首先下载act代码:https://github.com/tonyzhaozh/act
修改代码imitate_episodes.py,在第250行处增加:
torch.onnx.export(policy, (qpos, curr_image), "model.onnx", opset_version=13)
导出onnx模型结构如下: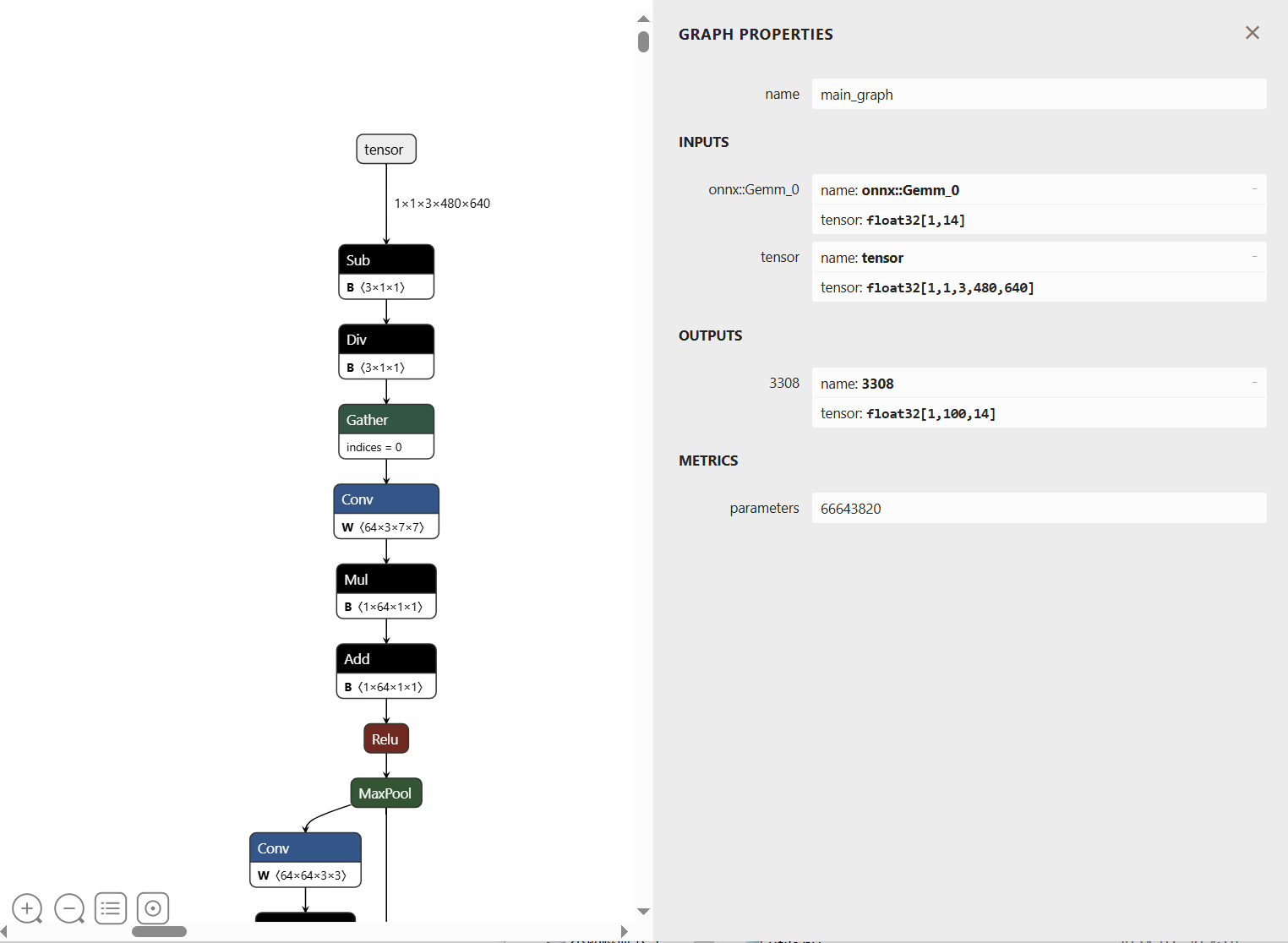
onnxruntime推理脚本:
import numpy as np
import onnxruntime
onnx_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession("model.onnx", providers=['CUDAExecutionProvider', 'CPUExecutionProvider'])
input_name = []
for node in onnx_session.get_inputs():
input_name.append(node.name)
output_name = []
for node in onnx_session.get_outputs():
output_name.append(node.name)
qpos = np.random.randn(1, 14).astype(np.float32)
curr_image = np.random.randn(1, 1, 3, 480, 640).astype(np.float32)
inputs = {}
inputs['onnx::Gemm_0'] = qpos
inputs['tensor'] = curr_image
outputs = onnx_session.run(None, inputs)
print(outputs)
tensorrt推理脚本(tensorrt版本>10):
import numpy as np
import tensorrt as trt
import common
logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING)
with open("model.engine", "rb") as f, trt.Runtime(logger) as runtime:
engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
context = engine.create_execution_context()
inputs, outputs, bindings, stream = common.allocate_buffers(engine)
qpos = np.random.randn(1, 14).astype(np.float32)
curr_image = np.random.randn(1, 1, 3, 480, 640).astype(np.float32)
np.copyto(inputs[0].host, qpos.ravel())
np.copyto(inputs[1].host, curr_image.ravel())
output = common.do_inference(context,engine=engine, bindings=bindings,inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, stream=stream,)
print(output)
其中common.py:
#
# SPDX-FileCopyrightText: Copyright (c) 1993-2023 NVIDIA CORPORATION & AFFILIATES. All rights reserved.
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
#
import argparse
import os
import ctypes
from typing import Optional, List
import numpy as np
import tensorrt as trt
from cuda import cuda, cudart
try:
# Sometimes python does not understand FileNotFoundError
FileNotFoundError
except NameError:
FileNotFoundError = IOError
EXPLICIT_BATCH = 1 << (int)(trt.NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag.EXPLICIT_BATCH)
def check_cuda_err(err):
if isinstance(err, cuda.CUresult):
if err != cuda.CUresult.CUDA_SUCCESS:
raise RuntimeError("Cuda Error: {}".format(err))
if isinstance(err, cudart.cudaError_t):
if err != cudart.cudaError_t.cudaSuccess:
raise RuntimeError("Cuda Runtime Error: {}".format(err))
else:
raise RuntimeError("Unknown error type: {}".format(err))
def cuda_call(call):
err, res = call[0], call[1:]
check_cuda_err(err)
if len(res) == 1:
res = res[0]
return res
def GiB(val):
return val * 1 << 30
def add_help(description):
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=description, formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter)
args, _ = parser.parse_known_args()
def find_sample_data(description="Runs a TensorRT Python sample", subfolder="", find_files=[], err_msg=""):
"""
Parses sample arguments.
Args:
description (str): Description of the sample.
subfolder (str): The subfolder containing data relevant to this sample
find_files (str): A list of filenames to find. Each filename will be replaced with an absolute path.
Returns:
str: Path of data directory.
"""
# Standard command-line arguments for all samples.
kDEFAULT_DATA_ROOT = os.path.join(os.sep, "usr", "src", "tensorrt", "data")
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=description, formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter)
parser.add_argument(
"-d",
"--datadir",
help="Location of the TensorRT sample data directory, and any additional data directories.",
action="append",
default=[kDEFAULT_DATA_ROOT],
)
args, _ = parser.parse_known_args()
def get_data_path(data_dir):
# If the subfolder exists, append it to the path, otherwise use the provided path as-is.
data_path = os.path.join(data_dir, subfolder)
if not os.path.exists(data_path):
if data_dir != kDEFAULT_DATA_ROOT:
print("WARNING: " + data_path + " does not exist. Trying " + data_dir + " instead.")
data_path = data_dir
# Make sure data directory exists.
if not (os.path.exists(data_path)) and data_dir != kDEFAULT_DATA_ROOT:
print(
"WARNING: {:} does not exist. Please provide the correct data path with the -d option.".format(
data_path
)
)
return data_path
data_paths = [get_data_path(data_dir) for data_dir in args.datadir]
return data_paths, locate_files(data_paths, find_files, err_msg)
def locate_files(data_paths, filenames, err_msg=""):
"""
Locates the specified files in the specified data directories.
If a file exists in multiple data directories, the first directory is used.
Args:
data_paths (List[str]): The data directories.
filename (List[str]): The names of the files to find.
Returns:
List[str]: The absolute paths of the files.
Raises:
FileNotFoundError if a file could not be located.
"""
found_files = [None] * len(filenames)
for data_path in data_paths:
# Find all requested files.
for index, (found, filename) in enumerate(zip(found_files, filenames)):
if not found:
file_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(data_path, filename))
if os.path.exists(file_path):
found_files[index] = file_path
# Check that all files were found
for f, filename in zip(found_files, filenames):
if not f or not os.path.exists(f):
raise FileNotFoundError(
"Could not find {:}. Searched in data paths: {:}\n{:}".format(filename, data_paths, err_msg)
)
return found_files
class HostDeviceMem:
"""Pair of host and device memory, where the host memory is wrapped in a numpy array"""
def __init__(self, size: int, dtype: np.dtype):
nbytes = size * dtype.itemsize
host_mem = cuda_call(cudart.cudaMallocHost(nbytes))
pointer_type = ctypes.POINTER(np.ctypeslib.as_ctypes_type(dtype))
self._host = np.ctypeslib.as_array(ctypes.cast(host_mem, pointer_type), (size,))
self._device = cuda_call(cudart.cudaMalloc(nbytes))
self._nbytes = nbytes
@property
def host(self) -> np.ndarray:
return self._host
@host.setter
def host(self, arr: np.ndarray):
if arr.size > self.host.size:
raise ValueError(
f"Tried to fit an array of size {arr.size} into host memory of size {self.host.size}"
)
np.copyto(self.host[:arr.size], arr.flat, casting='safe')
@property
def device(self) -> int:
return self._device
@property
def nbytes(self) -> int:
return self._nbytes
def __str__(self):
return f"Host:\n{self.host}\nDevice:\n{self.device}\nSize:\n{self.nbytes}\n"
def __repr__(self):
return self.__str__()
def free(self):
cuda_call(cudart.cudaFree(self.device))
cuda_call(cudart.cudaFreeHost(self.host.ctypes.data))
# Allocates all buffers required for an engine, i.e. host/device inputs/outputs.
# If engine uses dynamic shapes, specify a profile to find the maximum input & output size.
def allocate_buffers(engine: trt.ICudaEngine, profile_idx: Optional[int] = None):
inputs = []
outputs = []
bindings = []
stream = cuda_call(cudart.cudaStreamCreate())
tensor_names = [engine.get_tensor_name(i) for i in range(engine.num_io_tensors)]
for binding in tensor_names:
# get_tensor_profile_shape returns (min_shape, optimal_shape, max_shape)
# Pick out the max shape to allocate enough memory for the binding.
shape = engine.get_tensor_shape(binding) if profile_idx is None else engine.get_tensor_profile_shape(binding, profile_idx)[-1]
shape_valid = np.all([s >= 0 for s in shape])
if not shape_valid and profile_idx is None:
raise ValueError(f"Binding {binding} has dynamic shape, " +\
"but no profile was specified.")
size = trt.volume(shape)
if engine.has_implicit_batch_dimension:
size *= engine.max_batch_size
dtype = np.dtype(trt.nptype(engine.get_tensor_dtype(binding)))
# Allocate host and device buffers
bindingMemory = HostDeviceMem(size, dtype)
# Append the device buffer to device bindings.
bindings.append(int(bindingMemory.device))
# Append to the appropriate list.
if engine.get_tensor_mode(binding) == trt.TensorIOMode.INPUT:
inputs.append(bindingMemory)
else:
outputs.append(bindingMemory)
return inputs, outputs, bindings, stream
# Frees the resources allocated in allocate_buffers
def free_buffers(inputs: List[HostDeviceMem], outputs: List[HostDeviceMem], stream: cudart.cudaStream_t):
for mem in inputs + outputs:
mem.free()
cuda_call(cudart.cudaStreamDestroy(stream))
# Wrapper for cudaMemcpy which infers copy size and does error checking
def memcpy_host_to_device(device_ptr: int, host_arr: np.ndarray):
nbytes = host_arr.size * host_arr.itemsize
cuda_call(cudart.cudaMemcpy(device_ptr, host_arr, nbytes, cudart.cudaMemcpyKind.cudaMemcpyHostToDevice))
# Wrapper for cudaMemcpy which infers copy size and does error checking
def memcpy_device_to_host(host_arr: np.ndarray, device_ptr: int):
nbytes = host_arr.size * host_arr.itemsize
cuda_call(cudart.cudaMemcpy(host_arr, device_ptr, nbytes, cudart.cudaMemcpyKind.cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost))
def _do_inference_base(inputs, outputs, stream, execute_async):
# Transfer input data to the GPU.
kind = cudart.cudaMemcpyKind.cudaMemcpyHostToDevice
[cuda_call(cudart.cudaMemcpyAsync(inp.device, inp.host, inp.nbytes, kind, stream)) for inp in inputs]
# Run inference.
execute_async()
# Transfer predictions back from the GPU.
kind = cudart.cudaMemcpyKind.cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost
[cuda_call(cudart.cudaMemcpyAsync(out.host, out.device, out.nbytes, kind, stream)) for out in outputs]
# Synchronize the stream
cuda_call(cudart.cudaStreamSynchronize(stream))
# Return only the host outputs.
return [out.host for out in outputs]
def do_inference(context, engine, bindings, inputs, outputs, stream):
def execute_async_func():
context.execute_async_v3(stream_handle=stream)
# Setup context tensor address.
num_io = engine.num_io_tensors
for i in range(num_io):
context.set_tensor_address(engine.get_tensor_name(i), bindings[i])
return _do_inference_base(inputs, outputs, stream, execute_async_func)

























 665
665

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










