,不能大于2k;post传送的数据量较大
3 get安全性非常低,post安全性较高
首部:header
主体:body
二、接口测试常用请求
get方法:
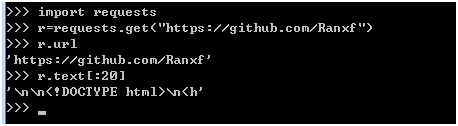
import requests
r=requests.get("https://github.com/Ranxf")
r.url
r.text[:20]
r.headers
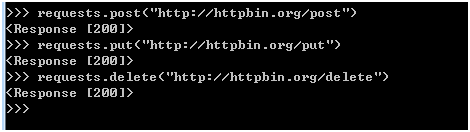
post请求
requests.post("http://httpbin.org/post")
put请求
requests.put("http://httpbin.org/put")
requests.delete("http://httpbin.org/delete")
2.1 带参数的get请求
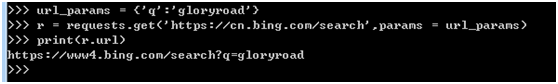
url_params = {'q':'gloryroad'} # 字典传递参数,如果值为None的键不会被添加到url中
r = requests.get('https://cn.bing.com/search',params = url_params)
print(r.url)
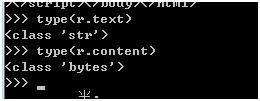
type(r.text)
type(r.content)
r.status_code
r.raw
三、注册一个用户
import requests
import json
import os
import hashlib
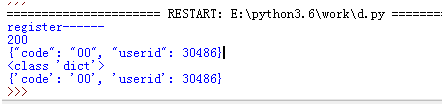
print ("register------")
data = json.dumps({'username': 'wxg', 'password': 'wxg123456', 'email': '1552049711@qq.com'}) #
r = requests.post('http://39.106.41.11:8080/register/', data= data)
print (r.status_code)
print (r.text)
print (type(r.json()))
print (r.json())
四、注册多个用户
import requests
import json
import os
import hashlib
import random
import string
username="".join([string.ascii_lowercase[random.randint(0,25)] for i in range(10)])
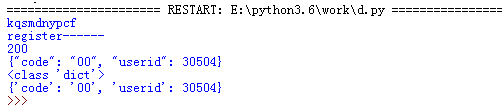
print (username)
print ("register------")
data = json.dumps({'username': username, 'password': 'wulaoshi12345', 'email': 'wulaoshi@qq.com'}) #
r = requests.post('http://39.106.41.11:8080/register/', data= data)
print (r.status_code)
print (r.text)
print (type(r.json()))
print (str(r.json()))
assert "{'code': '00', 'userid':" in str(r.json())
4.1 通过读、写文件注册多个用户名
import requests
import json
import os
import hashlib
import pickle
#需要默认文件里面写个初始值1即可
with open("E:\\http\\num.txt") as fp:
unique_number = fp.readline().strip()
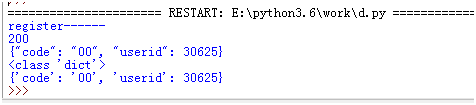
print ("register------")
data = json.dumps({'username': 'userdat'+unique_number, 'password': 'wulaoshi12345', 'email': 'wulaoshi@qq.com'}) #
r = requests.post('http://39.106.41.11:8080/register/', data= data)
print (r.status_code)
print (r.text)
print (type(r.json()))
print (str(r.json()))
assert "{'code': '00', 'userid':" in str(r.json())
with open("E:\\http\\num.txt",'w') as fp:
fp.write(str(int(unique_number)+1))
4.2用函数进行封装
import requests
import json
import os
import hashlib
import pickle
def send_request(interface,value):
r = requests.post(interface, data= value)
return r
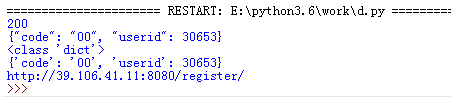
def get_response_info(response_obj):
print (response_obj.status_code)
print (response_obj.text)
print (type(response_obj.json()))
print (str(response_obj.json()))
print (response_obj.url)
def assert_response(response_obj,assert_word):
assert assert_word in str(response_obj.json())
#需要默认文件里面写个初始值1
with open("E:\\http\\num.txt","r+") as fp:
unique_number = fp.readline().strip()
fp.seek(0,0)
fp.write(str(int(unique_number)+1))
interface='http://39.106.41.11:8080/register/'
value = json.dumps({'username': 'wxg'+unique_number, 'password': 'wulaoshi12345', 'email': 'wulaoshi@qq.com'}) #
r=send_request(interface,value)
get_response_info(r)
assert_response(r,"{'code': '00', 'userid':")
4.3 配置数据和程序分离
import requests
import json
import os
import hashlib
import pickle
from conf import *
def send_request(interface,value):
r = requests.post(interface, data= value)
return r
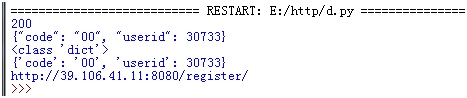
def get_response_info(response_obj):
print (response_obj.status_code)
print (response_obj.text)
print (type(response_obj.json()))
print (str(response_obj.json()))
print (response_obj.url)
def assert_response(response_obj,assert_word):
assert assert_word in str(response_obj.json())
#需要默认文件里面写个初始值1
with open("e:\\http\\num.txt","r+") as fp:
unique_number = fp.readline().strip()
fp.seek(0,0)
fp.write(str(int(unique_number)+10))
interface=register
value = json.dumps({'username': 'wxg'+unique_number, 'password': 'wulaoshi12345', 'email': 'wulaoshi@qq.com'}) #
r=send_request(interface,value)
get_response_info(r)
assert_response(r,"{'code': '00', 'userid':")





















 934
934

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








