Chapter 11 AC power Analysis
11.1 Introduction
功率分析很重要······
Power analysis is of paramount importance.Power is the most important quantity in electric utilities,electronic,and communication systems,because such systems involve transmission of power from one point to another.
Also,every industrial and household electrical device-every fan,motor,lamp,pressing iron,TV,personal computer–has a power rating thatindicates how much power the equipment requires;exceeding the power rating can do permanentdamage to an appliance.
The most common form of electric power is 50-or 60-Hz ac power.
The choice of ac over dc allowed high-voltage power transmission from the power generating plant to the consumer.
Howpower is measured?
How electric utility companies charge their customers?
11.2 Instantaneous and Average Power(瞬时功率和平均功率)
中文部分
瞬时功率p

平均功率P(有功功率)
一般工程计量及电气设备标识功率

PF=power factor,只是个字母表示,别想多啦


无功功率Q

无功:能量没有“消耗“,能量在往复交换
注意:无功功率≠无用功率
如:一盏20瓦的日光灯,其功率因数约为0.5
工作时除需20多瓦(镇流器需消耗一部分有功功率)的有功功率发光外,还需约35乏的无功功率供镇流器的线圈建立交变磁场
有电磁线圈的电气设备(如电动机、变压器等),正常情况下不但从电源取得有功功率,同时还需从电源取得无功功率

在电路系统中,电感和电容的无功功率有互补作用
工程上认为电感吸收无功功率,而电容发出无功功率
视在功率(表观功率)S
S=UI(单位:伏安VA)
它是满足一端口电路有功功率和无功功率两者的需要时,要求外部提供的功率容量;或指电气设备的容量
工程上常用视在功率衡量电气设备在额定电压、电流条件下最大的负荷能力
有功功率、无功功率和视在功率关系


解法一计算等效阻抗

解法二计算 U ˙ , I ˙ \dot{U},\dot{I} U˙,I˙

解法三分开计算,再加起来
英文部分
Instantaneous power(瞬时功率)

Average power(平均功率/有功功率)

φ是电压电流相位差

有源在这里就指电容电感

Reactive power(无功功率)
无功功率表示单位时间内储能元件与外部电路进行能量交换的最大值
quadrature:正交,两者乘积为0


Z = R + j X , 电 阻 + 电 抗 , 有 功 功 率 + 无 功 功 率 Z=R+jX,电阻+电抗,有功功率+无功功率 Z=R+jX,电阻+电抗,有功功率+无功功率


波形特点由sin那一项决定,Q>0,吸收无功功率,感性;Q<0,发出无功功率,容性

电阻时刻吸收功率,电感电容不吸收功率,平均功率=有功功率=实际功率
视在功率
Maximum Average Power Transfer(最大用功功率传输)
中文部分


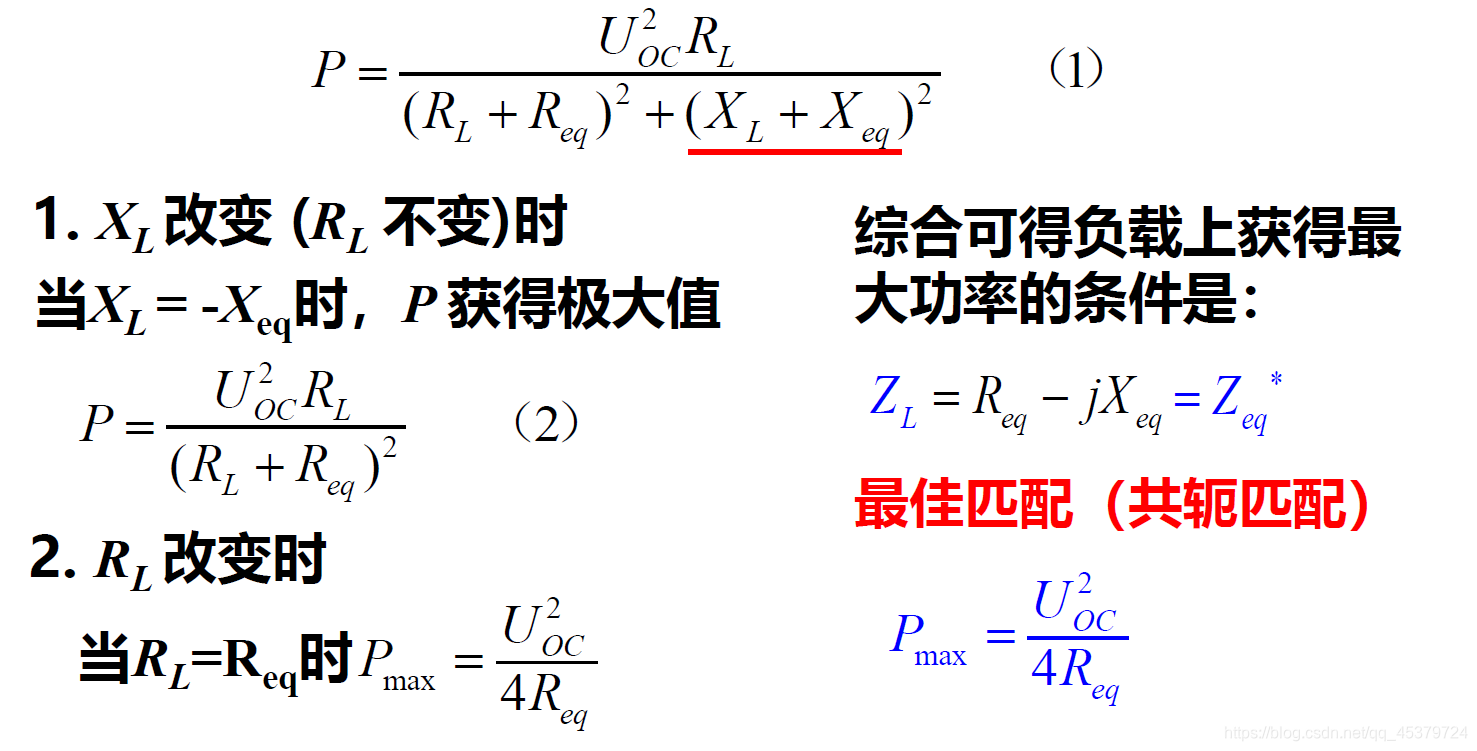
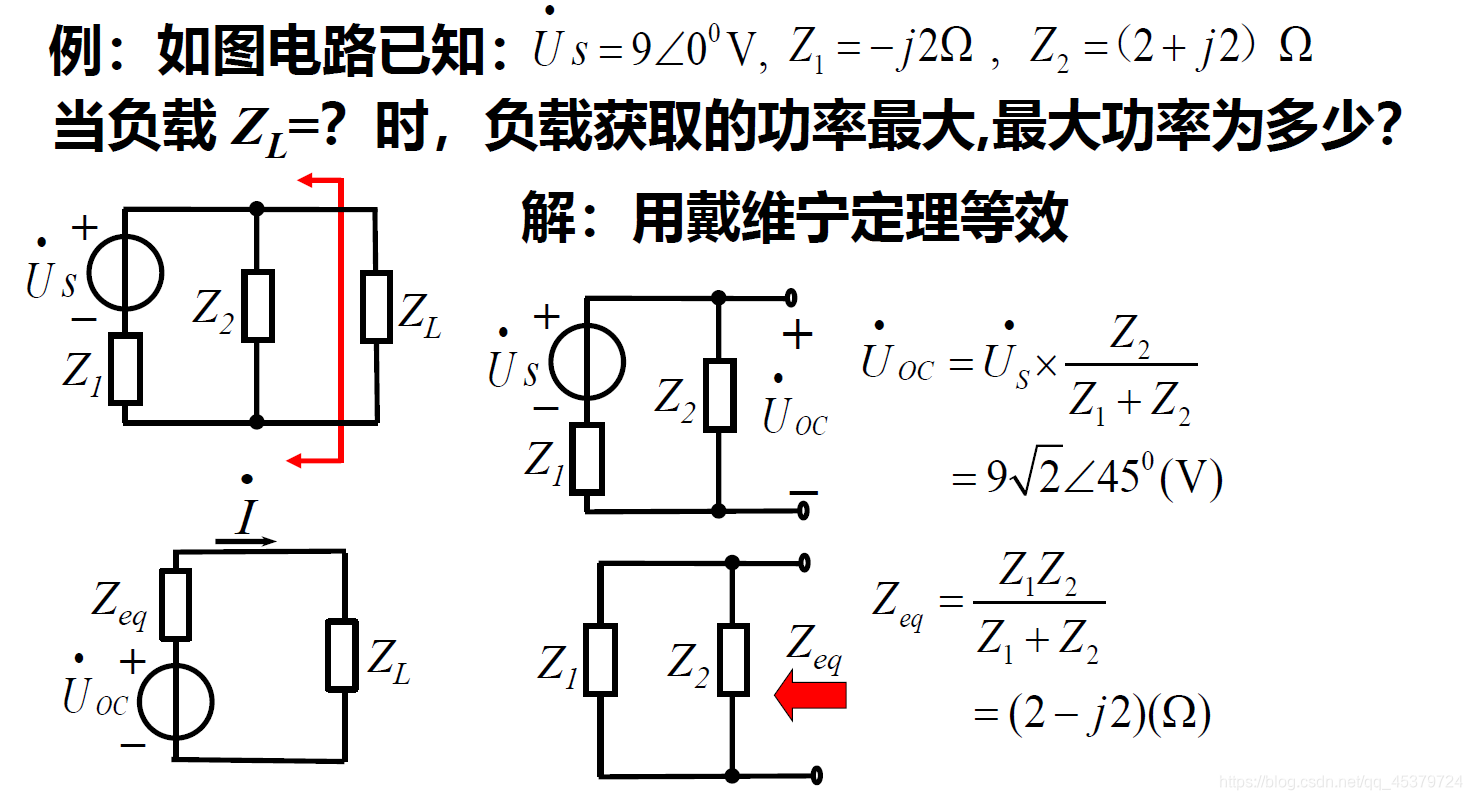
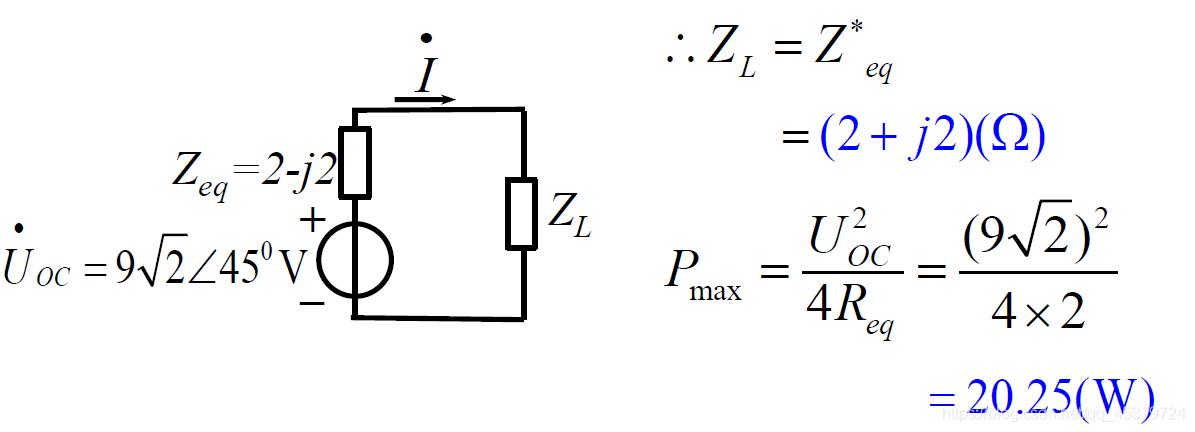
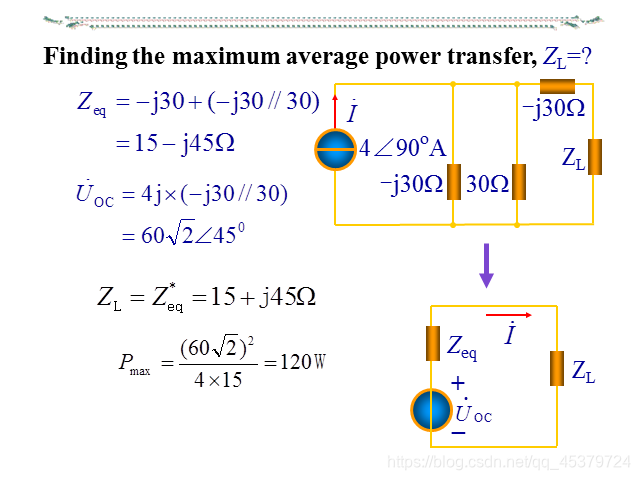
在通信系统、电子电路中,当传输的功率较小时,常常需要采取措施使阻抗匹配,实现信号的最大功率传输
英文部分
conjugate match(共轭匹配)


Magnitude match(模匹配)



加入动态元件,组成阻抗

并联导纳方便,电导+电纳









 本文深入探讨交流电的功率分析,包括瞬时功率、平均功率(有功功率)、无功功率和视在功率的概念。功率因数在电力系统中的重要性不言而喻,关系到设备的负荷能力和电能传输效率。文章还介绍了如何通过共轭匹配和模匹配实现最大功率传输,并讨论了功率因数校正的方法,以提高电力系统的效率。
本文深入探讨交流电的功率分析,包括瞬时功率、平均功率(有功功率)、无功功率和视在功率的概念。功率因数在电力系统中的重要性不言而喻,关系到设备的负荷能力和电能传输效率。文章还介绍了如何通过共轭匹配和模匹配实现最大功率传输,并讨论了功率因数校正的方法,以提高电力系统的效率。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








