Python 社区遵循 PEP 8 (Python Enhancement Proposal 8) 作为官方的风格指南。遵循这些规范可以使代码更加一致、易读,并与大多数 Python 项目保持兼容。
1. 代码布局
缩进
-
使用 4个空格 作为一级缩进
-
不要混合使用制表符和空格
# 正确
def function_name(var_one):
print(var_one)
# 错误 (制表符和空格混用)
def function_name(var_one):
print(var_one) # 这里可能混用了制表符
最大行长度
-
每行不超过 79 个字符 (文档字符串/注释不超过 72 个字符)
-
使用括号、方括号或花括号的隐式行连接
# 正确
with open('/path/to/some/file/you/want/to/read') as file_1, \
open('/path/to/some/file/being/written', 'w') as file_2:
file_2.write(file_1.read())
空行
-
顶层函数和类定义前后用 两个空行
-
类内方法定义前后用 一个空行
-
可以使用额外的空行分隔相关函数组或逻辑部分
# 正确
def function_one():
pass
def function_two():
pass
class MyClass:
def method_one(self):
pass
def method_two(self):
pass
2. 导入 (Imports)
-
导入应该分组,顺序为:
-
标准库导入
-
相关第三方库导入
-
本地应用/库特定导入
-
-
每组导入之间用空行分隔
# 正确
import os
import sys
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from my_local_module import MyClass
-
避免通配符导入 (
from module import *) -
使用绝对导入而非相对导入
3. 命名约定
变量和函数
-
使用 小写字母 和下划线 (
snake_case) -
描述性但不过长
# 正确
student_name = "Alice"
max_count = 100
def calculate_average_score():
pass
常量
-
使用 全大写字母 和下划线 (
UPPER_CASE)
# 正确
MAX_CONNECTIONS = 100
DEFAULT_TIMEOUT = 30
类名
-
使用 驼峰命名法 (
CamelCase)
# 正确
class MyClass:
pass
class DatabaseConnection:
pass
方法和实例变量
-
使用 小写字母 和下划线 (
snake_case) -
非公共方法和变量以单个下划线开头 (
_private_var)
class MyClass:
def public_method(self):
self.public_var = 10
self._private_var = 20
def _private_method(self):
pass
4. 表达式和语句中的空格
推荐使用空格的情况
-
二元运算符两侧
-
逗号、分号、冒号后
-
函数参数列表和索引/切片中的逗号后
# 正确
x = 1 + 2
y = (a + b) * (c - d)
spam(ham[1], {eggs: 2})
if x == 4: print(x, y); x, y = y, x
避免使用空格的情况
-
括号、方括号、花括号内侧
-
逗号、分号、冒号前
-
函数调用的参数列表前的左括号前
# 正确
spam(ham[1], {eggs: 2})
dict['key'] = list[index]
# 错误
spam( ham[ 1 ], { eggs: 2 } )
dict ['key'] = list [index]
5. 注释
行内注释
-
与代码至少间隔 2个空格
-
以
#和一个空格开始
# 正确
x = x + 1 # 补偿边界
文档字符串 (Docstrings)
-
公共模块、函数、类和方法都应该有文档字符串
-
使用三重双引号
""" -
第一行是简要描述,后跟空行,然后是详细描述
def complex(real=0.0, imag=0.0):
"""Form a complex number.
Keyword arguments:
real -- the real part (default 0.0)
imag -- the imaginary part (default 0.0)
"""
if imag == 0.0 and real == 0.0:
return complex_zero
...
6. 类型注解 (Python 3.5+)
-
使用类型注解提高代码可读性和可维护性
def greeting(name: str) -> str:
return 'Hello ' + name
Vector = list[float]
def scale(scalar: float, vector: Vector) -> Vector:
return [scalar * num for num in vector]
7. 其他建议
-
避免使用
==与True、False或None比较,使用is或is not -
使用字符串方法而非字符串模块
-
使用
''.startswith()和''.endswith()而非字符串切片 -
对象类型比较应该使用
isinstance()而非type()
工具支持
可以使用以下工具自动检查和格式化代码:
-
flake8: 检查 PEP 8 合规性
-
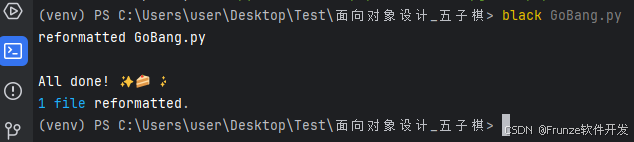
black: 自动格式化代码
-
isort: 自动排序导入
-
mypy: 静态类型检查
# 安装工具
pip install flake8 black isort mypy
# 使用 black 格式化代码
black your_script.py
# 使用 flake8 检查代码风格
flake8 your_script.py
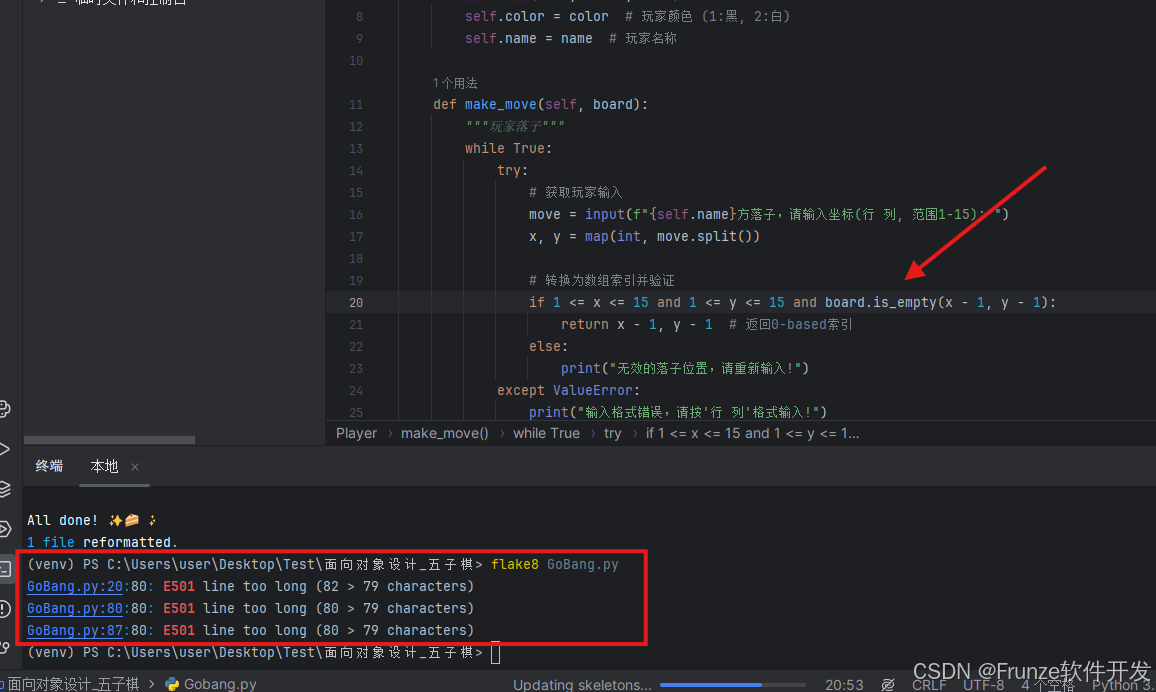
遵循这些编码规范将使 Python 代码更加专业、易读和易于维护,特别是在团队协作环境中。
 Python编码风格与标准化指南
Python编码风格与标准化指南






















 1470
1470

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








