点击下方卡片,关注“小白玩转Python”公众号
所有实现都参考了 yzd-v/FGD github 仓库,该仓库基于 mmdetection 深度学习框架。
介绍和实现工作流程
在这里,我们将从教师模型的颈部特征中提取知识,并以特征损失的形式将知识蒸馏到学生模型中。为了实现这一点,如果按照以下工作流程实施,理解起来会更容易。
您需要加载教师模型。教师模型当然是在相同数据集上训练过的预训练模型。
由于它是基于特征的知识蒸馏,因此必须从学生/教师模型的颈部提取特征。在这里,使用 pytorch hook函数提取特征。
提取的特征必须以损失的形式蒸馏到学生模型中。在 FGD 中实现的特征损失稍作修改以适应 Yolo 格式。
加载教师模型
我们可以像下面所示创建一个知识蒸馏的 Yaml 配置。这允许您更有用地实现知识蒸馏。
# model settings
temp : 0.5
alpha_fgd : 0.002
beta_fgd : 0.001
gamma_fgd : 0.001
lambda_fgd : 0.00001
scale_y : 1.0
scale_x : 1.0
distiller :
type : "DetectionDistiller"
teacher_pretrained : "yolov9e.pt"
student_model: "yolov9c.yaml"
distill_cfg :
- neck_15 :
name : "loss_fgd_neck_15"
type : "KDLOSS"
student_channels : 256
teacher_channels : 256
- neck_18 :
name : "loss_fgd_neck_18"
type : "KDLOSS"
student_channels : 512
teacher_channels : 512
- neck_21 :
name : "loss_fgd_neck_21"
type : "KDLOSS"
student_channels : 512
teacher_channels : 512从这里,您可以像下面所示加载教师模型。
self.teacher_model = check_model_file_from_stem(self.distill_cfg["distiller"]["teacher_pretrained"])将教师模型更改为评估模式,冻结梯度,使其不被学习,并设置与学生模型相同的属性。
self.teacher_model.eval()
self.teacher_model = self.teacher_model.to(self.device)for param in self.teacher_model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
self.teacher_model.nc = self.data["nc"]
self.teacher_model.names = self.data["names"]
self.teacher_model.args = self.args我们现在可以加载教师模型!那么我们如何从模型中提取特征呢?
从学生和教师模型中提取特征
我们在哪里以及如何提取特征?在论文中,它说从目标检测的颈部提取特征。颈部是特征金字塔网络的一部分,旨在检测多尺度对象,在下图中,红色框中的 P3、P4 和 P5 可以看作是颈部的特征。从 P3 到 P5,包含了更抽象的信息。
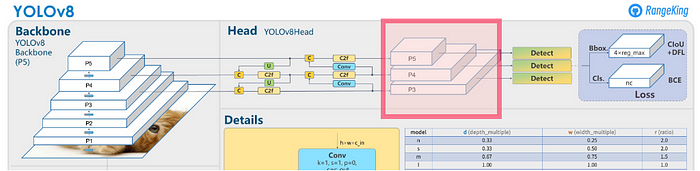
yolov8 模型架构图
Yolov9 也有相同的颈部。如果我们查看 YoloV9-c 的模型配置,如下所示。
# YOLOv9
# parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
# gelan backbone
backbone:
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [256, 128, 64, 1]] # 2
- [-1, 1, ADown, [256]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 256, 128, 1]] # 4
- [-1, 1, ADown, [512]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]] # 6
- [-1, 1, ADown, [512]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]] # 8
- [-1, 1, SPPELAN, [512, 256]] # 9
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [256, 256, 128, 1]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, ADown, [256]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, ADown, [512]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # DDetect(P3, P4, P5)我们最感兴趣的颈部层的位置在哪里?如果您查看最后一行的 Detect Layer 配置 ([[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]]),您可以看到从第 15、18 和 21 层进行检测,这就是颈部层。
教师模型 YoloV9-e 的颈部是 35、38 和 41。换句话说,我们需要从第 35、38 和 41 层提取特征,并与学生模型的颈部层 15、18 和 21 进行比较,创建损失函数。
提取特征可以通过创建 pytorch 的注册函数来完成。在学生模型的第 15、18 和 21 个位置注册hook的方法如下。
student_15_hook = self.model.model[15].register_forward_hook(student_15_hook_forward)
student_18_hook = self.model.model[18].register_forward_hook(student_18_hook_forward)
student_21_hook = self.model.model[21].register_forward_hook(student_21_hook_forward)hook函数必须有模块、输入和输出作为输入变量,如下所示。
def student_15_hook_forward(module, input, output):
global student_15_feature
student_15_feature = output
def student_18_hook_forward(module, input, output):
global student_18_feature
student_18_feature = output
def student_21_hook_forward(module, input, output):
global student_21_feature
student_21_feature = output声明特征 15、18 和 21 为全局变量,并将其用作特征损失函数的输入。
对于教师模型,在相应的层创建hook函数并注册注册hook。
teacher_35_hook = self.teacher_model.model[35].register_forward_hook(teacher_35_hook_forward)
teacher_38_hook = self.teacher_model.model[38].register_forward_hook(teacher_38_hook_forward)
teacher_41_hook = self.teacher_model.model[41].register_forward_hook(teacher_41_hook_forward)def teacher_35_hook_forward(module, input, output):
global teacher_35_feature
teacher_35_feature = output
def teacher_38_hook_forward(module, input, output):
global teacher_38_feature
teacher_38_feature = output
def teacher_41_hook_forward(module, input, output):
global teacher_41_feature
teacher_41_feature = output实现特征损失
我在 ultralytics/utils/loss.py 中实现了它。这种实现与这里的代码 (https://github.com/yzd-v/FGD/blob/master/mmdet/distillation/losses/fgd.py) 大致相同,但输入/输出界面是 mmdetection 框架和 ultralytics 框架。添加了一些修改以消除由差异引起的错误。
class FGDLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
student_channels,
teacher_channels,
name,
temp=0.5,
alpha_fgd=0.001,
beta_fgd=0.0005,
gamma_fgd=0.0005,
lambda_fgd=0.000005,
scale_y=1.0,
scale_x=1.0
):
super().__init__()
self.temp = temp
self.alpha_fgd = alpha_fgd
self.beta_fgd = beta_fgd
self.gamma_fgd = gamma_fgd
self.lambda_fgd = lambda_fgd
self.name = name
self.scale_y = scale_y
self.scale_x = scale_x
if student_channels != teacher_channels:
self.align = nn.Conv2d(student_channels, teacher_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, device='cuda', dtype=torch.half)
else:
self.align = None
self.conv_mask_s = nn.Conv2d(teacher_channels, 1, kernel_size=1, device='cuda', dtype=torch.half)
self.conv_mask_t = nn.Conv2d(teacher_channels, 1, kernel_size=1, device='cuda', dtype=torch.half)
# GcBlock
self.channel_add_conv_s = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(teacher_channels, teacher_channels//2, kernel_size=1, device='cuda', dtype=torch.half),
nn.LayerNorm([teacher_channels//2, 1, 1], device='cuda', dtype=torch.half),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(teacher_channels//2, teacher_channels, kernel_size=1, device='cuda', dtype=torch.half)
)
self.channel_add_conv_t = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(teacher_channels, teacher_channels//2, kernel_size=1, device='cuda', dtype=torch.half),
nn.LayerNorm([teacher_channels//2, 1, 1], device='cuda', dtype=torch.half),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(teacher_channels//2, teacher_channels, kernel_size=1, device='cuda', dtype=torch.half)
)
self.reset_parameters()
def forward(self,
preds_S,
preds_T,
batch,
):
batch_num = len(batch['img'])
gt_bboxes = [] # batched, cx, cy, w, h
obj_idx = 0
for i in range(batch_num):
obj_num = batch["batch_idx"].tolist().count(i)
xyxy = self.xywh2xyxy(batch["bboxes"])
gt_bboxes.append(xyxy[obj_idx:obj_idx + obj_num])
obj_idx += obj_num
img_metas = batch["resized_shape"] # resized image shape
# batch: im_file, ori_shape, resized_shape, img, cls, bboxes, batch_idx
scale_y = self.scale_y
scale_x = self.scale_x
assert preds_S.shape[-2:] == preds_T.shape[-2:], 'the output dim of teacher and student differ'
if self.align is not None:
preds_S = self.align(preds_S)
N, C, H, W = preds_S.shape
S_attention_t, C_attention_t = self.get_attention(preds_T, self.temp)
S_attention_s, C_attention_s = self.get_attention(preds_S, self.temp)
Mask_fg = torch.zeros_like(S_attention_t)
Mask_bg = torch.ones_like(S_attention_t)
wmin, wmax, hmin, hmax = [], [], [], []
for i in range(N):
new_bboxes = torch.ones_like(gt_bboxes[i])
new_bboxes[:, 0] = gt_bboxes[i][:, 0] * W / scale_x # xmin
new_bboxes[:, 2] = gt_bboxes[i][:, 2] * W / scale_x # xmax
new_bboxes[:, 1] = gt_bboxes[i][:, 1] * H / scale_y # ymin
new_bboxes[:, 3] = gt_bboxes[i][:, 3] * H / scale_y # ymax
wmin.append(torch.floor(new_bboxes[:, 0]).int())
wmax.append(torch.ceil(new_bboxes[:, 2]).int())
hmin.append(torch.floor(new_bboxes[:, 1]).int())
hmax.append(torch.ceil(new_bboxes[:, 3]).int())
area = 1.0/(hmax[i].view(1, -1) + 1 - hmin[i].view(1, -1))/(wmax[i].view(1,-1) + 1 - wmin[i].view(1, -1))
for j in range(len(gt_bboxes[i])):
Mask_fg[i][hmin[i][j]:hmax[i][j]+1, wmin[i][j]:wmax[i][j]+1] = \
torch.maximum(Mask_fg[i][hmin[i][j]:hmax[i][j]+1, wmin[i][j]:wmax[i][j]+1],
area[0][j])
Mask_bg[i] = torch.where(Mask_fg[i]>0, 0, 1)
if torch.sum(Mask_bg[i]):
Mask_bg[i] /= torch.sum(Mask_bg[i])
fg_loss, bg_loss = self.get_fea_loss(preds_S, preds_T, Mask_fg, Mask_bg,
C_attention_s, C_attention_t, S_attention_s, S_attention_t)
mask_loss = self.get_mask_loss(C_attention_s, C_attention_t, S_attention_s, S_attention_t)
rela_loss = self.get_rela_loss(preds_S, preds_T)
fg_loss *= self.alpha_fgd/scale_x/scale_y
bg_loss *= self.beta_fgd/scale_x/scale_y
mask_loss *= self.gamma_fgd/scale_x/scale_y
rela_loss *= self.lambda_fgd/scale_x/scale_y
return S_attention_t, S_attention_s, C_attention_t, C_attention_s, fg_loss, bg_loss, mask_loss, rela_loss
def get_attention(self, preds, temp):
N, C, H, W = preds.shape
value = torch.abs(preds) # shape [16, 128, 80, 80]
fea_map = value.mean(axis=1, keepdim=True) # shape [16, 1, 80, 80]
S_attention = (H*W*F.softmax((fea_map/temp).view(N, -1), dim=1)).view(N, H, W) # shape [16, 80, 80]
channel_map = value.mean(axis=2, keepdim=False).mean(axis=2, keepdim=False) # shape [16, 128]
C_attention = C * F.softmax(channel_map/temp, dim=1) # shape [16, 128]
return S_attention, C_attention
def get_fea_loss(self, preds_S, preds_T, Mask_fg, Mask_bg, C_s, C_t, S_s, S_t): # feature loss
loss_mse = nn.MSELoss(reduction='sum')
Mask_fg = Mask_fg.unsqueeze(dim=1)
Mask_bg = Mask_bg.unsqueeze(dim=1)
C_t = C_t.unsqueeze(dim=-1)
C_t = C_t.unsqueeze(dim=-1)
S_t = S_t.unsqueeze(dim=1)
C_s = C_s.unsqueeze(dim=-1)
C_s = C_s.unsqueeze(dim=-1)
S_s = S_s.unsqueeze(dim=1)
fea_t = torch.mul(preds_T, torch.sqrt(S_t))
fea_t = torch.mul(fea_t, torch.sqrt(C_t))
fg_fea_t = torch.mul(fea_t, torch.sqrt(Mask_fg))
bg_fea_t = torch.mul(fea_t, torch.sqrt(Mask_bg))
fea_s = torch.mul(preds_S, torch.sqrt(S_s))
fea_s = torch.mul(fea_s, torch.sqrt(C_s))
fg_fea_s = torch.mul(fea_s, torch.sqrt(Mask_fg))
bg_fea_s = torch.mul(fea_s, torch.sqrt(Mask_bg))
fg_loss = loss_mse(fg_fea_s / len(Mask_fg), fg_fea_t / len(Mask_fg))
bg_loss = loss_mse(bg_fea_s / len(Mask_bg), bg_fea_t / len(Mask_bg))
return fg_loss, bg_loss
def get_mask_loss(self, C_s, C_t, S_s, S_t): # Attention mask loss
mask_loss = torch.sum(torch.abs((C_s - C_t))) / len(C_s) + torch.sum(torch.abs((S_s - S_t))) / len(S_s)
return mask_loss
def spatial_pool(self, x, in_type):
batch, channel, width, height = x.size()
input_x = x
input_x = input_x.view(batch, channel, height * width)
input_x = input_x.unsqueeze(1)
if in_type == 0:
context_mask = self.conv_mask_s(x)
else:
context_mask = self.conv_mask_t(x)
context_mask = context_mask.view(batch, 1, height * width)
context_mask = F.softmax(context_mask, dim=2)
context_mask = context_mask.unsqueeze(-1)
context = torch.matmul(input_x, context_mask)
context = context.view(batch, channel, 1, 1)
return context
def get_rela_loss(self, preds_S, preds_T):
loss_mse = nn.MSELoss(reduction='sum')
context_s = self.spatial_pool(preds_S, 0)
context_t = self.spatial_pool(preds_T, 1)
out_s = preds_S
out_t = preds_T
channel_add_s = self.channel_add_conv_s(context_s)
out_s = out_s + channel_add_s
channel_add_t = self.channel_add_conv_t(context_t)
out_t = out_t + channel_add_t
rela_loss = loss_mse(out_s / (len(out_s)), out_t / (len(out_s)))
# rela_loss = loss_mse(out_s, out_t)
return rela_loss
def last_zero_init(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Sequential):
constant_init(m[-1].weight, val=0)
else:
constant_init(m.weight, val=0)
def reset_parameters(self):
kaiming_init(self.conv_mask_s.weight, mode='fan_in', nonlinearity='relu')
kaiming_init(self.conv_mask_t.weight, mode='fan_in', nonlinearity='relu')
self.conv_mask_s.inited = True
self.conv_mask_t.inited = True
self.last_zero_init(self.channel_add_conv_s)
self.last_zero_init(self.channel_add_conv_t)
def xywh2xyxy(self, x):
"""
Convert bounding box coordinates from (x, y, width, height) format to (x1, y1, x2, y2) format where (x1, y1) is the
top-left corner and (x2, y2) is the bottom-right corner.
Args:
x (np.ndarray | torch.Tensor): The input bounding box coordinates in (x, y, width, height) format.
Returns:
y (np.ndarray | torch.Tensor): The bounding box coordinates in (x1, y1, x2, y2) format.
"""
assert x.shape[-1] == 4, f"input shape last dimension expected 4 but input shape is {x.shape}"
y = torch.empty_like(x) if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.empty_like(x) # faster than clone/copy
dw = x[..., 2] / 2 # half-width
dh = x[..., 3] / 2 # half-height
y[..., 0] = x[..., 0] - dw # top left x
y[..., 1] = x[..., 1] - dh # top left y
y[..., 2] = x[..., 0] + dw # bottom right x
y[..., 3] = x[..., 1] + dh # bottom right y
return y接下来,为每个颈部层初始化特征损失。为每个层生成损失的原因是计算每个层的注意力图并计算损失。
self.kd_loss_15_fn = FGDLoss(student_channels=self.distill_cfg["distiller"]["distill_cfg"][0]["neck_15"]["student_channels"],
teacher_channels=self.distill_cfg["distiller"]["distill_cfg"][0]["neck_15"]["teacher_channels"],
name=self.distill_cfg["distiller"]["distill_cfg"][0]["neck_15"]["name"],
temp = self.distill_cfg["temp"],
alpha_fgd = self.distill_cfg["alpha_fgd"],
beta_fgd = self.distill_cfg["beta_fgd"],
gamma_fgd = self.distill_cfg["gamma_fgd"],
lambda_fgd = self.distill_cfg["lambda_fgd"],
scale_y = self.distill_cfg["scale_y"],
scale_x = self.distill_cfg["scale_x"],
)
self.kd_loss_18_fn = FGDLoss(student_channels=self.distill_cfg["distiller"]["distill_cfg"][1]["neck_18"]["student_channels"],
teacher_channels=self.distill_cfg["distiller"]["distill_cfg"][1]["neck_18"]["teacher_channels"],
name=self.distill_cfg["distiller"]["distill_cfg"][1]["neck_18"]["name"],
temp = self.distill_cfg["temp"],
alpha_fgd = self.distill_cfg["alpha_fgd"],
beta_fgd = self.distill_cfg["beta_fgd"],
gamma_fgd = self.distill_cfg["gamma_fgd"],
lambda_fgd = self.distill_cfg["lambda_fgd"],
scale_y = self.distill_cfg["scale_y"],
scale_x = self.distill_cfg["scale_x"],
)
self.kd_loss_21_fn = FGDLoss(student_channels=self.distill_cfg["distiller"]["distill_cfg"][2]["neck_21"]["student_channels"],
teacher_channels=self.distill_cfg["distiller"]["distill_cfg"][2]["neck_21"]["teacher_channels"],
name=self.distill_cfg["distiller"]["distill_cfg"][2]["neck_21"]["name"],
temp = self.distill_cfg["temp"],
alpha_fgd = self.distill_cfg["alpha_fgd"],
beta_fgd = self.distill_cfg["beta_fgd"],
gamma_fgd = self.distill_cfg["gamma_fgd"],
lambda_fgd = self.distill_cfg["lambda_fgd"],
scale_y = self.distill_cfg["scale_y"],
scale_x = self.distill_cfg["scale_x"],
)然后,通过将学生的特征、教师的特征和输入数据输入到每个损失中,计算教师和学生的时空/通道注意力图、前景、背景损失、掩码损失和相对损失。
self.kd_feat_15_spatial_t, self.kd_feat_15_spatial_s, self.kd_feat_15_channel_t, self.kd_feat_15_channel_s,self.kd_loss_15_fg, self.kd_loss_15_bg, self.kd_loss_15_ma, self.kd_loss_15_re = self.kd_loss_15_fn(student_15_feature, teacher_15_feature, batch)
self.kd_feat_18_spatial_t, self.kd_feat_18_spatial_s, self.kd_feat_18_channel_t, self.kd_feat_18_channel_s,self.kd_loss_18_fg, self.kd_loss_18_bg, self.kd_loss_18_ma, self.kd_loss_18_re = self.kd_loss_18_fn(student_18_feature, teacher_18_feature, batch)
self.kd_feat_21_spatial_t, self.kd_feat_21_spatial_s, self.kd_feat_21_channel_t, self.kd_feat_21_channel_s,self.kd_loss_21_fg, self.kd_loss_21_bg, self.kd_loss_21_ma, self.kd_loss_21_re = self.kd_loss_21_fn(student_21_feature, teacher_21_feature, batch)然后,计算最终损失并进行反向处理。
self.kd_loss_fg = self.kd_loss_15_fg + self.kd_loss_18_fg + self.kd_loss_21_fg
self.kd_loss_bg = self.kd_loss_15_bg + self.kd_loss_18_bg + self.kd_loss_21_bg
self.kd_loss_ma = self.kd_loss_15_ma + self.kd_loss_18_ma + self.kd_loss_21_ma
self.kd_loss_re = self.kd_loss_15_re + self.kd_loss_18_re + self.kd_loss_21_re
self.loss_items_kd = [self.kd_loss_fg, self.kd_loss_bg, self.kd_loss_ma, self.kd_loss_re]
self.tloss_kd = ([(x*i + y) / (i + 1) for x, y in zip(self.tloss_kd, self.loss_items_kd)] if self.tloss_kd is not None else self.loss_items_kd)
self.loss_kd = sum(self.loss_items_kd) * len(batch["im_file"])
self.loss_kd_total = self.loss + self.loss_kdself.scaler.scale(self.loss_kd_total).backward()查看结果
特征损失的目标是增加学生和教师的时空/通道注意力图之间的相似性。从图像中也可以确认,随着学习epoch的增加,相似性增加,损失也减少。
COCO 数据集,教师 (YoloV9-e),学生 (YoloV9-c)
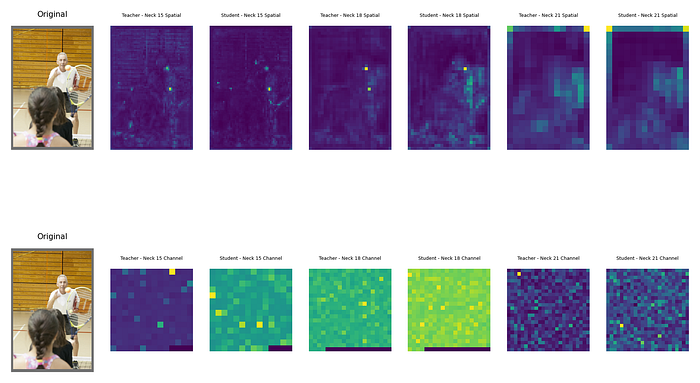
(第 2 个epoch)每个颈部层的空间注意力图(上)/每个颈部层的通道注意力图(下)
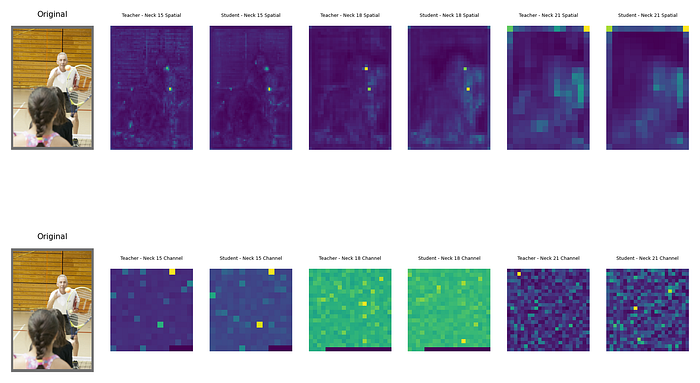
(第 52 个epoch)每个颈部层的空间注意力图(上)/每个颈部层的通道注意力图(下)
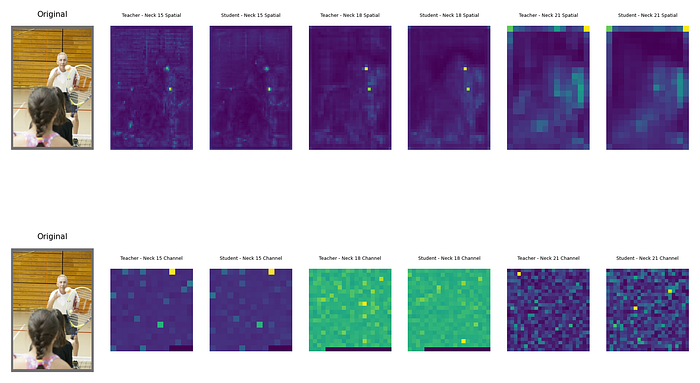
(第 116 个epoch)每个颈部层的空间注意力图(上)/每个颈部层的通道注意力图(下)
确认随着epoch数的增加,不仅空间注意力图的相似性增加,通道注意力图的相似性也增加。然而,mAP50:95 的性能并没有超过现有的 YoloV9-c 模型。
结论
尽管学生和教师的颈部之间的特征相似性增加了(保真度高),但这个结果并没有提高学生的泛化性能。
· END ·
🌟 想要变身计算机视觉小能手?快来「小白玩转Python」公众号!
回复“Python视觉实战项目”,解锁31个超有趣的视觉项目大礼包!🎁

本文仅供学习交流使用,如有侵权请联系作者删除























 2082
2082

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








