表面着色器光照示例
因为延时光照(Deferred lighting)不能与一些自定义 per-material 光照模式(lighting model)很好的运行,在下面大部分例子中我们只在着色器的正向渲染(Forward Rendering)中编译。
Diffuse 漫反射
Diffuse = 直射光颜色 * max(0,cos夹角(光和法线的夹角) ) Tip:cosθ = 光方向· 法线方向 我们从内置的Lambert光照模式(lighting model)开始:
Shader
"Example/Diffuse Texture"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex
(
"Texture"
,
2D
)
=
"white"
{
}
}
SubShader
{
Tags
{
"RenderType"
=
"Opaque"
}
CGPROGRAM
#
pragma
surface surf Lambert
struct
Input
{
float2
uv_MainTex
;
}
;
sampler2D
_MainTex
;
void
surf
(
Input
IN
,
inout
SurfaceOutput
o
)
{
o
.
Albedo
=
tex2D
(
_MainTex
,
IN
.
uv_MainTex
)
.
rgb
;
}
ENDCG
}
Fallback
"Diffuse"
}
下面是效果一个有纹理(texture)和一个没有真实的纹理(texture)。(在场景中有一个方向光):
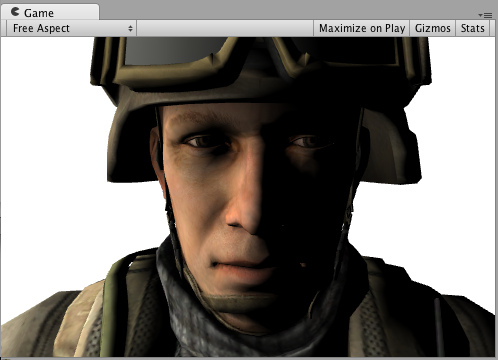
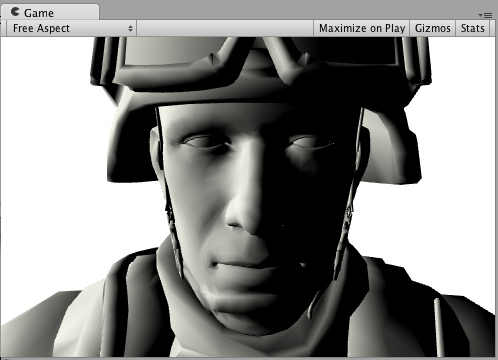
现在,让我们来做一个完全一样的。但,是我们自己编写的光照模式(lighting model)而不是使用内置的Lambert。
表面着色器光照模式(Surface Shader Lighting Models
)仅仅是需要我们编写的一些函数。下面是一个简单的Lambert。注意:"着色器部分"自身并没有改变(即下面的灰色部分)。
Shader
"Example/Diffuse Texture"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex
(
"Texture"
,
2D
)
=
"white"
{
}
}
SubShader
{
Tags
{
"RenderType"
=
"Opaque"
}
CGPROGRAM
#
pragma
surface surf SimpleLambert
half4
LightingSimpleLambert
(
SurfaceOutput
s
,
half3
lightDir
,
half
atten
)
{
fixed
diff
=
max
(
0
,
dot
(
s
.
Normal
,
lightDir
)
)
;
fixed4
c
;
c
.
rgb
=
s
.
Albedo
*
_LightColor0
.
rgb
*
(
diff
*
atten
*
2
)
;
c
.
a
=
s
.
Alpha
;
return
c
;
}
struct
Input
{
float2
uv_MainTex
;
}
;
sampler2D
_MainTex
;
void
surf
(
Input
IN
,
inout
SurfaceOutput
o
)
{
o
.
Albedo
=
tex2D
(
_MainTex
,
IN
.
uv_MainTex
)
.
rgb
;
}
ENDCG
}
Fallback
"Diffuse"
}
就这样我们这个点单的漫反射光照模式(Diffuse lighting model)是一个名叫LightingSimpleLambert的函数。它计算的是表面法线(surface normal)与灯光方向(light direction)的点积。然后应用于光线衰减和颜色。
Diffuse Wrap 漫反射遮蔽(半兰伯特)
下面是遮蔽的漫反射-漫反射光照的一种改进。照明"环绕(wraps around)"在物体的边缘。它对于假冒子表面(subsurface)散射效果(scattering effect)非常有用。同样的"着色器部分"自身并没有改变(即下面的灰色部分)。我们仅仅用了不同的光照函数(黑体字部分)。
Shader
"Example/Diffuse Wrapped"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex
(
"Texture"
,
2D
)
=
"white"
{
}
}
SubShader
{
Tags
{
"RenderType"
=
"Opaque"
}
CGPROGRAM
#
pragma
surface surf WrapLambert
half4
LightingWrapLambert
(
SurfaceOutput
s
,
half3
lightDir
,
half
atten
)
{
half
NdotL
=
dot
(
s
.
Normal
,
lightDir
)
;
half
diff
=
NdotL
*
0.5
+
0.5
;
half4
c
;
c
.
rgb
=
s
.
Albedo
*
_LightColor0
.
rgb
*
(
diff
*
atten
*
2
)
;
c
.
a
=
s
.
Alpha
;
return
c
;
}
struct
Input
{
float2
uv_MainTex
;
}
;
sampler2D
_MainTex
;
void
surf
(
Input
IN
,
inout
SurfaceOutput
o
)
{
o
.
Albedo
=
tex2D
(
_MainTex
,
IN
.
uv_MainTex
)
.
rgb
;
}
ENDCG
}
Fallback
"Diffuse"
}
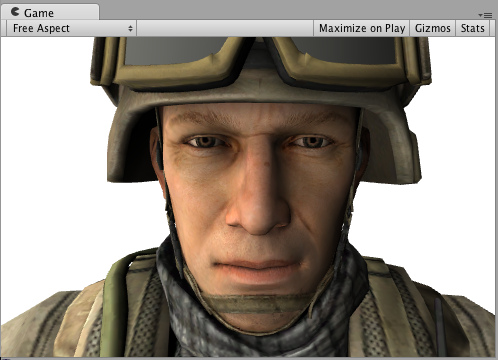
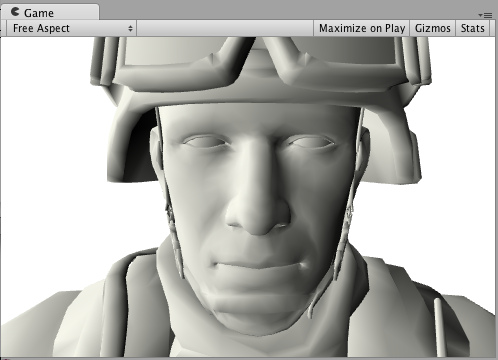
Toon Ramp 卡通渐变
下面是一个"渐变(Ramp)"光照模式。他使用一个纹理(texture)定义渐变怎样在表面做出反应,反应角度通过光照方向和法线求得。导入卡通光照(Toon lighting)可以实现多种效果。
Shader
"Example/Toon Ramp"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex
(
"Texture"
,
2D
)
=
"white"
{
}
_Ramp
(
"Shading Ramp"
,
2D
)
=
"gray"
{
}
}
SubShader
{
Tags
{
"RenderType"
=
"Opaque"
}
CGPROGRAM
#
pragma
surface surf Ramp
sampler2D
_Ramp
;
half4
LightingRamp
(
SurfaceOutput
s
,
half3
lightDir
,
half
atten
)
{
half
NdotL
=
dot
(
s
.
Normal
,
lightDir
)
;
half
diff
=
NdotL
*
0.5
+
0.5
;
half3
ramp
=
tex2D
(
_Ramp
,
float2
(
diff
,
diff
)
)
.
rgb
;
half4
c
;
c
.
rgb
=
s
.
Albedo
*
_LightColor0
.
rgb
*
ramp
*
(
atten
*
2
)
;
c
.
a
=
s
.
Alpha
;
return
c
;
}
struct
Input
{
float2
uv_MainTex
;
}
;
sampler2D
_MainTex
;
void
surf
(
Input
IN
,
inout
SurfaceOutput
o
)
{
o
.
Albedo
=
tex2D
(
_MainTex
,
IN
.
uv_MainTex
)
.
rgb
;
}
ENDCG
}
Fallback
"Diffuse"
}
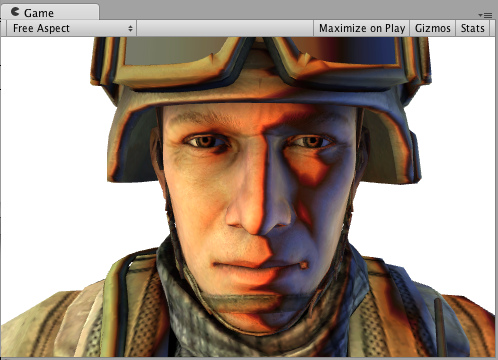
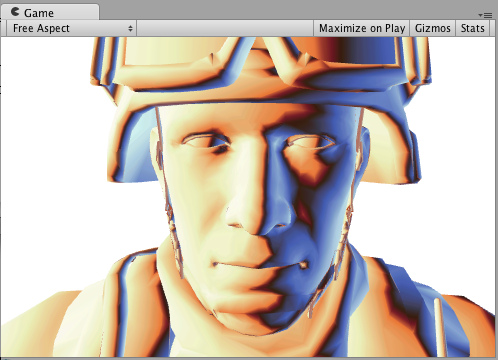

Simple Specular 简单的(phong)高光
Specular = 直射光*pow(max(cosθ,0),高光的参数) 下面是一个简单的高光光照模式(specular lighting model)。它是内置的Phong,实际上做起来非常简单。放在这里仅仅是为了说明它是如何工作的。
Shader
"Example/Simple Specular"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex
(
"Texture"
,
2D
)
=
"white"
{
}
_Spec
(
"SpecPower"
,
float
)
=
1
}
SubShader
{
Tags
{
"RenderType"
=
"Opaque"
}
CGPROGRAM
#
pragma
surface surf SimpleSpecular
half4
LightingSimpleSpecular
(
SurfaceOutput
s
,
half3
lightDir
,
half3
viewDir
,
half
atten
)
{
half
diff
=
max
(
0
,
dot
(
s
.
Normal
,
lightDir
)
)
;
//phong模型
//1.光线的反射方向.点到摄像机
half3
reflectDir
=
normalize
(
reflect
(
-
lightDir
,
s
.
Normal
)
)
;
//2.高光底数
float
nh
=
max
(
0
,
dot
(
reflectDir
,
viewDir
)
)
;
//3.高光系数:根据高光低数和高光指数求得
float
spec
=
pow
(
nh
,
_Spec
)
;
half4
c
;
c
.
rgb
=
(
s
.
Albedo
*
_LightColor0
.
rgb
*
diff
+
_LightColor0
.
rgb
*
spec
)
*
(
atten
*
2
)
;
c
.
a
=
s
.
Alpha
;
return
c
;
}
struct
Input
{
float2
uv_MainTex
;
}
;
sampler2D
_MainTex
;
void
surf
(
Input
IN
,
inout
SurfaceOutput
o
)
{
o
.
Albedo
=
tex2D
(
_MainTex
,
IN
.
uv_MainTex
)
.
rgb
;
}
ENDCG
}
Fallback
"Diffuse"
}
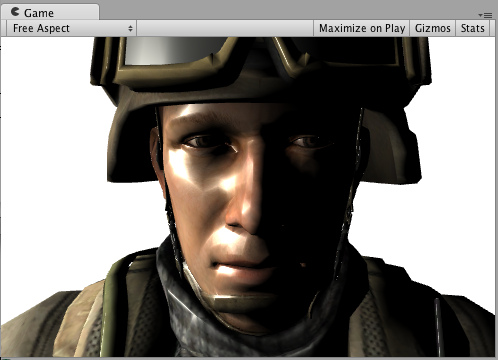
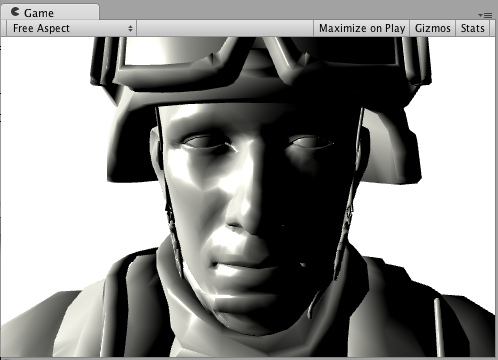
Simple Specular (BlinnPhong)高光
Specular = 直射光*pow(max(cosθ,0),高光的参数) Tips: θ:是反射光方向和视野方向的夹角 Tips: θ:是半角向量与法线向量的夹角 下面是一个简单的高光光照模式(specular lighting model)。它是内置的BlinnPhong,实际上做起来非常简单。放在这里仅仅是为了说明它是如何工作的。
Shader
"Example/Simple Specular"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex
(
"Texture"
,
2D
)
=
"white"
{
}
_Spec
(
"SpecPower"
,
float
)
=
1
}
SubShader
{
Tags
{
"RenderType"
=
"Opaque"
}
CGPROGRAM
#
pragma
surface surf
half4
LightingSimpleSpecular
(
SurfaceOutput
s
,
half3
lightDir
,
half3
viewDir
,
half
atten
)
{
half
diff
=
max
(
0
,
dot
(
s
.
Normal
,
lightDir
)
)
;
//Blinn-phong:半角向量 点x 发线向量
//1.半角向量:求(点到光源+点到摄像机)的单位向量,他们的中间平均值
half3
h
=
normalize
(
lightDir
+
viewDir
)
;
//2.高光底数【半角向量与法线向量的余弦值】
float
nh
=
max
(
0
,
dot
(
s
.
Normal
,
h
)
)
;
//3.高光系数:根据高光低数和高光指数求得
float
spec
=
pow
(
nh
,
_Spec
)
;
half4
c
;
c
.
rgb
=
(
s
.
Albedo
*
_LightColor0
.
rgb
*
diff
+
_LightColor0
.
rgb
*
spec
)
*
(
atten
*
2
)
;
c
.
a
=
s
.
Alpha
;
return
c
;
}
struct
Input
{
float2
uv_MainTex
;
}
;
sampler2D
_MainTex
;
void
surf
(
Input
IN
,
inout
SurfaceOutput
o
)
{
o
.
Albedo
=
tex2D
(
_MainTex
,
IN
.
uv_MainTex
)
.
rgb
;
}
ENDCG
}
Fallback
"Diffuse"
}





















 764
764

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








