非极大值抑制(NMS):去除掉与得分最高的目标框IOU值>thresh的目标框,保留与得分最高的目标框IOU值<thresh的目标框;
顾名思义就是抑制不是极大值的元素,搜索局部的极大值。例如在对象检测中,滑动窗口经提取特征,经分类器分类识别后,每个窗口都会得到一个分类及分数。但是滑动窗口会导致很多窗口与其他窗口存在包含或者大部分交叉的情况。这时就需要用到NMS来选取那些邻域里分数最高(是某类对象的概率最大),并且抑制那些分数低的窗口
用图片来理解一下:

基于前面的网络(如RPN)能为每个框给出一个score,score越大证明框越接近期待值。如上图,两个目标分别有多个选择框,现在要去掉多余的选择框。分别在局部选出最大框,然后去掉和这个框IOU>0.7的框。
非极大值抑制嘛,就是只留下极大值的意思。只留下极大值之后,就是下面的样子了:

算法:
输入:dets[x1,y1,x2,y2,score]为框列表 ,thresh为IOU值
1.将所有框按score值从大到小排序,将索引存储为列表order
2.取order中的第一个值(对应为score最大的框)
3.计算该框与其他框的IOU值
4.选取IOU<thresh的框
5.将选定的框的索引赋值给order
6.如果order中有值,则执行步骤2
下面时Fast R-CNN关于NMS的源代码(python版),Faster R-CNN也是用的这段代码。
import numpy as np
import cv2
def py_cpu_nms(dets, thresh):
"""Pure Python NMS baseline."""
x1 = dets[:, 0]
y1 = dets[:, 1]
x2 = dets[:, 2]
y2 = dets[:, 3]
scores = dets[:, 4]
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
#数组值从大到小的索引值,argsort()得到数组值从小到大的索引值,[::-1]倒序值
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
#求其他框与评分最高的框的共有区域
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]]) #xx1的值是按order中的排序返回的
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
#共有区域与两个框总面积的比值,获取其他目标框与得分最高的框IOU值
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= thresh)[0]
order = order[inds + 1] #获取与最高得分的边框IOU值小于thresh的框
return keep
if __name__=="__main__":
dets=np.array([[ -83., -39., 100., 56.,0.8],
[-175., -87., 192., 104.,0.7],
[-359., -183., 376., 200.,0.6],
[ -55., -55., 72., 72.,0.5],
[-119., -119., 136., 136.,0.55],
[-247., -247., 264., 264.,0.65],
[ -35., -79., 52., 96.,0.75],
[ -79., -167., 96., 184.,0.85],
[-167., -343., 184., 360.,0.9]])
print(dets.shape)
keep=py_cpu_nms(dets,0.3)
print(keep)
输出结果
(9, 5)
[8, 7, 0]
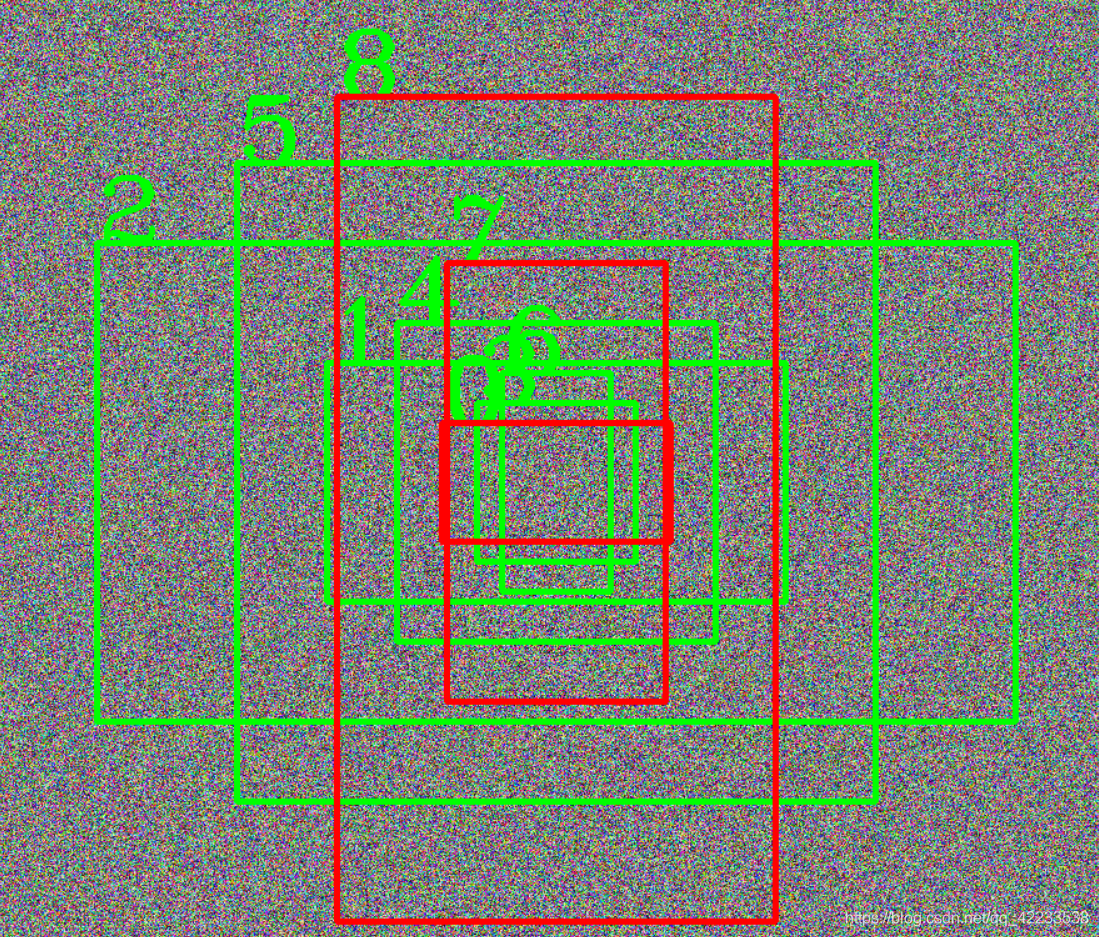
图像显示
import numpy as np
import cv2
dets = np.array([[-83., -39., 100., 56., 0.8],
[-175., -87., 192., 104., 0.7],
[-359., -183., 376., 200., 0.6],
[-55., -55., 72., 72., 0.5],
[-119., -119., 136., 136., 0.55],
[-247., -247., 264., 264., 0.65],
[-35., -79., 52., 96., 0.75],
[-79., -167., 96., 184., 0.85],
[-167., -300., 184., 360., 0.9]])
path='D:\document\\image1.jpg'
#图像只支持uint8类型数据,可以通过astype转变数据类型
img = np.array(np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(1024, 1024, 3)), dtype=np.uint8)
print(img)
#img=cv2.imread(path)
print(type(img))
w,h,c=img.shape
dets_t=dets[:,:4]+[h/2,w/2-100,h/2,w/2-100]
print(dets_t)
print(w,h,c)
for i in range(9):
x1=int(dets_t[i][0])
y1 = int(dets_t[i][1])
x2 = int(dets_t[i][2])
y2 = int(dets_t[i][3])
#x_center=int((x1+x2)/2)
#y_center=int((y1+y2)/2)
cv2.rectangle(img,(x1,y1), (x2,y2),(0,255,0),3)
cv2.putText(img,str(i),(x1,y1),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX_SMALL,4,(0,255,0),3)
for i in [8,7,0]:
x1= int(dets_t[i][0])
y1 = int(dets_t[i][1])
x2 = int(dets_t[i][2])
y2 = int(dets_t[i][3])
cv2.rectangle(img,(x1,y1), (x2,y2),(0,0,255),3)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()























 276
276

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








