吴恩达机器学习 课堂笔记 Chapter8 正则化(Regularization)
The problem of overfitting
If we have too many features, the learned hypothesis may fit the training set very well, but fail to generalize to new examples.
- Underfitting => high bias
- Overfitting => high variance
Methods for addressing overfitting
- Reduce number of features
Manually choose which features to keep => Drop some information meanwhile.
Model selection algorithm - Regularization
Keep all the features, but reduce magnitude/values of parameter θ j \theta_j θj
Works well when we have lots of features, each of which contributes a bit to predicting y.
Cost function
Intuition
Small values for parameters θ 0 , θ 1 , . . . , θ n \theta_0, \theta_1, ..., \theta_n θ0,θ1,...,θn
- “Simpler” hypothesis
- Less prone to overfitting
- We cannot know in advance which ones to pick. So we ask for every parameter to be small.
Cost function
J
(
θ
)
=
1
2
m
(
∑
i
=
0
m
(
h
θ
(
x
(
i
)
−
y
i
)
2
)
+
λ
∑
i
=
1
n
θ
j
2
)
J(\theta) = \frac{1}{2m}(\sum_{i=0}^{m}(h_\theta(x^{(i)}-y^{i})^2) + \lambda \sum_{i=1}^n\theta_j^2)
J(θ)=2m1(i=0∑m(hθ(x(i)−yi)2)+λi=1∑nθj2)
NOTE:
We do not penalize
θ
0
\theta_0
θ0.
λ
\lambda
λ:regularization parameter. Need to choose it well.
Regularized linear regression
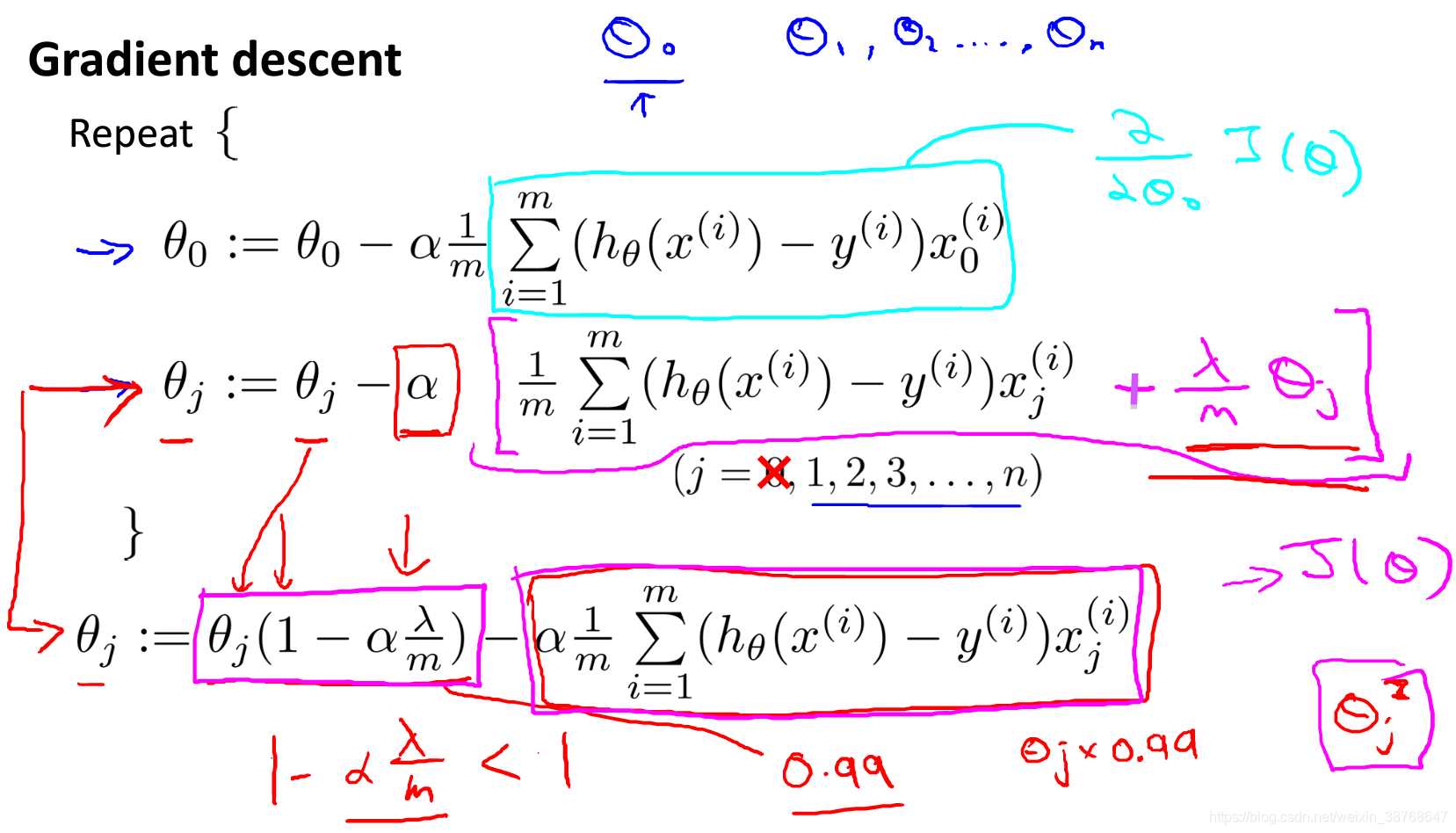
Gradient descent
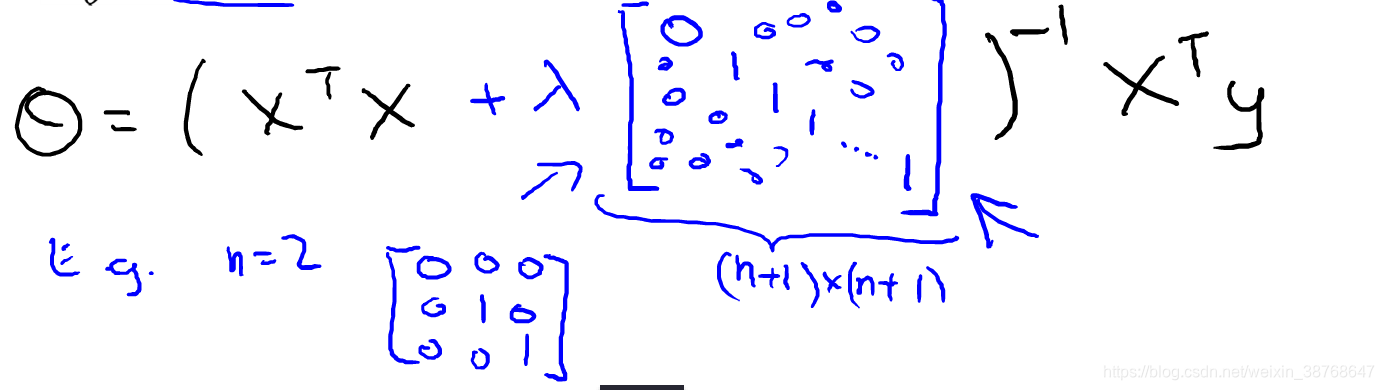
Normal equation
Regularized logistic regression
Cost function
J ( θ ) = − 1 m ∑ ( y l o g h θ ( x ) ( 1 − y ) l o g ( 1 − h θ ( x ) ) ) + 1 2 m ∑ i = 1 n θ j 2 J(\theta)=-\frac{1}{m}\sum(ylogh_\theta(x)(1-y)log(1-h_\theta(x)))+\frac{1}{2m}\sum_{i=1}^n\theta_j^2 J(θ)=−m1∑(yloghθ(x)(1−y)log(1−hθ(x)))+2m1i=1∑nθj2
Gradient descent
Same as above.








 本文探讨了机器学习中过拟合的问题,介绍了减少特征数量、模型选择算法和正则化三种解决方法。详细讲解了正则化在逻辑回归和线性回归中的应用,包括成本函数、梯度下降和正规方程等关键概念。
本文探讨了机器学习中过拟合的问题,介绍了减少特征数量、模型选择算法和正则化三种解决方法。详细讲解了正则化在逻辑回归和线性回归中的应用,包括成本函数、梯度下降和正规方程等关键概念。
















 283
283

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








