文章目录
前情提要
deps目录(redis依赖的第三方、一些客户端的redis演进发展代码和Lua的脚本源码),src目录(功能模块源码),tests目录(功能测试代码),utils目录(Redis系统的一些辅助功能模块)。本博客主要学习src目录结构下的知识,可能涉及学习的知识包括:C语言、网络编程、数据结构算法等【学习jksj】,捡有用的学习。
SDS数据结构学习
为了节省内存空间,学会使用attribute(packed)结构的数据封装方式。

【sds结构:数据实际长度,分配的内存空间,SDS数据类型,实际数据存放的字符数组位置】

hash表学习
hash表的定义和hash链表节点的定义 (注意结构体中的union使用进行节省内存的小技巧)

注意:新版本的Redis不再定义单独的表结构


C语言的二级指针用法



Rehash过程学习
字典结构实际上有两张hash表之间的扩容与拷贝(总是从表0扩容到表1,并同时进行拷贝操作,最后再释放相应的表1)

下面这段扩容的逻辑值得好好品味一下(包括检查相应的backet是否为空,进行相应的backet的扩容位置序号的增加,以及相应两张表的承载键值对数量的增减,以及相应的表0与表1之间的互换操作)
/* Performs N steps of incremental rehashing. Returns 1 if there are still
* keys to move from the old to the new hash table, otherwise 0 is returned.
*
* Note that a rehashing step consists in moving a bucket (that may have more
* than one key as we use chaining) from the old to the new hash table, however
* since part of the hash table may be composed of empty spaces, it is not
* guaranteed that this function will rehash even a single bucket, since it
* will visit at max N*10 empty buckets in total, otherwise the amount of
* work it does would be unbound and the function may block for a long time. */
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
int empty_visits = n*10; /* Max number of empty buckets to visit. */
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;
while(n-- && d->ht_used[0] != 0) {
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
/* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more
* elements because ht[0].used != 0 */
assert(DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0]) > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx);
while(d->ht_table[0][d->rehashidx] == NULL) {
d->rehashidx++;
if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1;
}
de = d->ht_table[0][d->rehashidx];
/* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */
while(de) {
uint64_t h;
nextde = de->next;
/* Get the index in the new hash table */
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & DICTHT_SIZE_MASK(d->ht_size_exp[1]);
de->next = d->ht_table[1][h];
d->ht_table[1][h] = de;
d->ht_used[0]--;
d->ht_used[1]++;
de = nextde;
}
d->ht_table[0][d->rehashidx] = NULL;
d->rehashidx++;
}
/* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */
if (d->ht_used[0] == 0) {
zfree(d->ht_table[0]);
/* Copy the new ht onto the old one */
d->ht_table[0] = d->ht_table[1];
d->ht_used[0] = d->ht_used[1];
d->ht_size_exp[0] = d->ht_size_exp[1];
_dictReset(d, 1);
d->rehashidx = -1;
return 0;
}
/* More to rehash... */
return 1;
}
之后在每进行一次增/删/改/查都会执行一步进行扩容的操作,即函数_dictRehashStep(dict *d)被调用,注意这里dictRehash()函数中传入的执行步数都是1。






Zset有序set结构
(注意:源码位于server.h和t_zset.c文件中)
Zset结构=dict字典结构+跳表结构



注意:当元素比较少时采用的是压缩列表的结构–listpack结构,此时可以节省内存空间(可以从zset的add源码可以看出,添加元素需要先判断编码方式属于:listpack结构还是dict&skiplist结构)



skiplist寻找元素的逻辑

跳表结构在本层级寻找下一个元素的两个条件(如果两个条件均不满足,此时就会去寻找下一个层级):

跳表节点指针层级–随机生成
注意:这里不适用每个层级按照两倍关系进行设计(此时进行二分查找的复杂度也是log(N)),主要是因为这种关系太难维系了,一旦出现删除或者新增加新的元素就会出现这个两倍关系被破坏,防止引起连锁更新。

ziplist–>listpack结构转换
ziplist的节点中记录前节点的长度引起了连锁更新问题,于是listpack结构不再记录前节点的长度(问题:这个listpack结构如何移动自己的指针呢)



Listpack结构更新指针的方式:主要是依靠大量约定的编码方式实现的
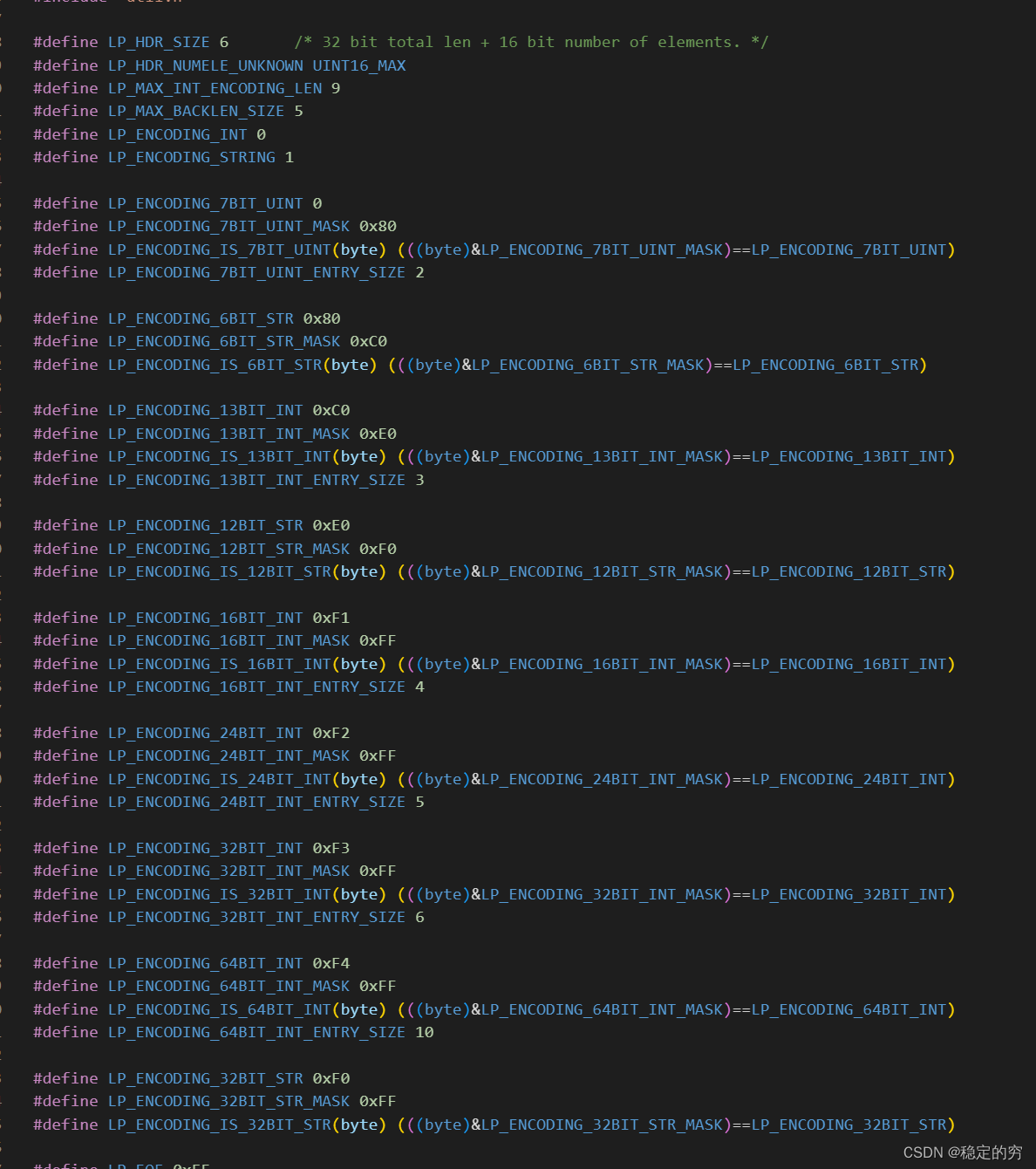
从左往右移动指针(前向移动指针)


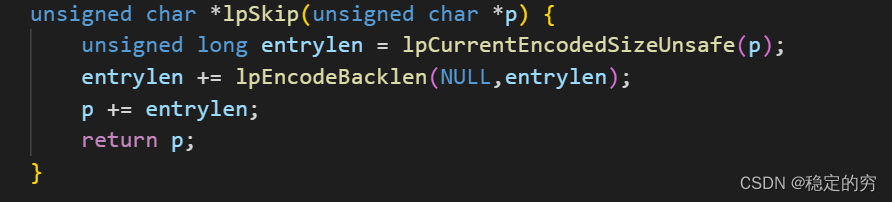
从右往左移动指针(后向移动指针)—实现方式;依赖于entry-len的大端保存方式(entry-len 每个字节的低 7 位采⽤了⼤端模式存储,也就是说,entry-len
的低位字节保存在内存⾼地址上。)

这里没有看懂的举手???









 本文深入探讨Redis中的数据结构,包括SDS的内存优化,哈希表的扩容与Rehash机制,C语言的二级指针应用,以及Zset的有序集合实现,特别关注了跳跃表(skiplist)的查找逻辑和ziplist到listpack的转换过程。
本文深入探讨Redis中的数据结构,包括SDS的内存优化,哈希表的扩容与Rehash机制,C语言的二级指针应用,以及Zset的有序集合实现,特别关注了跳跃表(skiplist)的查找逻辑和ziplist到listpack的转换过程。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








