Farey Sequence
Time Limit:
1000MS
Memory Limit: 65536K
Description
The Farey Sequence Fn for any integer n with n >= 2 is the set of irreducible rational numbers a/b with 0 < a < b <= n and gcd(a,b) = 1 arranged in increasing order. The first few are
F2 = {1/2}
F3 = {1/3, 1/2, 2/3}
F4 = {1/4, 1/3, 1/2, 2/3, 3/4}
F5 = {1/5, 1/4, 1/3, 2/5, 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5}
You task is to calculate the number of terms in the Farey sequence Fn.
F2 = {1/2}
F3 = {1/3, 1/2, 2/3}
F4 = {1/4, 1/3, 1/2, 2/3, 3/4}
F5 = {1/5, 1/4, 1/3, 2/5, 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5}
You task is to calculate the number of terms in the Farey sequence Fn.
Input
There are several test cases. Each test case has only one line, which contains a positive integer n (2 <= n <= 10
6). There are no blank lines between cases. A line with a single 0 terminates the input.
Output
For each test case, you should output one line, which contains N(n) ---- the number of terms in the Farey sequence Fn.
Sample Input
2 3 4 5 0
Sample Output
1 3 5 9
思路:
1. 由于Farey数列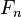 包含了
包含了 的全部项和与n互质的每个数的相应分数,故有
的全部项和与n互质的每个数的相应分数,故有
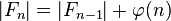 ,
,
从而
 。
。
又由于 ,所以要用long long处理。
,所以要用long long处理。
2. 如何递推地计算φ(n)?——从素数入手
若p|n,那么
若p不整除(n/p),φ(n)=φ(n/p)*φ(p)=φ(n/p)*(p-1)
若p|(n/p),则由φ(p^k)=p*φ(p^(k-1))及素因子分解式,得
φ(n)=φ(n/p)*p
*注:此法制表速度比一般的快不少。
完整代码,已优化:
/*32ms,13204KB*/
#include <cstdio>
const int len = 1000002;
const int le = 78498;
int prime[le], phi[len];
bool unprime[len];
long long sum[len];
inline void Euler()
{
int i, j, k = 0;
for (i = 2; i < len; i++)
{
if (!unprime[i])
{
prime[k++] = i;
phi[i] = i - 1;
}
for (j = 0; j < k && prime[j] * i < len; j++)
{
unprime[prime[j] * i] = true;
if (i % prime[j])///若p不整除(n/p),φ(n)=φ(n/p)*(p-1)
{
phi[prime[j] * i] = phi[i] * (prime[j] - 1);
///不break是因为与p互素的i后面不可能出现(因为i越来越大),所以要继续算
}
else///若p|(n/p),φ(n)=φ(n/p)*p
{
phi[prime[j] * i] = phi[i] * prime[j];
break;///后面遇到比p1大的p2就不用算了,因为k*p1 * p2 = k*p2 * p1,后面i=k*p2时会算出来的
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
Euler();
int i, n;
for (i = 2; i < len; i++)
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + phi[i];
while (scanf("%d", &n), n)
printf("%lld\n", sum[n]);
return 0;
}








 本文介绍了一种高效计算Farey数列项数的方法,利用欧拉函数φ(n)的性质,通过筛法预处理φ(n)并递推计算∑φ(n),实现了快速求解。
本文介绍了一种高效计算Farey数列项数的方法,利用欧拉函数φ(n)的性质,通过筛法预处理φ(n)并递推计算∑φ(n),实现了快速求解。
















 1189
1189

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








