各位客官实在是抱歉,最近开始上班了,导致没时间更新博客,好不容易有个周末,来把没有写完的写上。
这个是我在GitHub上下载的一个master,具体链接不记得了,下载完结构如下图
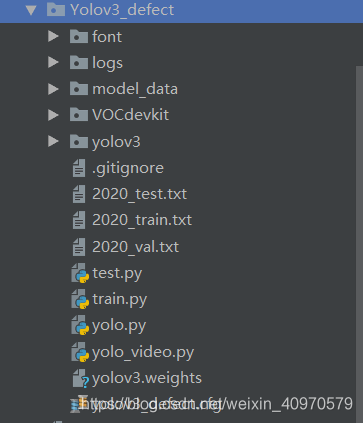
大家自己在GitHub上找一找,这个代码有很多大神都已经写完了,先说一说需要改动的地方吧。
我们来依次介绍,font就是个放字体文件的文件夹,要是想要简体中文的话自己在网上下载个文件就可以了,放在yolo.py文件里的154行就可以了、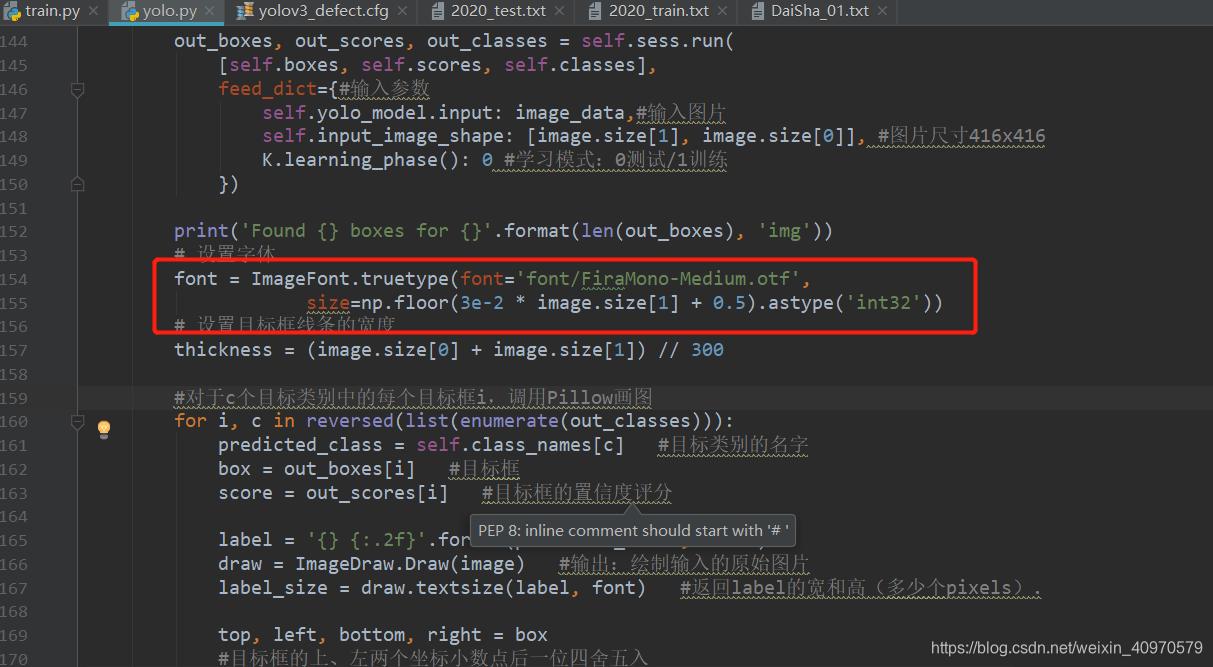
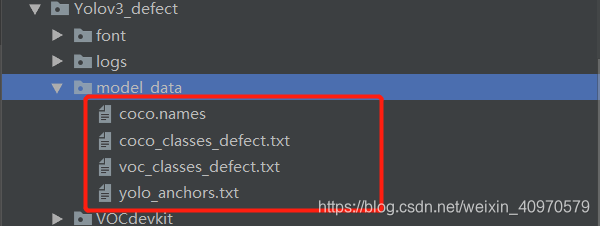
下一个文件夹log这个是用来存放训练的模型的,这个大神的代码保存的是**.h5模型,所以用的就是tensorflow中的keras进行的训练。接下来是model_data文件夹
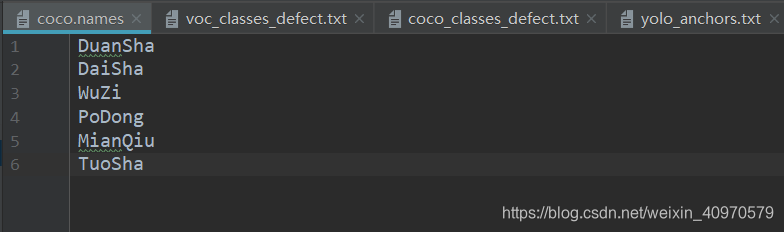
把这里的文本改成你要检测的类别,比如说我的,就改成了DuanSha、DaiSha、WuZi、PoDong、MianQiu、TuoSha 这几类
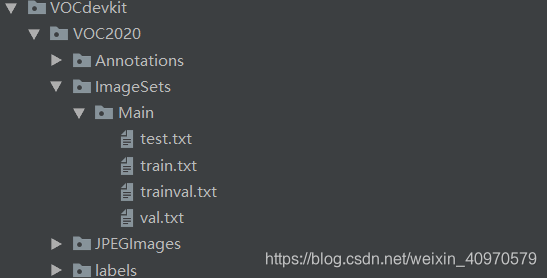
再然后是VOCdevikt**文件夹,这个就是上面做的数据存放的文件夹,里面就是标准VOC格式数据集的内容
来一条华丽的分割线
接下来就是重点了。先来介绍yolov3文件夹,先是 model.py 文件。我下载的这个代码中,作者已经注释的很全面了,下面全放上去,让大家伙瞅瞅。我把tiny的框架给删除了,要用咱就用多的,哈哈哈
"""YOLO_v3 Model Defined in Keras."""
from functools import wraps
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from keras import backend as K
from keras.layers import Conv2D, Add, ZeroPadding2D, UpSampling2D, Concatenate, MaxPooling2D
from keras.layers.advanced_activations import LeakyReLU
from keras.layers.normalization import BatchNormalization
from keras.models import Model
from keras.regularizers import l2
from yolov3.utils import compose
@wraps(Conv2D)
def DarknetConv2D(*args, **kwargs):
"""Wrapper to set Darknet parameters for Convolution2D."""
darknet_conv_kwargs = {
'kernel_regularizer': l2(5e-4)}
darknet_conv_kwargs['padding'] = 'valid' if kwargs.get('strides')==(2,2) else 'same'
darknet_conv_kwargs.update(kwargs)
return Conv2D(*args, **darknet_conv_kwargs)
def DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(*args, **kwargs):
"""Darknet Convolution2D followed by BatchNormalization and LeakyReLU."""
no_bias_kwargs = {
'use_bias': False}
no_bias_kwargs.update(kwargs)
return compose(
DarknetConv2D(*args, **no_bias_kwargs),
BatchNormalization(),
LeakyReLU(alpha=0.1))
def resblock_body(x, num_filters, num_blocks):
'''A series of resblocks starting with a downsampling Convolution2D'''
# Darknet uses left and top padding instead of 'same' mode
x = ZeroPadding2D(((1,0),(1,0)))(x)
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (3,3), strides=(2,2))(x)
for i in range(num_blocks):
y = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters//2, (1,1)),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (3,3)))(x)
x = Add()([x,y])
return x
def darknet_body(x):
'''Darknent body having 52 Convolution2D layers'''
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(32, (3,3))(x)
x = resblock_body(x, 64, 1)
x = resblock_body(x, 128, 2)
x = resblock_body(x, 256, 8)
x = resblock_body(x, 512, 8)
x = resblock_body(x, 1024, 4)
return x
def make_last_layers(x, num_filters, out_filters):
'''6 Conv2D_BN_Leaky layers followed by a Conv2D_linear layer'''
x = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (1,1)),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters*2, (3,3)),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (1,1)),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters*2, (3,3)),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (1,1)))(x)
y = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters*2, (3,3)),
DarknetConv2D(out_filters, (1,1)))(x)
return x, y
def yolo_body(inputs, num_anchors, num_classes):
"""Create YOLO_V3 model CNN body in Keras."""
darknet = Model(inputs, darknet_body(inputs))
x, y1 = make_last_layers(darknet.output, 512, num_anchors*(num_classes+5))
x = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(256, (1,1)),
UpSampling2D(2))(x)
x = Concatenate()([x,darknet.layers[152].output])
x, y2 = make_last_layers(x, 256, num_anchors*(num_classes+5))
x = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(128, (1,1)),
UpSampling2D(2))(x)
x = Concatenate()([x,darknet.layers[92].output])
x, y3 = make_last_layers(x, 128, num_anchors*(num_classes+5))
return Model(inputs, [y1,y2,y3])
def yolo_head(feats, anchors, num_classes, input_shape, calc_loss=False):
"""Convert final layer features to bounding box parameters."""
# feats,即:feature maps
num_anchors = len(anchors)
# Reshape to batch, height, width, num_anchors, box_params.
anchors_tensor = K.reshape(K.constant(anchors), [1, 1, 1, num_anchors, 2])
grid_shape = K.shape(feats)[1:3] # # height, width #13x13或26x26或52x5
# 通过arange、reshape、tile的组合,根据grid_shape(13x13、26x26或52x52)创建y轴的0~N-1的组合grid_y,
# 再创建x轴的0~N-1的组合grid_x,将两者拼接concatenate,形成NxN的grid(13x13、26x26或52x52)
grid_y = K.tile(K.reshape(K.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[0]), [-1, 1, 1, 1]),
[1, grid_shape[1], 1, 1])
grid_x = K.tile(K.reshape(K.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[1]), [1, -1, 1, 1]),
[grid_shape[0], 1, 1, 1])
grid = K.concatenate([grid_x, grid_y])
grid = K.cast(grid, K.dtype(feats))
# 从待处理的feature map的最后一维数据中,先将num_anchors这个维度与num_classes+5这个维度的数据分离,
# 再取出4个框值tx、ty(最后一维数据的0:1)、tw和th(最后一维数据的2:3)
feats = K.reshape(
feats, [-1, grid_shape[0], grid_shape[1], num_anchors, num_classes + 5])
# Adjust preditions to each spatial grid point and anchor size.
# 用sigmoid()函数计算目标框的中心点box_xy,用exp()函数计算目标框的宽和高box_wh
# 使用特征图尺寸(如:13x13、26x26或52x52)在水平x、垂直y两个维度对box_xy进行归一化,确定目标框的中心点的相对位置
# 使用标准图片尺寸(416x416)在宽和高两个维度对box_wh
# (因为,3组9个anchor box是基于416x416尺寸定义的)进行归一化,确定目标框的高和宽的相对位置
box_xy = (K.sigmoid(feats[..., :2]) + grid) / K.cast(grid_shape[::-1], K.dtype(feats))
box_wh = K.exp(feats[..., 2:4]) * anchors_tensor / K.cast(input_shape[::-1], K.dtype(feats))
# 用sigmoid()函数计算目标框的置信度box_confidence
box_confidence = K.sigmoid(feats[..., 4:5])
# 用sigmoid()函数计算目标框的类别置信度box_class_probs
box_class_probs = K.sigmoid(feats[..., 5:])
if calc_loss == True:
return grid, feats, box_xy, box_wh
return box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probs
def yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape):
'''Get corrected boxes'''
# 将box_xy, box_wh转换为输入图片上的真实坐标,输出boxes是框的左下、右上两个坐标(y_min, x_min, y_max, x_max)
# np.array[i:j:s],当s<0时,i缺省时,默认为-1;j缺省时,默认为-len(a)-1;所以array[::-1]相当于array[-1:-len(a)-1:-1],
# 也就是从最后一个元素到第一个元素复制一遍,即倒序
box_yx = box_xy[..., ::-1]
box_hw = box_wh[..., ::-1]
input_shape = K.cast(input_shape, K.dtype(box_yx))
image_shape = K.cast(image_shape, K.dtype(box_yx))
new_shape = K.round(image_shape * K.min(input_shape/image_shape))
offset = (input_shape-new_shape)/2./input_shape
scale = input_shape/new_shape
box_yx = (box_yx - offset) * scale
box_hw *= scale
box_mins = box_yx - (box_hw / 2.)
box_maxes = box_yx + (box_hw / 2.)
boxes = K.concatenate([
box_mins[..., 0:1], # y_min
box_mins[..., 1:2], # x_min
box_maxes[..., 0:1], # y_max
box_maxes[..., 1:2] # x_max
])
# Scale boxes back to original image shape.
boxes *= K.concatenate([image_shape, image_shape])
return boxes
def yolo_boxes_and_scores(feats, anchors, num_classes, input_shape, image_shape):
'''Process Conv layer output'''
# feats:需要处理的featue map
# shape:(?,13,13,255),(?,26,26,255)或(?,52,52,255)
# anchors:每层对应的3个anchor box
# num_classes:类别数(80)
# input_shape:(416,416)
# image_shape:图像尺寸
box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probs = yolo_head(feats,
anchors, num_classes, input_shape)
boxes = yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape)
boxes = K.reshape(boxes, [-1, 4])#形成框的列表boxes(?, 4)
box_scores = box_confidence * box_class_probs #框的得分=框的置信度x类别置信度
box_scores = K.reshape(box_scores, [-1, num_classes]) #形成框的得分列表box_scores(?, 80)
return boxes, box_scores
def yolo_eval(yolo_outputs,
anchors,
num_classes,
image_shape,
max_boxes=20,#每张图每类最多检测到20个框
score_threshold=.6,
iou_threshold=.5):
"""Evaluate YOLO model on given input and return filtered boxes."""
#将anchor_box分为3组,分别分配给13x13、26x26、52x52等3个yolo_model输出的feature map
num_layers = len(yolo_outputs)
anchor_mask = [[6,7,8], [3,4,5], [0,1,2]] if num_layers==3 else [[3,4,5], [1,2,3]] # 默认设置
input_shape = K.shape(yolo_outputs[0])[1:3] * 32
boxes = []
box_scores = []
#分别对3个feature map运行
for l in range(num_layers):
_boxes, _box_scores = yolo_boxes_and_scores(yolo_outputs[l],
anchors[anchor_mask[l]], num_classes, input_shape, image_shape)
boxes.append(_boxes)
box_scores.append(_box_scores)
#将运算得到的目标框用concatenate()函数拼接为(?, 4)的元组,将目标框的置信度拼接为(?,1)的元组
boxes = K.concatenate(boxes, axis=0)
box_scores = K.concatenate(box_scores, axis=0)
#计算MASK掩码,过滤小于score阈值的值,只保留大于阈值的值
mask = box_scores >= score_threshold
max_boxes_tensor = K.constant(max_boxes, dtype='int32')
boxes_ = []
scores_ = []
classes_ = []
for c in range(num_classes):
# TODO: use keras backend instead of tf.
class_boxes = tf.boolean_mask(boxes, mask[:, c])#通过掩码MASK和类别C筛选框boxes
class_box_scores = tf.boolean_mask(box_scores[:, c], mask[:, c])#通过掩码MASK和类别C筛选scores
nms_index = tf.image.non_max_suppression(
class_boxes, class_box_scores, max_boxes_tensor, iou_threshold=iou_threshold)
#运行非极大抑制non_max_suppression(),每类最多检测20个框
#K.gather:根据索引nms_index选择class_boxes和class_box_scores,标出选出的框的类别classes
class_boxes = K.gather(class_boxes, nms_index)
class_box_scores = K.gather(class_box_scores, nms_index)
classes = K.ones_like(class_box_scores, 'int32') * c
boxes_.append(class_boxes)
scores_.append(class_box_scores)
classes_.append(classes)
#用concatenate()函数把选出的class_boxes、class_box_scores和classes拼接,形成(?,4)、(?,1)和(?,80)的元组返回
boxes_ = K.concatenate(boxes_, axis=0)
scores_ = K.concatenate(scores_, axis=0)
classes_ = K.concatenate(classes_, axis=0)
return boxes_, scores_, classes_
def preprocess_true_boxes(true_boxes, input_shape, anchors, num_classes):
'''Preprocess true boxes to training input format
Parameters
----------
true_boxes: array, shape=(m, T, 5)
Absolute x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max, class_id relative to input_shape.
input_shape: array-like, hw, multiples of 32
anchors: array, shape=(N, 2), wh
num_classes: integer
Returns
-------
y_true: list of array, shape like yolo_outputs, xywh are reletive value
'''
assert (true_boxes[..., 4]<num_classes).all(), 'class id must be less than num_classes'
num_layers = len(anchors)//3 # default setting
anchor_mask = [[6,7,8], [3,4,5], [0,1,2]] if num_layers==3 else [[3,4,5], [1,2,3]]
true_







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








