矩阵相乘(百度图片)
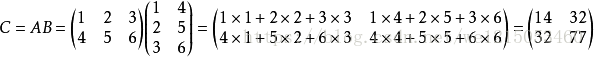
斐波那契数列的定义如下:
F(0) = 0
F(1) = 1
F(n) = F(n - 1) + F(n - 2) (n >= 2)
(1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233, 377, ...)
给出n,求F(n),由于结果很大,输出F(n) % 1000000009的结果即可。
Input输入1个数n(1 <= n <= 10^18)。Output输出F(n) % 1000000009的结果。Sample Input11Sample Output
89
#include<stdio.h>
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef vector<ll>vec;
typedef vector<vec>mat;
const int M = 1000000009;
mat mul(mat &a,mat &b)
{
mat c(a.size(),vec(b[0].size()));
for(int i=0;i<a.size();i++)
for(int k=0;k<b.size();k++)
for(int j=0;j<b[0].size();j++)
{
c[i][j]+=(a[i][k]%M)*(b[k][j]%M);
c[i][j]%=M;
}
return c;
}
mat pow(mat a,ll n)
{
mat b(a.size(),vec(a.size()));
for(int i=0;i<a.size();i++)
b[i][i]=1;
while(n > 0)
{
if(n&1) b=mul(b,a);
a=mul(a,a);
n>>=1;
}
return b;
}
int main()
{
ll n;
while(~scanf("%lld",&n))
{
mat a(2,vec(2));
a[0][0]=1;
a[0][1]=1;
a[1][0]=1;
a[1][1]=0;
a=pow(a,n);
printf("%lld\n",a[1][0]);
}
return 0;
}第二种:因为不能返回数组型,所以用结构体返回
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define N 1000000009
#define ll long long
struct node
{
ll a[2][2]
};
node mul(node a,node b)
{
node c={0}; //一定要清零,否则为1
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
for(int k=0;k<2;k++)
for(int j=0;j<2;j++)
{
c.a[i][j]+=(a.a[i][k]%N)*(b.a[k][j]%N);
c.a[i][j]%=N;
}
return c;
}
node pow(node t,ll n)
{
node b={0}; //一定要清零
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
b.a[i][i]=1;
while(n>0)
{
if(n&1) b=mul(b,t);
t=mul(t,t);
n>>=1;
}
return b;
}
int main()
{
ll n;
while(~scanf("%lld",&n))
{
node t;
t.a[0][0]=1;
t.a[0][1]=1;
t.a[1][0]=1;
t.a[1][1]=0;
t=pow(t,n);
printf("%lld\n",t.a[1][0]);
}
return 0;
}




 本文介绍了一种高效计算斐波那契数列第n项的方法,利用矩阵快速幂运算,解决了传统递归算法的时间复杂度过高的问题。通过两种实现方式展示了如何将斐波那契数列计算转化为矩阵运算,适用于处理大规模数值。
本文介绍了一种高效计算斐波那契数列第n项的方法,利用矩阵快速幂运算,解决了传统递归算法的时间复杂度过高的问题。通过两种实现方式展示了如何将斐波那契数列计算转化为矩阵运算,适用于处理大规模数值。
















 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








