在Linux系统中,IOMMU是指Input/Output Memory Management Unit是一种硬件设备,用于管理输入输出设备的内存映射以及访问权限。IOMMU可以提高系统的安全性和性能,通过对DMA请求进行隔离和管理,防止恶意设备访问系统内存并提高内存使用效率。
在IOMMU的实现中,一个IOMMU设备通常会管理多个I/O设备,而这些IO设备可能需要共享同一块物理内存。为了有效管理这些IO设备,Linux内核使用IOMMU Group进行设备的分组和隔离。
IOMMU group是一组物理设备和其对应的DMA地址空间,一般来说,IOMMU group中的所有设备共享相同的DMA地址空间,并受到相同的IOMMU保护,如果一个设备与多个IOMMU GROUP关联,或者一个IOMMU group中包含多个设备,可能需要重新配置系统以确保正确的IOMMU保护,在IOMMU GROUP中,IO设备可以访问统一块物理内存。但不能访问其它IOMMU GROUP的内存,这样可以保护系统的安全性。
从硬件架构上看一下iommu,iommu就是上图所展示的DMA Remapping Unit,通常一台硬件服务器上会有多个DMA Remapping Unit,它下面可以对接pcie设备。简称为DMAR,通常DMA Remapping Unit集成在Root Complex当中,系统当中所有的外设的DMA操作理论上都要经过DMAR(例外就是在p2p通信的场景下且pcie switch 开了ATS功能那就不用再到DMAR转一圈了)。下图展示了一个pci设备在有iommu的场景下其进行一次read dma操作的相关流程。


IOMMU 工作模型

C->B:ioremap
B->A:physical address -> bus address(pci bar mmio).
X->Y: alloc pages.
Z->Y:dma_map_xxx
查看系统中的iommu group
使用如下脚本查看系统中的iommu group以及旗下设备列表
for iommu_group in $(find /sys/kernel/iommu_groups/ -maxdepth 1 -mindepth 1 -type d); do
echo "IOMMU Group $(basename "$iommu_group")";
for device in $(ls "$iommu_group"/devices/); do
echo -e "\t$(lspci -nns "$device")";
done;
done;
输出如下:


和启动启动时候的注册过程打印做对比,是匹配的:

可以看到,有些group里面只有1个设备,而有些group里面则有多个设备。
iommu goup id的分配


iommu_group_alloc callstack

GROUP ID分配逻辑
group id的最终分配来源于iommu_group_ida,通过如下的调用堆栈进行创建和初始化:
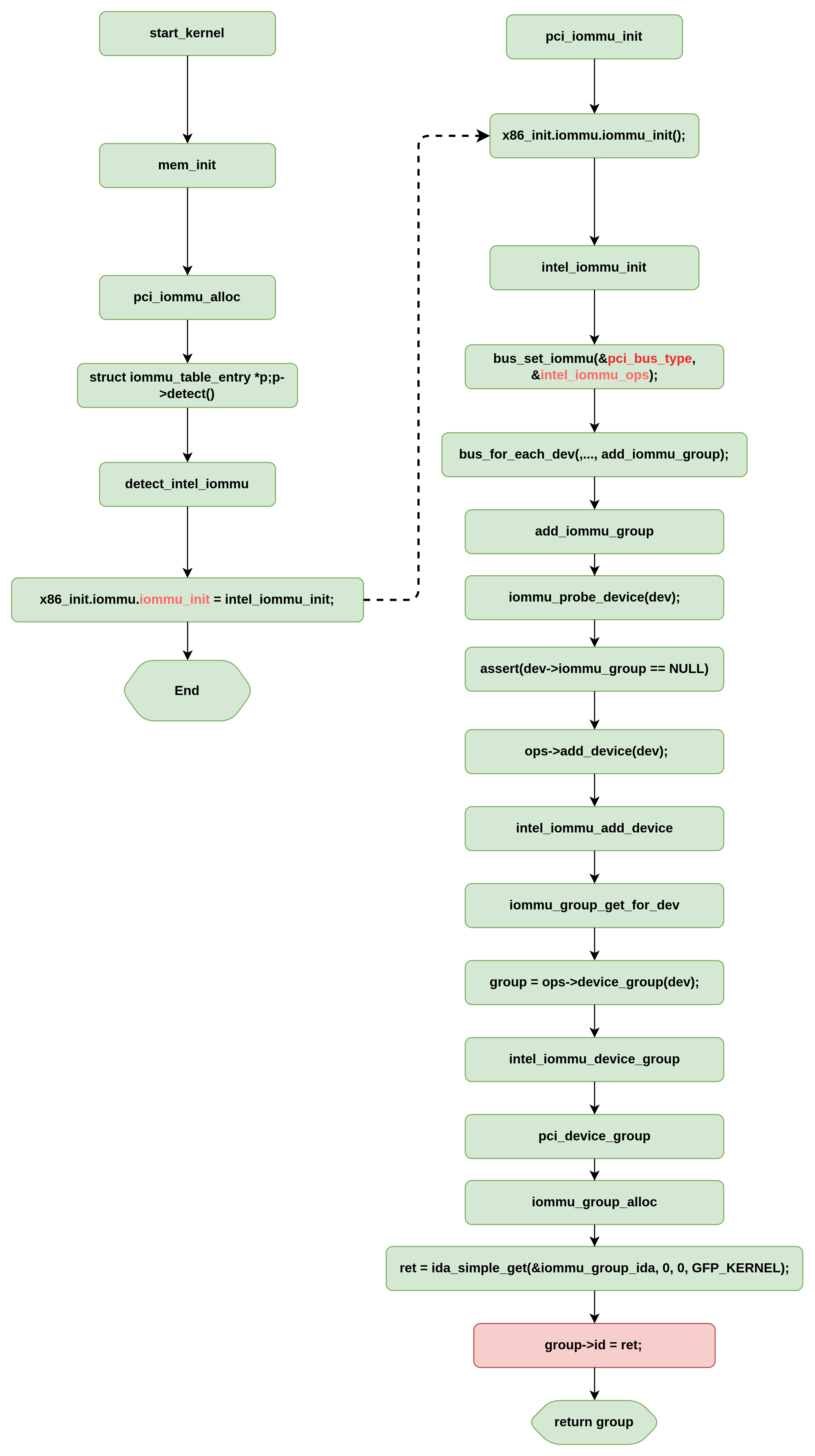
为什么有些PCI设备在一个GROUP,而有些在不同的GROUP,依据是什么?

从图中可以看出,有两个group比较特殊,他们的ID分贝为3和8,别的GORUP只有一个设备,而这两个GROUP则分别有2个和4个设备。
通过BDF分析他们的共性,可以看属于同一个IOMMU GROUP PCI设备的BUS号和Device(slot)号是相同的,只有功能号不同,而根据PCI设备的定义,BUS号和DEVICE号确定了一个物理上的PCI设备,对应一个PCI插槽,而funcdtion则是对PCI设备的逻辑划分而并非物理划分,同一个设备的不同的function共用同一个PCI 插槽。所以猜测,内核判断设备是否是同一个IOMMU GROUP的依据是否是根据BUS和SLOT号呢?查看逻辑确实如此:

并且发现,分组内的第一个设备负责调用iommu_group_alloc分配iommu group,其它设备则通过1339行得到第一个设备的GROUP信息并分配给自身。


PCIe协议允许P2P传输,这就意味着同一个PCIE Switch下连接不同End Point可以在不经过RC的情况下相互通信。除了End Point和End Point之间(End Point和End Point都是挂在同一个PCIE Switch下)可以peer-to-peer传输,同一个Poot Complex下的Root Port之间也可以支持peer-to-peer传输。而对于多功能的PCIe dev,dev的不同功能之间也可以进行peer-to-peer传输。
另外也可以看出,iommu domain分配的最小粒度是 iommug group,属于同一个iommu group的设备也属于同一个iommu domain.
bus号和function号相同是必要条件,并非充分条件,当设备支持ACS访问控制功能时,不能和其它具有相同的BUS和SLOT号的设备同组,必须单独创建一个IOMMU组,如下图中的00:14.3设备的GROUP。


dev->iommu_group被设置后,会继续给设备做DMA映射,iommu_group_create_direct_mappings函数主要是将设备对应的虚拟机地址空间映射到物理地址空间,其会遍历设备映射的地址段,然后调用iommu_map给每段虚拟地址空间都映射到相应的物理内存上。





IOMMU GROUP和IOMMU是对应的,相同IOMMU GROUP的设备指向相同的iommu domain,而每个iommu domain分配对应一个页表PGD,所以,同一个IOMMU GROUP内的设备,是可以互相访问彼此的IOMMU 映射的。

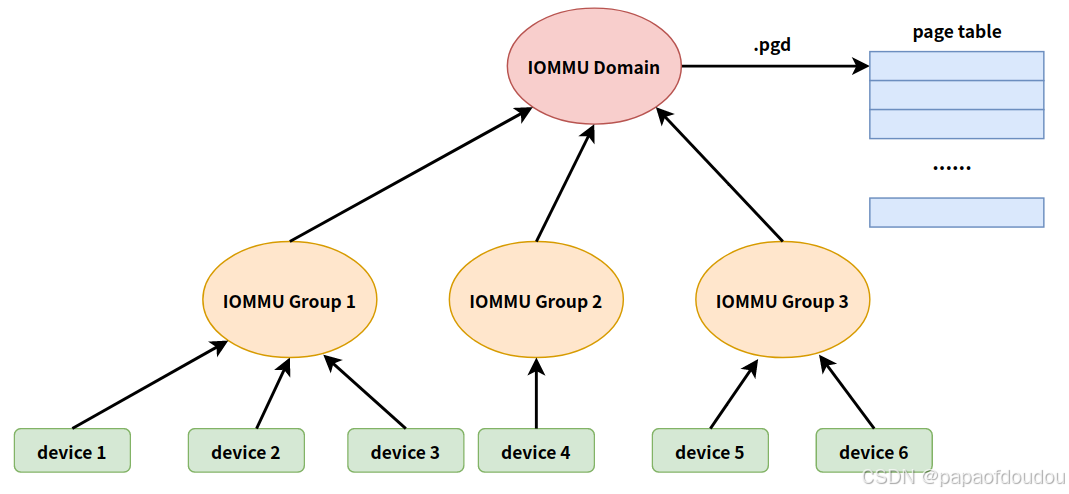
iommu_domain对应了一张page table pgd.

一个struct iommu_group下面可以对应多个或者一个硬件设备,一个struct iommu_domain里面可以有多个iommu_group,然后每个iommu_group通过iommu_domain最终找到dmar_domain进行转换。
acs影响IOMMU 分组的理由
看分析主要是为了保护IOVA地址空间的可见性和隔离。
An IOMMU group is defined as the smallest set of devices that can be considered isolated from the IOMMU’s perspective. The first step to achieve isolation is granularity. If the IOMMU cannot differentiate devices into separate IOVA spaces, they are not isolated. For example, if multiple devices attempt to alias to the same IOVA space, the IOMMU is not able to distinguish between them. This is the reason why a typical x86 PC will group all conventional-PCI devices together, with all of them aliased to the same requester ID, the PCIe-to-PCI bridge. Legacy KVM device assignment allows a user to assign these conventional-PCI devices separately, but the configuration fails because the IOMMU cannot distinguish between the devices. As VFIO is governed by IOMMU groups, it prevents any configuration that violates this most basic requirement of IOMMU granularity.
The next step is to determine whether the transactions from the device actually reach the IOMMU. The PCIe specification allows for transactions to be re-routed within the interconnect fabric. A PCIe downstream port can re-route a transaction from one downstream device to another. The downstream ports of a PCIe switch may be interconnected to allow re-routing from one port to another. Even within a multifunction endpoint device, a transaction from one function may be delivered directly to another function. These transactions from one device to another are called peer-to-peer transactions and can destroy the isolation of devices operating in separate IOVA spaces. Imagine for instance, if the network interface card assigned to a guest virtual machine, attempts a DMA write operation to a virtual address within its own IOVA space. However in the physical space, that same address belongs to a peer disk controller owned by the host. As the IOVA to physical translation for the device is only performed at the IOMMU, any interconnect attempting to optimize the data path of that transaction could mistakenly redirect the DMA write operation to the disk controller before it gets to the IOMMU for translation.
To solve this problem, the PCI Express specification includes support for PCIe Access Control Services (ACS), which provides visibility and control of these redirects. This is an essential component for isolating devices from one another, which is often missing in interconnects and multifunction endpoints. Without ACS support at every level from the device to the IOMMU, it must be assumed that redirection is possible. This will, therefore, break the isolation of all devices below the point lacking ACS support in the PCI topology. IOMMU groups in a PCI environment take this isolation into account, grouping together devices which are capable of untranslated peer-to-peer DMA.
In summary, the IOMMU group represents the smallest set of devices for which the IOMMU has visibility and which is isolated from other groups. VFIO uses this information to enforce safe ownership of devices for user space. With the exception of bridges, root ports, and switches (all examples of interconnect fabric), all devices within an IOMMU group must be bound to a VFIO device driver or known safe stub driver. For PCI, these drivers are vfio-pci and pci-stub. pci-stub is allowed simply because it is known that the host does not interact with devices via this driver[2]. If an error occurs indicating the group is not viable when using VFIO, it means that all of the devices in the group need to be bound to an appropriate host driver. Using virsh nodedev-dumpxml to explore the composition of an IOMMU group and virsh nodedev-detach to bind devices to VFIO compatible drivers, will help resolve such problems.
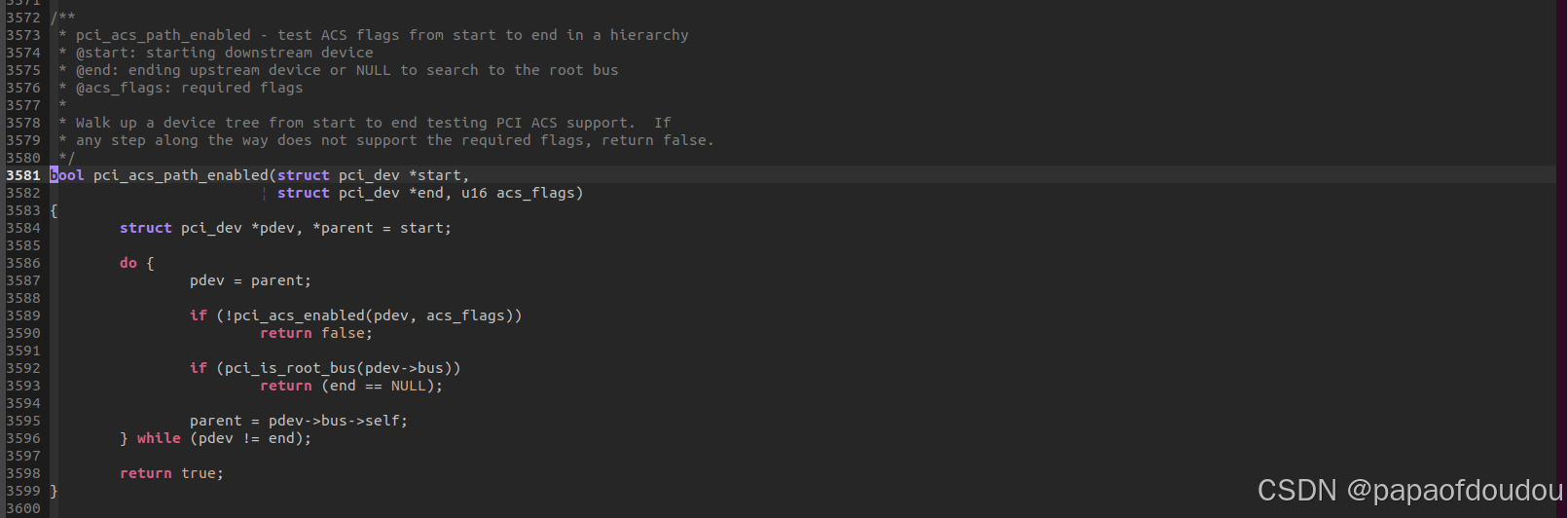
这个函数的核心逻辑在于pci_acs_path_enabled,简单来说如果是pcie的设备则检查该设备到root complex的路径上如果都开启了ACS则这个设备就单独成一个iommu_group,如果不是则找到它的alias group就行了比如如果这个是传统的pci bus(没有pcie这些ACS的特性)则这个pci bus下面的所有设备就组合成一个iommu_group。
PCIe技术允许peer-to-peer通信,即PCIe设备间的数据包无需一直传递至根节点,而是可在中间的PCIe Switch处直接进行转发,实现设备间的快速通信。然而,这种通信方式会绕过IOMMU的控制,导致无法有效隔离设备,





 文章详细介绍了Linux系统中的IOMMU机制,包括IOMMU的作用——管理输入输出设备的内存映射和访问权限,提升系统安全性和性能。IOMMUGroup用于设备分组和隔离,确保DMA请求的正确管理。内容还涉及到IOMMUGroup的分配逻辑,以及PCI设备如何根据BUS和SLOT号被分到同一组。此外,文章探讨了IOMMUDomain的页表结构,以及在不同IOMMU模式(如关闭、非PT模式、PT模式)下,物理地址和IOMMU映射地址的关系。最后,提到了启用IOMMUPASS-THROUGH模式的影响和设备间内存访问的规则。
文章详细介绍了Linux系统中的IOMMU机制,包括IOMMU的作用——管理输入输出设备的内存映射和访问权限,提升系统安全性和性能。IOMMUGroup用于设备分组和隔离,确保DMA请求的正确管理。内容还涉及到IOMMUGroup的分配逻辑,以及PCI设备如何根据BUS和SLOT号被分到同一组。此外,文章探讨了IOMMUDomain的页表结构,以及在不同IOMMU模式(如关闭、非PT模式、PT模式)下,物理地址和IOMMU映射地址的关系。最后,提到了启用IOMMUPASS-THROUGH模式的影响和设备间内存访问的规则。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 2164
2164

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










