📝 面试求职: 「面试试题小程序」 ,内容涵盖 测试基础、Linux操作系统、MySQL数据库、Web功能测试、接口测试、APPium移动端测试、Python知识、Selenium自动化测试相关、性能测试、性能测试、计算机网络知识、Jmeter、HR面试,命中率杠杠的。(大家刷起来…)
📝 职场经验干货:
想象一下:你是一名JavaScript开发者,正盯着一个有着数千行未测试代码的遗留代码库。你的经理刚刚宣布了一个重大重构的截止日期,而你昨天就需要全面的测试覆盖……这听起来是不是很熟悉?
如果我告诉你,人工智能可以自动生成、优先排序和维护你的测试套件,将测试开销减少70%,同时提高覆盖质量,你会怎么想?欢迎来到软件测试的未来。
测试危机:传统方法为何力不从心
数据不会说谎
根据最近的行业调查,开发者将23%的时间用于编写和维护测试。然而,尽管投入巨大:
-
64%的生产环境漏洞本可以通过更好的测试覆盖来发现
-
测试维护消耗了40%的QA预算
-
手动测试优先级排序导致35%的冗余测试执行
JavaScript测试困境
JavaScript的动态特性使其难以进行全面测试:
// Traditional approach - Manual test writing
function calculateTax(income, deductions, state) {
if (typeof income !== 'number' || income < 0) {
throw new Error('Invalid income');
}
const taxableIncome = Math.max(0, income - deductions);
const stateTaxRate = getStateTaxRate(state);
return taxableIncome * (0.22 + stateTaxRate); // Federal + State
}
// Manual test cases - Time-consuming and potentially incomplete
describe('calculateTax', () => {
it('should calculate tax for valid inputs', () => {
expect(calculateTax(50000, 5000, 'CA')).toBe(/* manual calculation */);
});
it('should handle zero income', () => {
expect(calculateTax(0, 0, 'TX')).toBe(0);
});
// What about edge cases? Boundary values? Error conditions?
});问题在于:人工测试人员无法考虑到所有边界场景,而且随着代码的演进,维护这些测试会变成一场噩梦。
人工智能革命:智能测试生成
用于测试用例生成的机器学习
现代人工智能能够分析你的代码结构、数据流和执行路径,从而自动生成全面的测试套件。其工作原理如下:
// AI-Enhanced Test Generator
class AITestGenerator {
constructor() {
this.mlModel = new TestGenerationModel();
this.codeAnalyzer = new StaticCodeAnalyzer();
this.executionTracer = new DynamicAnalyzer();
}
async generateTests(functionCode, functionName) {
// Step 1: Static analysis for code structure
const codeStructure = this.codeAnalyzer.analyze(functionCode);
// Step 2: Generate input variations using ML
const inputVariations = await this.mlModel.generateInputs({
parameters: codeStructure.parameters,
types: codeStructure.parameterTypes,
constraints: codeStructure.constraints
});
// Step 3: Execute and trace to understand behavior
const executionPaths = await this.executionTracer.trace(
functionCode,
inputVariations
);
// Step 4: Generate comprehensive test cases
return this.createTestSuite(functionName, inputVariations, executionPaths);
}
createTestSuite(functionName, inputs, paths) {
const testCases = [];
// Generate boundary value tests
testCases.push(...this.generateBoundaryTests(inputs));
// Generate error condition tests
testCases.push(...this.generateErrorTests(inputs));
// Generate path coverage tests
testCases.push(...this.generatePathTests(paths));
return {
describe: `AI-Generated Tests for ${functionName}`,
tests: testCases,
coverage: this.calculateCoverage(paths),
confidence: this.calculateConfidence(testCases)
};
}
generateBoundaryTests(inputs) {
return inputs.boundaries.map(boundary => ({
name: `should handle boundary value: ${boundary.description}`,
input: boundary.value,
expectedBehavior: boundary.expected,
category: 'boundary'
}));
}
}
// Usage Example
const generator = new AITestGenerator();
const tests = await generator.generateTests(calculateTax.toString(), 'calculateTax');
console.log(tests);
/* Output:
{
describe: "AI-Generated Tests for calculateTax",
tests: [
{
name: "should handle boundary value: negative income",
input: [-1, 0, 'CA'],
expectedBehavior: "throws Error",
category: "boundary"
},
{
name: "should handle boundary value: maximum safe integer",
input: [Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER, 0, 'TX'],
expectedBehavior: "returns number",
category: "boundary"
},
// ... 47 more test cases
],
coverage: 94.7,
confidence: 0.89
}
*/智能测试优先级排序
并非所有测试的重要性都相同。人工智能可以分析历史数据、代码变更和失败模式,从而确定优先运行哪些测试:
class IntelligentTestPrioritizer {
constructor() {
this.riskModel = new RiskPredictionModel();
this.historyAnalyzer = new TestHistoryAnalyzer();
this.impactAnalyzer = new CodeImpactAnalyzer();
}
async prioritizeTests(testSuite, codeChanges, gitHistory) {
const tests = testSuite.tests;
const priorities = [];
for (const test of tests) {
// Calculate risk score based on multiple factors
const riskScore = await this.calculateRiskScore(test, codeChanges, gitHistory);
priorities.push({
test: test,
priority: riskScore,
reasoning: this.explainPriority(test, riskScore),
estimatedExecutionTime: test.metadata.avgExecutionTime
});
}
// Sort by priority (highest risk first)
return priorities.sort((a, b) => b.priority - a.priority);
}
async calculateRiskScore(test, codeChanges, gitHistory) {
// Factor 1: Code change impact (0-40 points)
const changeImpact = this.impactAnalyzer.calculateImpact(
test.targetCode,
codeChanges
);
// Factor 2: Historical failure rate (0-30 points)
const failureHistory = this.historyAnalyzer.getFailureRate(
test.name,
gitHistory
);
// Factor 3: Code complexity (0-20 points)
const complexity = this.calculateComplexity(test.targetCode);
// Factor 4: Business criticality (0-10 points)
const criticality = test.metadata.businessCriticality || 5;
const totalScore = changeImpact + failureHistory + complexity + criticality;
return Math.min(100, totalScore); // Cap at 100
}
explainPriority(test, score) {
if (score > 80) return `High risk: Recent changes affect core logic tested by ${test.name}`;
if (score > 60) return `Medium risk: Moderate complexity with some historical failures`;
return `Low risk: Stable code with good test history`;
}
}
// Example usage
const prioritizer = new IntelligentTestPrioritizer();
const prioritizedTests = await prioritizer.prioritizeTests(
generatedTestSuite,
recentCodeChanges,
projectGitHistory
);
console.log('Top 5 Priority Tests:');
prioritizedTests.slice(0, 5).forEach((item, index) => {
console.log(`${index + 1}. ${item.test.name}`);
console.log(` Priority: ${item.priority}/100`);
console.log(` Reason: ${item.reasoning}`);
console.log(` Est. Time: ${item.estimatedExecutionTime}ms\n`);
});自动化测试维护:自愈式测试
人工智能在测试领域最令人兴奋的应用之一是自动化维护。当你的代码发生变化时,测试能够自动适应:
class SelfHealingTestSuite {
constructor() {
this.codeAnalyzer = new CodeChangeAnalyzer();
this.testUpdater = new IntelligentTestUpdater();
this.validator = new TestValidityChecker();
}
async maintainTests(oldCode, newCode, existingTests) {
// Step 1: Analyze what changed
const changes = this.codeAnalyzer.compareVersions(oldCode, newCode);
// Step 2: Identify affected tests
const affectedTests = this.identifyAffectedTests(changes, existingTests);
// Step 3: Automatically update tests
const updatedTests = [];
for (const test of affectedTests) {
const updateResult = await this.updateTest(test, changes);
if (updateResult.success) {
updatedTests.push(updateResult.updatedTest);
console.log(`✅ Auto-updated: ${test.name}`);
} else {
console.log(`⚠️ Manual review needed: ${test.name}`);
console.log(` Reason: ${updateResult.reason}`);
}
}
return {
updatedTests,
requiresManualReview: affectedTests.length - updatedTests.length,
confidenceScore: this.calculateUpdateConfidence(updatedTests)
};
}
async updateTest(test, changes) {
// Handle different types of changes
if (changes.type === 'parameter_added') {
return this.handleParameterAddition(test, changes);
}
if (changes.type === 'return_type_changed') {
return this.handleReturnTypeChange(test, changes);
}
if (changes.type === 'logic_modified') {
return this.handleLogicModification(test, changes);
}
return { success: false, reason: 'Unsupported change type' };
}
handleParameterAddition(test, changes) {
const newParameter = changes.details.newParameter;
// Generate sensible default values for the new parameter
const defaultValue = this.generateDefaultValue(newParameter.type);
// Update test input
const updatedInput = [...test.input, defaultValue];
// Verify the test still makes sense
if (this.validator.validateTestLogic(updatedInput, test.expectedOutput)) {
return {
success: true,
updatedTest: {
...test,
input: updatedInput,
metadata: {
...test.metadata,
autoUpdated: true,
updateReason: `Added default value for new parameter: ${newParameter.name}`
}
}
};
}
return { success: false, reason: 'Unable to generate valid default value' };
}
generateDefaultValue(type) {
const defaults = {
'string': '',
'number': 0,
'boolean': false,
'array': [],
'object': {},
'null': null
};
return defaults[type] || null;
}
}
// Real-world example
const maintainer = new SelfHealingTestSuite();
// Simulate a function change
const oldFunction = `
function calculateDiscount(price, percentage) {
return price * (percentage / 100);
}
`;
const newFunction = `
function calculateDiscount(price, percentage, maxDiscount = 100) {
const discount = price * (percentage / 100);
return Math.min(discount, maxDiscount);
}
`;
const existingTests = [
{
name: 'should calculate 10% discount',
input: [100, 10],
expectedOutput: 10
},
{
name: 'should calculate 25% discount',
input: [200, 25],
expectedOutput: 50
}
];
const maintenanceResult = await maintainer.maintainTests(
oldFunction,
newFunction,
existingTests
);
console.log('Maintenance Result:', maintenanceResult);
/* Output:
✅ Auto-updated: should calculate 10% discount
✅ Auto-updated: should calculate 25% discount
Maintenance Result: {
updatedTests: [
{
name: 'should calculate 10% discount',
input: [100, 10, 100], // Auto-added default maxDiscount
expectedOutput: 10,
metadata: {
autoUpdated: true,
updateReason: 'Added default value for new parameter: maxDiscount'
}
},
// ... other updated tests
],
requiresManualReview: 0,
confidenceScore: 0.95
}
*/故障模式识别:从错误中学习
人工智能擅长在大型数据集中识别模式。通过分析测试失败、错误报告和代码变更,它可以预测错误可能发生的位置:
class FailurePatternAnalyzer {
constructor() {
this.patternModel = new PatternRecognitionModel();
this.bugDatabase = new BugHistoryDatabase();
}
async analyzeFailurePatterns(testResults, codeMetrics, bugHistory) {
// Collect failure data
const failures = testResults.filter(result => !result.passed);
// Extract features from failures
const features = failures.map(failure => ({
testType: failure.category,
codeComplexity: codeMetrics[failure.targetFunction].complexity,
linesOfCode: codeMetrics[failure.targetFunction].loc,
cyclomatic: codeMetrics[failure.targetFunction].cyclomatic,
changeFrequency: this.getChangeFrequency(failure.targetFunction, bugHistory),
authorExperience: this.getAuthorExperience(failure.targetFunction),
errorType: this.categorizeError(failure.error),
timeOfDay: new Date(failure.timestamp).getHours(),
dayOfWeek: new Date(failure.timestamp).getDay()
}));
// Train or update the pattern recognition model
const patterns = await this.patternModel.findPatterns(features);
return {
criticalPatterns: patterns.filter(p => p.severity === 'high'),
recommendations: this.generateRecommendations(patterns),
riskAreas: this.identifyRiskAreas(patterns, codeMetrics)
};
}
generateRecommendations(patterns) {
const recommendations = [];
for (const pattern of patterns) {
if (pattern.type === 'complexity_correlation') {
recommendations.push({
type: 'refactoring',
priority: 'high',
message: `Functions with cyclomatic complexity > ${pattern.threshold} are ${pattern.failureRate}x more likely to fail`,
action: 'Consider breaking down complex functions',
affectedFunctions: pattern.affectedFunctions
});
}
if (pattern.type === 'temporal_pattern') {
recommendations.push({
type: 'process',
priority: 'medium',
message: `${pattern.percentage}% of failures occur during ${pattern.timeWindow}`,
action: 'Schedule additional testing during high-risk periods',
schedule: pattern.suggestedSchedule
});
}
}
return recommendations;
}
categorizeError(error) {
const errorPatterns = {
'TypeError': 'type_mismatch',
'ReferenceError': 'undefined_reference',
'RangeError': 'boundary_violation',
'SyntaxError': 'syntax_issue',
'AssertionError': 'logic_error'
};
for (const [errorType, category] of Object.entries(errorPatterns)) {
if (error.name.includes(errorType)) {
return category;
}
}
return 'unknown';
}
}
// Usage example
const analyzer = new FailurePatternAnalyzer();
const analysis = await analyzer.analyzeFailurePatterns(
lastWeekTestResults,
codeComplexityMetrics,
sixMonthBugHistory
);
console.log('Critical Patterns Found:');
analysis.criticalPatterns.forEach(pattern => {
console.log(`• ${pattern.description}`);
console.log(` Confidence: ${pattern.confidence}%`);
console.log(` Impact: ${pattern.impact} functions affected\n`);
});
console.log('Recommendations:');
analysis.recommendations.forEach(rec => {
console.log(`${rec.priority.toUpperCase()}: ${rec.message}`);
console.log(`Action: ${rec.action}\n`);
});预测性测试分析
人工智能驱动测试的终极目标是预测。通过分析趋势、模式和历史数据,我们可以预测测试结果并优化测试策略:
class PredictiveTestAnalytics {
constructor() {
this.predictionModel = new TestOutcomePredictionModel();
this.trendAnalyzer = new TrendAnalyzer();
this.optimizer = new TestStrategyOptimizer();
}
async generatePredictions(codeChanges, testSuite, historicalData) {
// Predict test outcomes before running tests
const predictions = await this.predictTestOutcomes(codeChanges, testSuite);
// Analyze trends in test performance
const trends = this.trendAnalyzer.analyzeTrends(historicalData);
// Generate optimization recommendations
const optimizations = await this.optimizer.optimizeStrategy(
predictions,
trends,
testSuite
);
return {
predictions,
trends,
optimizations,
dashboard: this.createDashboard(predictions, trends, optimizations)
};
}
async predictTestOutcomes(codeChanges, testSuite) {
const predictions = [];
for (const test of testSuite.tests) {
const features = this.extractFeatures(test, codeChanges);
const prediction = await this.predictionModel.predict(features);
predictions.push({
testName: test.name,
predictedOutcome: prediction.outcome, // 'pass', 'fail', 'flaky'
confidence: prediction.confidence,
estimatedRuntime: prediction.runtime,
riskFactors: prediction.riskFactors,
recommendation: this.getRecommendation(prediction)
});
}
return predictions;
}
extractFeatures(test, codeChanges) {
return {
testComplexity: this.calculateTestComplexity(test),
codeChangeImpact: this.calculateChangeImpact(test, codeChanges),
historicalStability: test.metadata.historicalPassRate,
lastFailureDate: test.metadata.lastFailure,
testAge: Date.now() - test.metadata.created,
dependencyCount: test.dependencies.length,
executionTime: test.metadata.avgExecutionTime
};
}
getRecommendation(prediction) {
if (prediction.confidence < 0.7) {
return {
action: 'review',
message: 'Low confidence prediction - manual review recommended'
};
}
if (prediction.outcome === 'flaky') {
return {
action: 'stabilize',
message: 'Test shows flaky behavior - consider refactoring'
};
}
if (prediction.outcome === 'fail' && prediction.confidence > 0.9) {
return {
action: 'fix_first',
message: 'High probability of failure - fix before running full suite'
};
}
return {
action: 'run_normal',
message: 'Test appears stable - run as normal'
};
}
createDashboard(predictions, trends, optimizations) {
const dashboard = {
summary: {
totalTests: predictions.length,
predictedFailures: predictions.filter(p => p.predictedOutcome === 'fail').length,
estimatedRuntime: predictions.reduce((sum, p) => sum + p.estimatedRuntime, 0),
confidenceAverage: predictions.reduce((sum, p) => sum + p.confidence, 0) / predictions.length
},
alerts: [],
recommendations: optimizations.recommendations,
charts: {
outcomeDistribution: this.calculateOutcomeDistribution(predictions),
confidenceDistribution: this.calculateConfidenceDistribution(predictions),
runtimePrediction: this.calculateRuntimePrediction(predictions)
}
};
// Generate alerts for high-risk situations
if (dashboard.summary.predictedFailures > predictions.length * 0.3) {
dashboard.alerts.push({
level: 'warning',
message: `High failure rate predicted: ${dashboard.summary.predictedFailures} out of ${predictions.length} tests`
});
}
return dashboard;
}
}
// Implementation example
const analytics = new PredictiveTestAnalytics();
const results = await analytics.generatePredictions(
latestCodeChanges,
currentTestSuite,
sixMonthTestHistory
);
console.log('Predictive Analytics Dashboard');
console.log('================================');
console.log(`Total Tests: ${results.dashboard.summary.totalTests}`);
console.log(`Predicted Failures: ${results.dashboard.summary.predictedFailures}`);
console.log(`Estimated Runtime: ${results.dashboard.summary.estimatedRuntime}ms`);
console.log(`Average Confidence: ${(results.dashboard.summary.confidenceAverage * 100).toFixed(1)}%`);
console.log('\nTop Recommendations:');
results.optimizations.recommendations.slice(0, 3).forEach((rec, index) => {
console.log(`${index + 1}. ${rec.title}`);
console.log(` Impact: ${rec.impact}`);
console.log(` Effort: ${rec.effort}\n`);
});整合:一个完整的人工智能测试框架
以下是这些组件如何在一个统一的框架中协同工作的方式:
class AITestingFramework {
constructor() {
this.generator = new AITestGenerator();
this.prioritizer = new IntelligentTestPrioritizer();
this.maintainer = new SelfHealingTestSuite();
this.analyzer = new FailurePatternAnalyzer();
this.predictor = new PredictiveTestAnalytics();
}
async runIntelligentTestCycle(codebase, options = {}) {
console.log('🤖 Starting AI-powered test cycle...\n');
// Phase 1: Generate tests for new/changed code
console.log('Phase 1: Generating tests...');
const generatedTests = await this.generator.generateTests(
codebase.changedFunctions,
options.generationOptions
);
console.log(`✅ Generated ${generatedTests.length} new tests\n`);
// Phase 2: Maintain existing tests
console.log('Phase 2: Maintaining existing tests...');
const maintenanceResult = await this.maintainer.maintainTests(
codebase.previousVersion,
codebase.currentVersion,
codebase.existingTests
);
console.log(`✅ Updated ${maintenanceResult.updatedTests.length} tests automatically\n`);
// Phase 3: Prioritize all tests
console.log('Phase 3: Prioritizing test execution...');
const allTests = [...generatedTests, ...maintenanceResult.updatedTests];
const prioritizedTests = await this.prioritizer.prioritizeTests(
{ tests: allTests },
codebase.changes,
codebase.history
);
console.log(`✅ Prioritized ${prioritizedTests.length} tests\n`);
// Phase 4: Predict outcomes
console.log('Phase 4: Generating predictions...');
const predictions = await this.predictor.generatePredictions(
codebase.changes,
{ tests: allTests },
codebase.testHistory
);
console.log(`✅ Generated predictions with ${(predictions.dashboard.summary.confidenceAverage * 100).toFixed(1)}% avg confidence\n`);
// Phase 5: Execute tests intelligently
console.log('Phase 5: Executing tests...');
const executionResults = await this.executeTestsIntelligently(
prioritizedTests,
predictions,
options.executionOptions
);
// Phase 6: Analyze results and learn
console.log('Phase 6: Analyzing results...');
const analysis = await this.analyzer.analyzeFailurePatterns(
executionResults,
codebase.metrics,
codebase.bugHistory
);
return {
testResults: executionResults,
predictions: predictions,
analysis: analysis,
recommendations: this.generateFinalRecommendations(
executionResults,
predictions,
analysis
),
metrics: this.calculateMetrics(executionResults, predictions)
};
}
async executeTestsIntelligently(prioritizedTests, predictions, options) {
const results = [];
let totalTime = 0;
const maxTime = options.maxExecutionTime || 300000; // 5 minutes default
for (const testItem of prioritizedTests) {
if (totalTime >= maxTime) {
console.log(`⏰ Time limit reached. Skipping remaining ${prioritizedTests.length - results.length} tests`);
break;
}
const prediction = predictions.predictions.find(p => p.testName === testItem.test.name);
// Skip tests predicted to pass with high confidence if we're running out of time
if (prediction && prediction.predictedOutcome === 'pass' &&
prediction.confidence > 0.95 && totalTime > maxTime * 0.8) {
console.log(`⏭️ Skipping high-confidence pass: ${testItem.test.name}`);
continue;
}
const startTime = Date.now();
const result = await this.executeTest(testItem.test);
const executionTime = Date.now() - startTime;
results.push({
...result,
executionTime,
prediction: prediction,
priority: testItem.priority
});
totalTime += executionTime;
// Early termination if we find critical failures
if (!result.passed && testItem.priority > 90) {
console.log(`🚨 Critical test failure detected: ${testItem.test.name}`);
console.log('Consider fixing this before continuing...');
}
}
return results;
}
generateFinalRecommendations(results, predictions, analysis) {
const recommendations = [];
// Accuracy assessment
const predictionAccuracy = this.calculatePredictionAccuracy(results, predictions);
if (predictionAccuracy < 0.8) {
recommendations.push({
type: 'model_improvement',
priority: 'high',
message: `Prediction accuracy is ${(predictionAccuracy * 100).toFixed(1)}% - consider retraining models`
});
}
// Test suite optimization
const redundantTests = this.identifyRedundantTests(results);
if (redundantTests.length > 0) {
recommendations.push({
type: 'optimization',
priority: 'medium',
message: `${redundantTests.length} potentially redundant tests identified`,
details: redundantTests.map(t => t.name)
});
}
// Combine with pattern analysis recommendations
recommendations.push(...analysis.recommendations);
return recommendations.sort((a, b) => {
const priorityOrder = { 'high': 3, 'medium': 2, 'low': 1 };
return priorityOrder[b.priority] - priorityOrder[a.priority];
});
}
}
// Usage example
const aiFramework = new AITestingFramework();
const result = await aiFramework.runIntelligentTestCycle({
changedFunctions: [calculateTax, processPayment, validateUser],
previousVersion: previousCodebase,
currentVersion: currentCodebase,
existingTests: existingTestSuite,
changes: gitDiff,
history: projectHistory,
testHistory: testExecutionHistory,
metrics: codeMetrics,
bugHistory: bugTrackingData
}, {
generationOptions: {
coverage: 'comprehensive',
includeEdgeCases: true
},
executionOptions: {
maxExecutionTime: 180000, // 3 minutes
parallelExecution: true
}
});
console.log('\n🎯 AI Testing Framework Results');
console.log('================================');
console.log(`Tests Executed: ${result.testResults.length}`);
console.log(`Pass Rate: ${(result.metrics.passRate * 100).toFixed(1)}%`);
console.log(`Prediction Accuracy: ${(result.metrics.predictionAccuracy * 100).toFixed(1)}%`);
console.log(`Time Saved: ${result.metrics.timeSaved}ms`);
console.log('\n📋 Top Recommendations:');
result.recommendations.slice(0, 5).forEach((rec, index) => {
console.log(`${index + 1}. [${rec.priority.toUpperCase()}] ${rec.message}`);
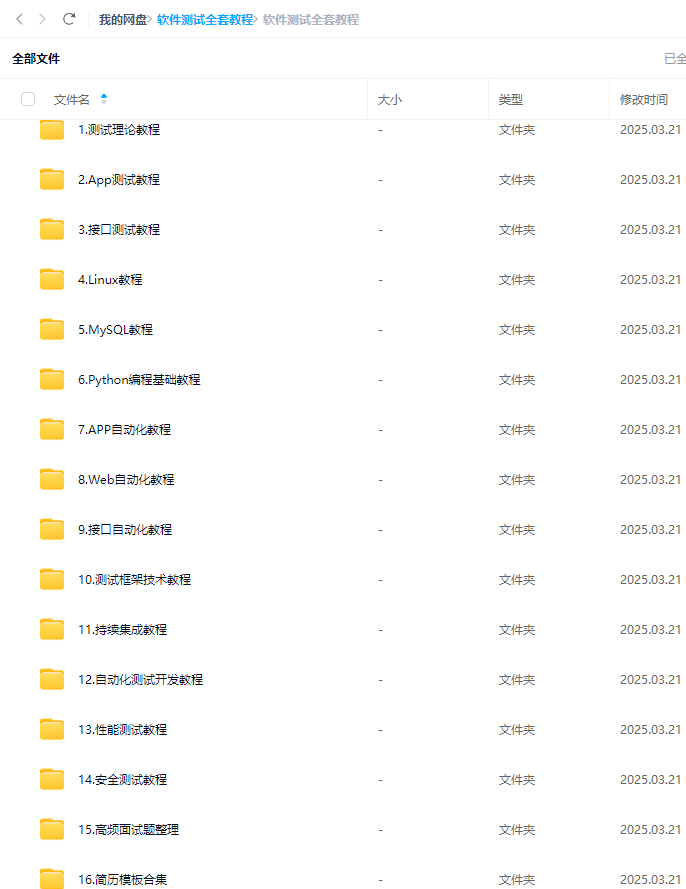
});最后: 下方这份完整的软件测试视频教程已经整理上传完成,需要的朋友们可以自行领取【保证100%免费】

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








