注:机翻,未校。
Exploring the Network Routing Process
This lesson explores the packet routing process from the perspective of a router. This includes a mapping between layer 2 and layer 3 addresses , as well as the ability of the router to calculate the best path toward the destination. In verifying the configuration resulting in connectivity, we will review several commands like show ip arp, ping, and trace.
本文从路由器的角度探讨数据包路由过程。这包括 第 2 层和第 3 层地址之间的映射,以及路由器计算通往目的地的最佳路径的能力。在验证导致连接的配置时,将查看几个命令,如 show ip arp、ping 和 trace 。
Layer 2 Addressing. MAC Addresses
第 2 层寻址- MAC 地址
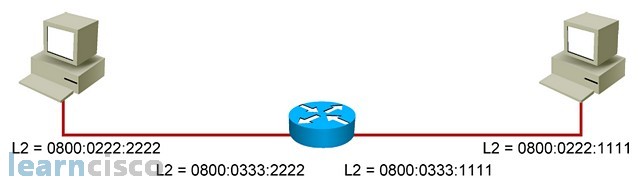
In exploring the packet delivery process, when having the router in the middle, we’re going to use layer 2 and layer 3 addresses. Our example’s going to be based on those MAC addresses for both the endpoints and the router. Remember at some point we’re going to resolve the MAC addresses of the router to send packets from one machine in one segment to another machine in another segment.
在探索数据包传输过程时,当路由器位于中间时,将使用第 2 层和第 3 层地址。示例将基于终端节点和路由器的 MAC 地址。请记住,在某些时候,将解析路由器的 MAC 地址,以将数据包从一个分段中的一台计算机发送到另一个分段中的另一台计算机。
Layer 3 Addressing. IP Addresses
第 3 层寻址 - IP 地址
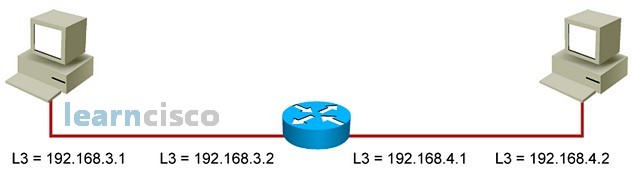
This is a layer 3 view with IP addresses for both the hosts and the router itself. Remember, your design will probably come from the fact that you want to split the two segments for performance or security reasons or some other reasons and insert a router in the middle so that you can do the forwarding of packets to the right destinations. We are going to assume only the routing function in these diagrams; however, the router could be performing security functions, packet filtering functions, firewalling, and implementing quality of service mechanisms. All of these could change the way the router forwards packets, but here we are only considering routing.
这是一个第 3 层视图,其中包含主机和路由器本身的 IP 地址。请记住,设计可能来自这样一个事实,即希望出于性能或安全原因或其他一些原因将两个段分开,并在中间插入路由器,以便可以将数据包转发到正确的目的地。将只假设这些图中的 routing 函数;但是,路由器可以执行安全功能、数据包过滤功能、防火墙和实施服务质量机制。所有这些都可以改变路由器转发数据包的方式,但这里只考虑路由。
IP Routing. Packet Delivery Process
IP 路由 - 数据包投递流程
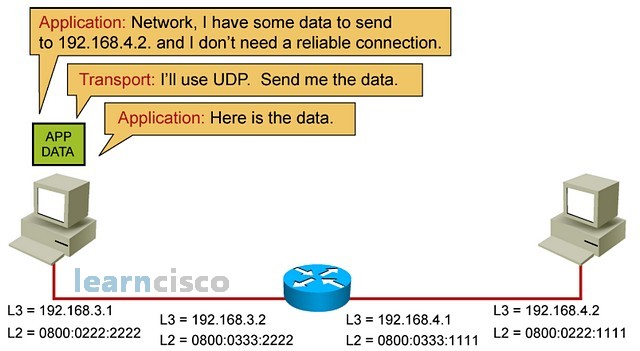
The first step is for applications to resolve DNS names if they use DNS names, translate them into an IP address and select the transport protocol to use. In this example, we are using UDP. As the information trickles down the layered model and it gets to the network layer, then the next question becomes, where is the destination, is it local or is it remote?
第一步是让应用程序解析 DNS 名称(如果它们使用 DNS 名称),将它们转换为 IP 地址并选择要使用的传输协议。在此示例中,使用的是 UDP。随着信息沿着分层模型向下渗透并到达网络层,那么下一个问题就变成了,目的地在哪里,是本地的还是远程的?
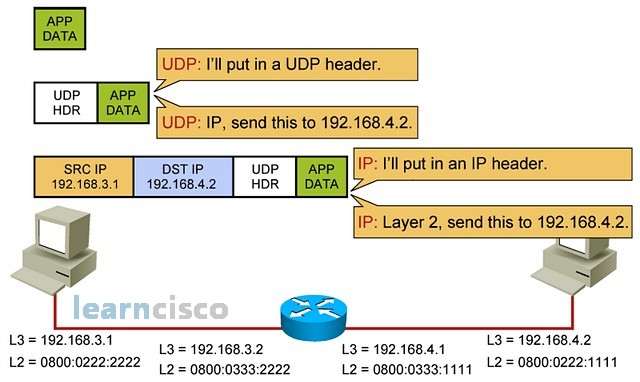
Each layer will add its own overhead in the form of headers until it reaches again layer 3, which will put it in IP header and then request the layer 2 to actually send a packet.
每一层都将以报头的形式添加自己的开销,直到它再次到达第 3 层,这将将其放入 IP 报头中,然后请求第 2 层实际发送数据包。
Layer 2 replies saying “I do not have information on that IP, I do not have the MAC address and so I am going to try to resolve via an ARP request.” The packet will be parked and remain in buffers until the ARP request is completed.
第 2 层回复说:“我没有关于该 IP 的信息,我没有 MAC 地址,因此我将尝试通过 ARP 请求进行解析。数据包将被停放并保留在缓冲区中,直到 ARP 请求完成。
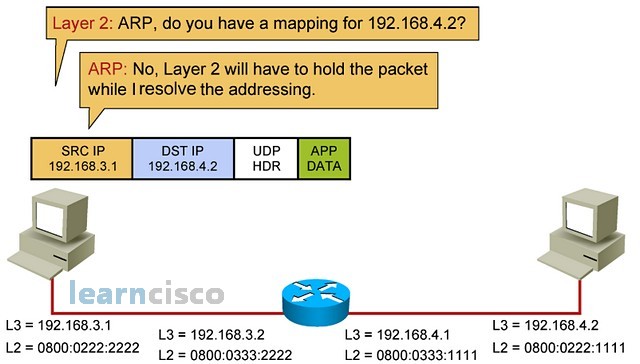
At this point of the process, right between layer 3 and 2, the device will say, “Well, according to this IP address and this mask, we have /24 here. The destination is in a different network. I am in network 192.168.3 and the destination is on network 192.168.4.”
在该过程的这一点上,就在第 3 层和第 2 层之间,设备会说,“嗯,根据这个 IP 地址和这个掩码,这里有 /24。目标位于不同的网络中。我在网络 192.168.3 中,目的地在网络 192.168.4 上。

This is again because of the subnet mask, which is saying that the network identifier is located in the first 3 bytes of the IP address. So the ARP process says, “Well, I do not need to resolve them for the MAC address of the intended destination. I am not a router and I do not know how to send this, but my default gateway will know, so I am going to try to resolve for the MAC address of the default gateway, which is configured in the IP protocol configuration of the device.”
这又是因为子网掩码,即网络标识符位于 IP 地址的前 3 个字节中。因此,ARP 进程说,“嗯,我不需要为预期目的地的 MAC 地址解析它们。我不是路由器,也不知道如何发送这个,但我的默认网关会知道,所以我将尝试解析默认网关的 MAC 地址,该地址在设备的 IP 协议配置中配置。
This is probably one of the first and most common sources of errors and mistakes and in troubleshooting this, we should make sure that the right default gateway IP address is configured. If I do not know where to send it or which router should process this, then the packet will not get there.
这可能是错误和失误的首要也是最常见的来源之一,在对此进行故障排除时,应该确保配置了正确的默认网关 IP 地址。如果我不知道将数据包发送到何处或哪个路由器应该处理此数据包,则数据包将无法到达那里。
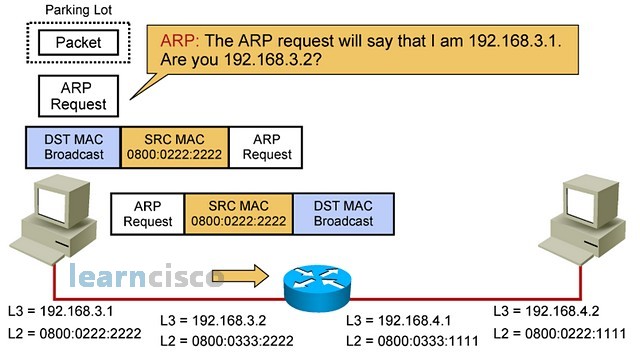
Here is the ARP request. It is a destination broadcast at layer 2 and the request itself contains the IP address to resolve, which in this case is 192 168 32, the IP address of the router. It is probably interesting to mention the existence of a functionality called proxy ARP, in which routers may be configured to reply to any ARP request, even though the request may not be directed to the IP address of that router. This is to treat them as gateways of last resort and be able to reply to calls for a default gateway that may be coming from misconfigured machines. This will have its own set of security implications and issues and so it is probably disregarded by certain security policies.
下面是 ARP 请求。它是第 2 层的目标广播,请求本身包含要解析的 IP 地址,在本例中为 192 168 32,即路由器的 IP 地址。值得一提的是,存在一种称为代理 ARP 的功能,其中路由器可以配置为响应任何 ARP 请求,即使该请求可能不会定向到该路由器的 IP 地址。这是为了将它们视为最后的网关,并能够响应可能来自配置错误的计算机的默认网关的呼叫。这将有其自身的一组安全影响和问题,因此某些安全策略可能会忽略它。
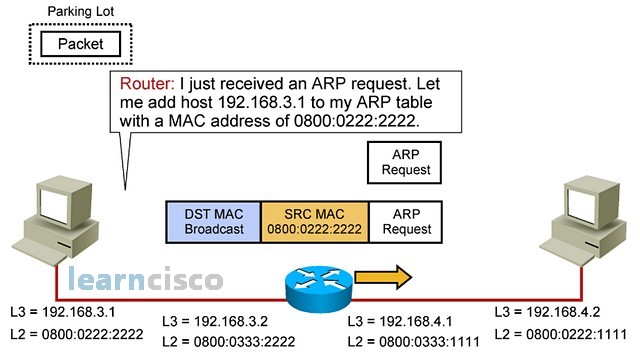
In any case, the router will receive the request and start the packet forwarding process. It will first save the MAC address and IP address of the sending machine in its own ARP table. The router is an IP device just like any other and so it will comply with all the rules of IP.
无论如何,路由器都会收到请求并启动数据包转发过程。它将首先将发送机器的 MAC 地址和 IP 地址保存在自己的 ARP 表中。路由器和其他任何设备一样,都是 IP 设备,因此它将遵守 IP 的所有规则。
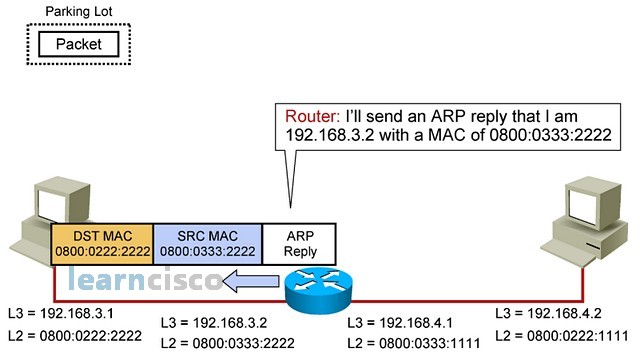
At this point, the router will send an ARP reply saying, “Hey, this is me and here is my MAC address; start forwarding packets to me.”
此时,路由器会发送一个 ARP 回复说:“嘿,这是我,这是我的 MAC 地址;开始向我转发数据包。
Now the sending host has a mapping in its ARP table that links the gateway IP address to the gateway MAC address. It is ready to send packets to that gateway for them to be forwarded toward the destination.
现在,发送主机的 ARP 表中有一个映射,该映射将网关 IP 地址链接到网关 MAC 地址。它已准备好将数据包发送到该网关,以便将其转发到目的地。
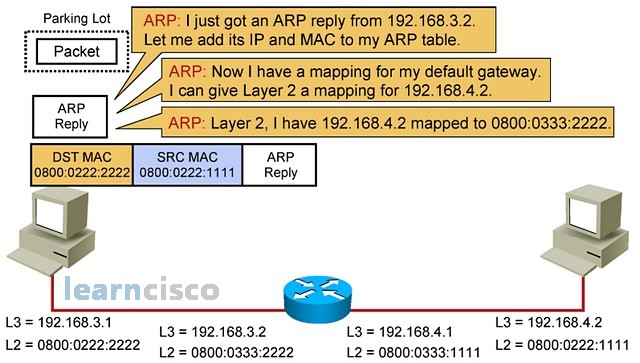
Remember, those entries will eventually time out and so the ARP process may be repeated throughout the conversation depending on idle times and absolute times.
请记住,这些条目最终会超时,因此 ARP 流程可能会在整个对话中重复,具体取决于空闲时间和绝对时间。
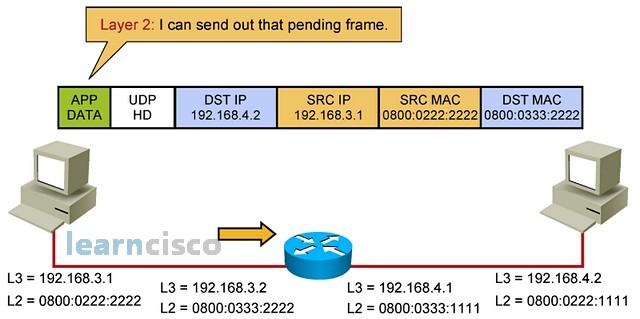
The packet that was on hold is released and sent using the intended destination’s IP address, the source IP address of the sender, the source MAC of the sender, and the destination MAC is the router’s MAC address.
使用预期目标的 IP 地址、发送方的源 IP 地址、发送方的源 MAC 释放和发送保留的数据包,目标 MAC 是路由器的 MAC 地址。
Since we are talking about routing function only in the router, then we understand how this device will get up to a certain layer with only the routing function. The router works at layer 3 only, and so it will see the frame coming in. It will digest it and process it, because it is destined to itself in terms of MAC address at layer 2. It will decapsulate and send to layer 3 and it is at layer 3, where the routing and forwarding function takes place. That is why even though the destination IP address is not that of the router, the router will say, “Well I am a router, so I want to forward this according to my routing table.”
由于只在谈论路由器中的路由功能,那么了解该设备如何仅通过路由功能到达某个层。路由器仅在第 3 层工作,因此它会看到传入的帧。它将消化并处理它,因为它在第 2 层的 MAC 地址方面注定是属于自己的。它将解封装并发送到第 3 层,在第 3 层,路由和转发功能发生在这里。这就是为什么即使目标 IP 地址不是路由器的 IP 地址,路由器也会说:“嗯,我是一个路由器,所以我想根据我的路由表转发它。

In browsing the routing table, the router will realize that the destination IP is an entry in that table. Look at 192.168.4.0 with the appropriate mask is a directly connected segment; it is actually located on Fast Ethernet 0/1. The decision is then to send directly to the layer 2 process and have layer 2 resolve the MAC address of the destination. If this was not a directly connected segment, then the entry in the routing table would point to the next-hop in the form of an IP address of another router in the path. At that point, the router would request forwarding to that intermediate device and so the ARP resolution would go on against that device to find its own MAC address. Now the case here, this is a simple scenario with two connected networks.
在浏览路由表时,路由器将意识到目标 IP 是该表中的一个条目。查看具有适当掩码的 192.168.4.0 是一个直接连接的段;它实际上位于快速以太网 0/1 上。然后,决定直接发送到第 2 层进程,并让第 2 层解析目标的 MAC 地址。如果这不是直接连接的网段,则路由表中的条目将以路径中另一个路由器的 IP 地址的形式指向下一跃点。此时,路由器将请求转发到该中间设备,因此 ARP 解析将继续针对该设备以查找自己的 MAC 地址。现在,这是一个具有两个连接网络的简单方案。
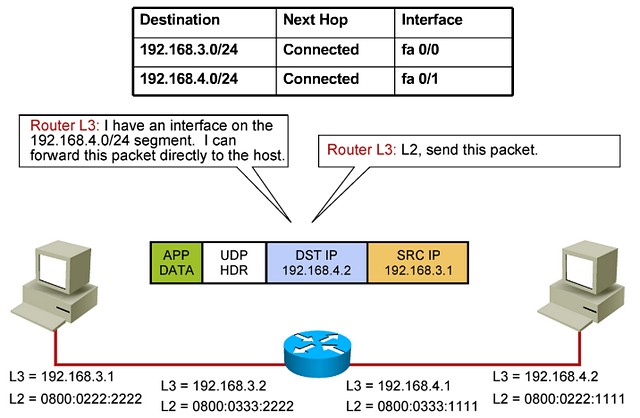
Because of that, the network layer of the router will assemble the IP header, including the IP address of the destination machine in the destination IPs field. Notice how the source address is still the original sending machine. The router is a broker that will simply forward a packet and aid and help in the communications process. At layer 2, it is an intermediate step, and that is why the MAC address is changed. But at layer 3, we are still talking about a packet being sent from this source to that destination.
因此,路由器的网络层将组装 IP 标头,包括目标 IP 字段中目标计算机的 IP 地址。请注意,源地址仍然是原始发送计算机。路由器是一个代理,它只会转发数据包并在通信过程中提供帮助。在第 2 层,这是一个中间步骤,这就是更改 MAC 地址的原因。但在第 3 层,仍在谈论从此源发送到该目标的数据包。
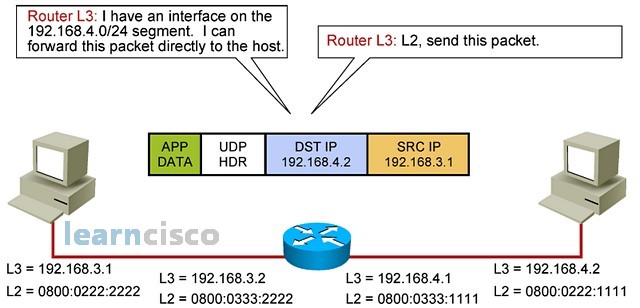
Layer 2 will say, “Hey, that is very good, but I still do not have the MAC address of the destination machine, so as a process of the router, I am going to try to resolve that address according to the IP address in the ARP request.” Remember, this is a broadcast at layer 2, and so all machines in that segment will see it, process it, and determine whether they need to reply or not.
第 2 层会说,“嘿,这很好,但我仍然没有目标机器的 MAC 地址,所以作为路由器的一个进程,我将尝试根据 ARP 请求中的 IP 地址解析该地址。请记住,这是第 2 层的广播,因此该 Segment 中的所有机器都会看到它,处理它,并确定它们是否需要回复。
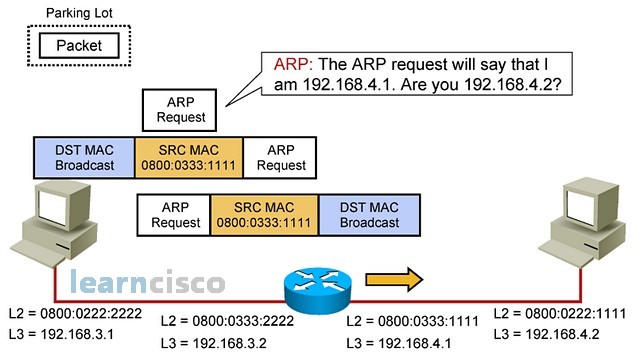
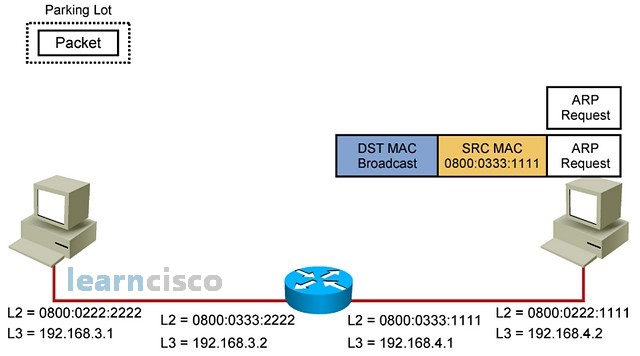
So the destination machine will receive and process the ARP request.
因此,目标计算机将接收并处理 ARP 请求。
Quickly notice that the IP address is a match and reply with its own MAC address.
快速注意到 IP 地址是匹配项,并使用自己的 MAC 地址进行回复。
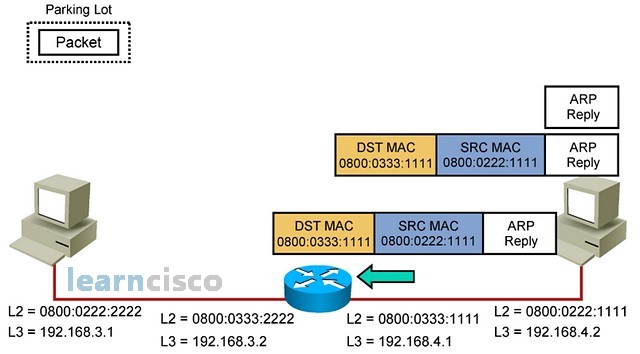
Before the ARP reply is sent, the destination machine will also save the mapping of the router’s IP to its MAC address in the ARP table. So it is interesting to see how machines will populate the ARP table, not only when they see an ARP reply, but also when they se an ARP request. This process is not very efficient, because it uses broadcasts, but it is pretty effective; all machines will quickly know who is around in terms of layer 3 to layer 2 mappings.
在发送 ARP 回复之前,目标计算机还将在 ARP 表中保存路由器 IP 到其 MAC 地址的映射。因此,看看机器如何填充 ARP 表是很有趣的,不仅当它们看到 ARP 回复时,而且当它们看到 ARP 请求时也是如此。这个过程不是很有效,因为它使用广播,但它非常有效;所有计算机都将很快知道第 3 层到第 2 层的映射。
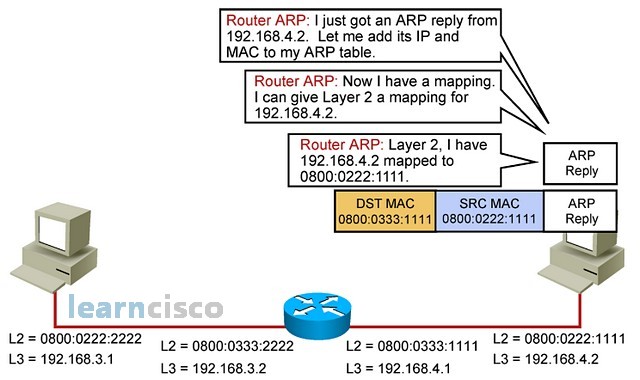
The router will see the ARP reply, know the MAC address of the destination machine, and be ready to assemble the full packet with source and destination IPs related to the original source and the intended destination and the source MAC being the routers MAC, and destination MAC being that machine’s MAC.
路由器将看到 ARP 应答,知道目标计算机的 MAC 地址,并准备好将完整的数据包与与原始源和预期目标相关的源 IP 和目标 IP 组合在一起,源 MAC 是路由器的 MAC,目标 MAC 是该计算机的 MAC。
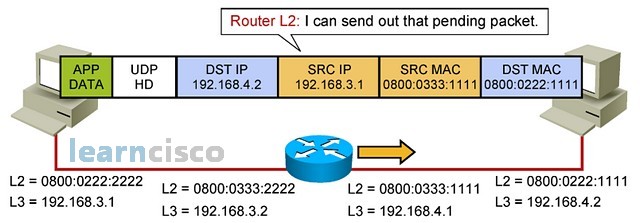
So IP communications in remote networks is nothing more than the incremental work of a series of brokers called routers that will sit in the middle of the path and forward the traffic according to certain intelligence. However, the overall process in terms of ARP, mappings, etc., is exactly the same.
因此,远程网络中的 IP 通信只不过是一系列称为路由器的代理的增量工作,这些代理将位于路径中间并根据某些情报转发流量。但是,ARP、映射等方面的整体过程是完全相同的。
If you want to verify the ARP table in routers, you can use the show IP ARP command. Here you see the IP addresses, the mapping MAC addresses, and the interfaces where those MAC addresses are located.
如果要验证路由器中的 ARP 表,可以使用 show IP ARP 命令。在这里,可以看到 IP 地址、映射 MAC 地址以及这些 MAC 地址所在的接口。
Router#sh ip arp Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface Internet 10.10.98.1 - 7081.0597.ca61 ARPA GigabitEthernet0/1.1098 Internet 10.10.98.2 18 649e.f32c.7571 ARPA GigabitEthernet0/1.1098 Internet 10.10.98.3 76 001d.709f.d1e0 ARPA GigabitEthernet0/1.1098 Internet 10.100.0.1 237 0000.0c07.ac82 ARPA GigabitEthernet0/2.2939 Internet 10.100.0.2 14 000d.6630.a01a ARPA GigabitEthernet0/2.2939 Internet 10.100.0.3 30 000d.6630.9c1a ARPA GigabitEthernet0/2.2939 Internet 10.100.0.4 - 7081.0597.ca62 ARPA GigabitEthernet0/2.2939 Internet 10.100.0.5 - 0000.0c07.ac64 ARPA GigabitEthernet0/2.2939 Internet 10.201.1.1 138 a0f3.e433.6485 ARPA GigabitEthernet0/2.3057 Internet 10.201.1.2 92 001c.5821.968d ARPA GigabitEthernet0/2.3057 Internet 10.201.1.3 243 001a.6dbe.406c ARPA GigabitEthernet0/2.3057 Internet 10.201.1.4 221 001c.f6d5.f64d ARPA GigabitEthernet0/2.3057 Internet 10.201.1.5 148 649e.f32c.7572 ARPA GigabitEthernet0/2.3057
You may see static increase under the type column and that means that with no regards to the ARP process that mapping will always take place toward that IP address. This is useful in some situations but very dangerous in some others.
可能会在 type 列下看到 static 增加,这意味着无论 ARP 进程如何,该映射将始终朝着该 IP 地址进行。这在某些情况下很有用,但在某些情况下非常危险。
In order the troubleshoot the process, a few layer 3 tools are available. The ping command initiates the ping request. Ping is in the diagnosis tool that allows you to test connectivity and in the process of doing that, find information about the conditions of that connectivity; it is layer 3 and so you will ping a host name or an IP address. This will use ICMP echo requests, ICMP being a layer 3 protocol, and it will wait until it sees an ICMP echo reply from the destination. It has certain settings in terms of how long it will wait, and how many probes or requests it will send, and with what size of the packet.
为了对该过程进行故障排除,可以使用一些第 3 层工具。ping 命令启动 ping 请求。Ping 位于诊断工具中,允许测试连接,并在执行此操作的过程中查找有关该连接条件的信息;它是第 3 层,因此将 ping 主机名或 IP 地址。这将使用 ICMP 回应请求,ICMP 是第 3 层协议,它将等待,直到看到来自目标的 ICMP 回应回复。它在等待多长时间、发送多少个探测或请求以及数据包的大小方面有一定的设置。
Trace will give you a visual as to the routers in the path toward the destination. It will list all these hops along with their IP address or DNS name and along with certain additional information like roundtrip times. As you see the output of trace, it is going to be nothing more than series of lines where each line is a router that is processing the packet and forwarding it to the destination. This can be used similar to ping, as a testing tool to determine whether a host is alive and kicking, but it can also be used to try to determine performance issues, path determination issues, failed links or failed hops, and roundtrip delay from source to destination. In Cisco routers, the trace function is enabled with the traceroute command.
Trace 将为提供有关通往目的地的路径中的路由器的可视化信息。它将列出所有这些跃点及其 IP 地址或 DNS 名称,以及某些其他信息,例如往返时间。如所见,trace 的输出只不过是一系列行,其中每行都是一个路由器,用于处理数据包并将其转发到目的地。这可以类似于 ping 使用,作为确定主机是否处于活动状态和启动状态的测试工具,但也可用于尝试确定性能问题、路径确定问题、失败的链路或失败的跃点,以及从源到目标的往返延迟。在 Cisco 路由器中,使用 traceroute 命令启用跟踪功能。
via:
-
How IP Routing Process Works - Step-by-Step Guide
https://www.learncisco.net/courses/icnd-1/lan-connections/packet-delivery-process-at-l3.html





















 3287
3287

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








