文章目录
- 1. HelloWorld
- 2.springboot web 开发
- 3. SpringMVC自动配置原理--用于扩展各种需要的组件
- 4.Spring Boot 员工管理模块--(伪造的数据库--MAP键值对)版本--大多前端的知识(理清逻辑)
- 5. 整合JDBC(jdbctemplate)--不重要
- 6.整合Druid(阿里巴巴的数据库连接池)
- 7.整合mybatis
- 8.Spring Security(都是现成的东西 ,调用API即可---理清功能逻辑)--安全框架
- 9. Shiro(对比Spring Security)简单的安全框架--整合了数据库Mybatis的版本
- 10.Swagger(API在线文档的框架)--随着代码的改变实时更新API文档
- 11.异步、定时、邮件(使用对应的注解)
- 12.分布式:Dubbo和Zookeeper+Springboot集成
1. HelloWorld
插件爆红给,加入版本号

打包为jar包,点击package

打包不了或者用不了package,检查MavenHomePath是不是自己下载的maven

shfit+右键打开相应文件位置下的powershell窗口,测试自己打包的jar包

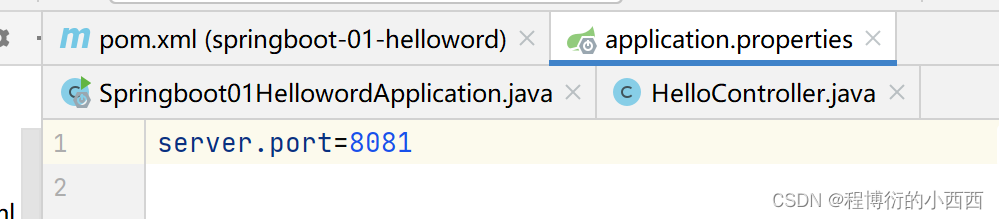
1.1更改服务器的访问端口号
1.2自定义springboot的banner

自定义网站

启动后的效果

1.3环境切换Spring profiles &&JSR303
properties的切换方式
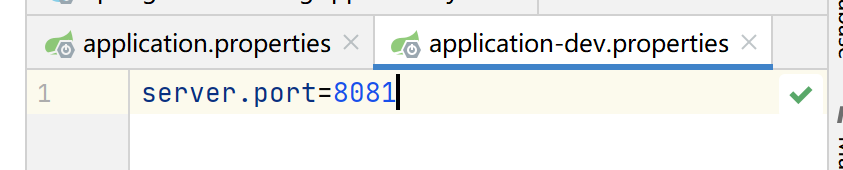

yaml的切换方式

JSR303数据校验

1.4自动配置的原理


2.springboot web 开发

2.1静态资源
2.1.1 官方默认的路径(看源码–WebMvcAutoConfiguration)


相同的文件名下,优先级依次降低


2.1.2 自定义的路径(最好别这样)


2.2模板引擎–thymeleaf
<!--thymeleaf-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
3. SpringMVC自动配置原理–用于扩展各种需要的组件
(@Bean注册一下自己定义的组件类—不在MyMvcConfig文件)
如果想让springboot来自动配置,@Configuration+实现WebMvcConfigurer接口

//同于扩展springmvc
//所以说,我们如果想要使用自己定制化的东西,我们只需要给容器中添加这个组件就好了
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
// 浏览器发送/kuang , 就会跳转到test页面;
registry.addViewController("/kuang").setViewName("test");
}
}
如果不想让springboot来自动配置,加上@EnableWebMvc的注解

4.Spring Boot 员工管理模块–(伪造的数据库–MAP键值对)版本–大多前端的知识(理清逻辑)
4.1首页配置

thymeleaf的命名空间
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
4.2 页面国际化

idea的设置里面确保所有的编码都是utf-8





//别忘了将这个本地解析器组件注册到我们的MyMvcConfig
public class MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver {
//解析请求
@Override
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) {
//获取请求中的国际化参数
String language = request.getParameter("l");
//默认的地区
Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();
//如果请求的链接参数不为空,携带了国际化参数
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(language)) {
String[] split = language.split("_");//zh_CN(语言_地区)
locale = new Locale(split[0], split[1]);//国家地区
}
return locale;
}
@Override
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) {
}
}
//本地解析器组件注册到我们的MyMvcConfig
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}
4.3 登录+拦截器(保证只有用户成功登陆后才能进入main.html)
逻辑1:用户名和密码正确的才会注册seesion&&并重定向访问main.html
逻辑2:为了只有登陆正确(等价于session注册后非空)的才能进入main.html,搞一个拦截器–只有session注册非空的才能进入main.html,其余情况都是被拦截的
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@RequestMapping("/user/login")
public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username,
@RequestParam("password") String password,
Model model,
HttpSession session){
//如果用户名和密码正确(就根据用户名来注册seesion)
if ("admin".equals(username) && "123456".equals(password)){
//只有用户名和密码正确的才会获得session
session.setAttribute("loginUser",username);
return "redirect:/main.html";//跳转到dashboard页面(重定向--保证安全型)
}
//如果用户名或者密码不正确
else {
model.addAttribute("msg", "用户名或者密码错误");//显示错误信息
return "index";//跳转到首页
}
}
}
public class LoginHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
//用户登录成功后,应该有自己的session
Object session = request.getSession().getAttribute("loginUser");
if (session == null) {
request.setAttribute("msg", "权限不够,请先登录");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.html").forward(request, response);
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
注册拦截器组件到mvc自动配置文件
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginHandlerInterceptor()).
addPathPatterns("/**").
excludePathPatterns("/index.html","/","/user/login","/css/*","/js/**","/img/**");
}
用到这个session的位置
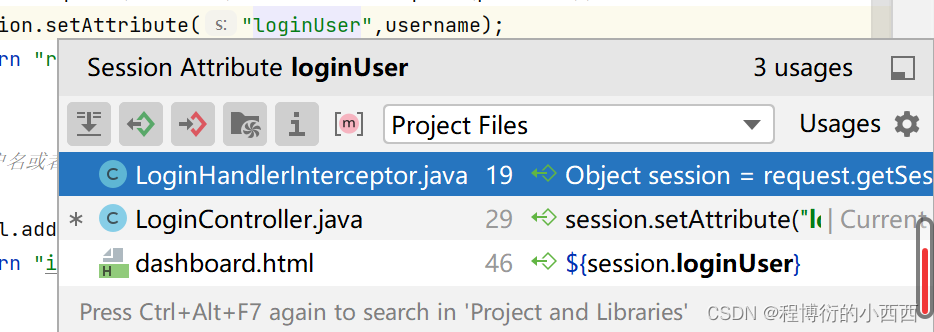
4.4展示员工列表
小技巧:如何复用相同的代码–thymeleaf的fragment碎片标签
<nav class="col-md-2 d-none d-md-block bg-light sidebar" th:fragment="sidebar">
<div th:insert="~{dashboard::sidebar}"></div>
小技巧:直接提取公共页面(建一个只存放公共部分代码的html)


前端的东西
<table class="table table-striped table-sm">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>id</th>
<th>lastName</th>
<th>email</th>
<th>gender</th>
<th>department</th>
<th>date</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="emp:${emps}">
<td th:text="${emp.getId()}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.getLastName()}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.getEmail()}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.getGender()==0?'女':'男'}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.getDepartment().getDepartmentName()}"></td>
<td th:text="${#dates.format(emp.getDate(),'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')}"></td>
<td>
<a class="btn btn-sm btn-primary">编辑</a>
<a class="btn btn-sm btn-danger">删除</a>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
4.5 增加员工的实现
<form th:action="@{/emp}" method="post">
<div class="form-group">
<label>LastName</label>
<input type="text" name="lastName" class="form-control" placeholder="lastname:zsr">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Email</label>
<input type="email" name="email" class="form-control" placeholder="email:xxxxx@qq.com">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Gender</label><br/>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gender" value="1">
<label class="form-check-label">男</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gender" value="0">
<label class="form-check-label">女</label>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>department</label>
<!--注意这里的name是department.id,因为传入的参数为id-->
<select class="form-control" name="department.id">
<option th:each="department:${departments}" th:text="${department.getDepartmentName()}" th:value="${department.getId()}"></option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Birth</label>
<!--springboot默认的日期格式为yy/MM/dd-->
<input type="text" name="date" class="form-control" placeholder="birth:yyyy/MM/dd">
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">添加</button>
</form>
注意待用dao层别忘了自动注入Autowired
@GetMapping("/emp")
public String add(Model model) {
//查出所有的部门信息,添加到departments中,用于前端接收
Collection<Department> departments = departmentDao.getDepartments();
model.addAttribute("departments", departments);
return "emp/add";//返回到添加员工页面
}
@PostMapping("/emp")
public String addEmp(Employee employee) {
employeeDao.addEmployee(employee);//添加一个员工
return "redirect:/emps";//重定向到/emps,刷新列表,返回到list页面
}
4.6修改员工的信息
别忘了在list.html中的编辑按钮加上跳转链接
<form th:action="@{/add}" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="id" th:value="${empByID.getId()}">
<div class="form-group">
<label>LastName</label>
<input th:value="${empByID.getLastName()}" type="text" name="lastName" class="form-control"
placeholder="lastname:zsr">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Email</label>
<input th:value="${empByID.getEmail()}" type="email" name="email" class="form-control"
placeholder="email:xxxxx@qq.com">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Gender</label><br/>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<input th:checked="${empByID.getGender()==1}" class="form-check-input" type="radio"
name="gender" value="1">
<label class="form-check-label">男</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<input th:checked="${empByID.getGender()==0}" class="form-check-input" type="radio"
name="gender" value="0">
<label class="form-check-label">女</label>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>department</label>
<!--注意这里的name是department.id,因为传入的参数为id-->
<select class="form-control" name="department.id">
<option th:selected="${department.getId()==empByID.department.getId()}"
th:each="department:${departments}" th:text="${department.getDepartmentName()}"
th:value="${department.getId()}">
</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Birth</label>
<!--springboot默认的日期格式为yy/MM/dd-->
<input th:value="${#dates.format(empByID.getDate(),'yyyy/MM/dd')}" type="text" name="date" class="form-control"
placeholder="birth:yy/MM/dd">
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">修改</button>
</form>
//restful风格接收参数
@RequestMapping("/edit/{id}")
public String edit(@PathVariable("id") int id, Model model) {
//查询指定id的员工,添加到empByID中,用于前端接收
Employee employeeByID = employeeDao.getEmployeeByID(id);
model.addAttribute("empByID", employeeByID);
//查出所有的部门信息,添加到departments中,用于前端接收
Collection<Department> departments = departmentDao.getDepartments();
model.addAttribute("departments", departments);
return "/emp/edit";//返回到编辑员工页面
}
@PostMapping("/add")
public String EditEmp(Employee employee) {
employeeDao.addEmployee(employee);//添加一个员工
return "redirect:/emps";//添加完成重定向到/emps,刷新列表
}
4.7删除一个员工信息
别忘了在list.html中的删除按钮加上跳转链接
@GetMapping("/delete/{id}")
public String delete(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
employeeDao.deleteEmployeeByID(id);
return "redirect:/emps";
}
4.8自定义404页面
只需要在templates目录下新建一个error包,然后将404.html放入其中,报错SpringBoot就会自动找到这个页面
4.9注销
<a class="nav-link" th:href="@{/user/logout}">注销</a>
@RequestMapping("/user/logout")
public String logout(HttpSession session) {
session.invalidate();
return "redirect:/index.html";
}
4.10 整个的逻辑梳理
按照controller层调dao层,controller层和前端交互

扩展Springmvc的组件:语言切换的本地解析器 + 拦截器

整个的前端与controller层之间的逻辑关系总结

登录的controller层
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@RequestMapping("/user/login")
public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username,
@RequestParam("password") String password,
Model model,
HttpSession session){
//如果用户名和密码正确(就根据用户名来注册seesion)
if ("admin".equals(username) && "123456".equals(password)){
//只有用户名和密码正确的才会获得session
session.setAttribute("loginUser",username);
return "redirect:/main.html";//跳转到dashboard页面(重定向--保证安全型)
}
//如果用户名或者密码不正确
else {
model.addAttribute("msg", "用户名或者密码错误");//显示错误信息
return "index";//跳转到首页
}
}
}
员工增删改查的controller层
@Controller
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeDao employeeDao;
@Autowired
private DepartmentDao departmentDao;
//来自于主页的侧边栏公共部分点击“员工列表”的跳转到列表list.html的控制
@RequestMapping("/emps")
public String list(Model model) {
Collection<Employee> employees = employeeDao.getAllEmployees();
model.addAttribute("emps",employees);
return "emp/list";//返回到list页面
}
//在list.html中,我们点击“添加员工列表”希望跳转到add.html的页面
@GetMapping("/emp")
public String add(Model model) {
//查出所有的部门信息,添加到departments中,用于前端接收
Collection<Department> departments = departmentDao.getDepartments();
model.addAttribute("departments", departments);
return "emp/add";//返回到添加员工页面
}
//在add.html中我们添加完后,提交能够重定向至员工列表的页面list.html
@PostMapping("/emp")
public String addEmp(Employee employee) {
employeeDao.addEmployee(employee);//添加一个员工
return "redirect:/emps";//重定向到/emps,刷新列表,返回到list页面
}
//在list.html中,我们点击“编辑”希望跳转到edit.html的页面
//restful风格接收参数
@RequestMapping("/edit/{id}")
public String edit(@PathVariable("id") int id, Model model) {
//查询指定id的员工,添加到empByID中,用于前端接收
Employee employeeByID = employeeDao.getEmployeeByID(id);
model.addAttribute("empByID", employeeByID);
//查出所有的部门信息,添加到departments中,用于前端接收
Collection<Department> departments = departmentDao.getDepartments();
model.addAttribute("departments", departments);
return "/emp/edit";//返回到编辑员工页面
}
//在edit.html中我们编辑修改完后,提交能够重定向至员工列表的页面list.html
@PostMapping("/add")
public String EditEmp(Employee employee) {
employeeDao.addEmployee(employee);//添加一个员工
return "redirect:/emps";//添加完成重定向到/emps,刷新列表
}
//在list.html中,我们点击“删除”希望重定向到list.html的页面
@GetMapping("/delete/{id}")
public String delete(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
employeeDao.deleteEmployeeByID(id);
return "redirect:/emps";
}
@RequestMapping("/user/logout")
public String logout(HttpSession session) {
//搞掉session
session.invalidate();
return "redirect:/index.html";
}
}
5. 整合JDBC(jdbctemplate)–不重要
6.整合Druid(阿里巴巴的数据库连接池)
7.整合mybatis
我发现我第一遍做错了(HellloController测试了一遍),后来删了重新来了一遍
UserMapper.xml实现需要别名+注册绑定mapper.xml(文件路径别写错了)
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=111111
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.kuang.pojo
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
dao/mapper层调用pojo层,使用@Repository注解
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> queryUserList();
}
controller层调用dao层
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
@RequestMapping("/u")
@ResponseBody
public List<User> queryUserList(){
List<User> users = userMapper.queryUserList();
return users;
}
}


8.Spring Security(都是现成的东西 ,调用API即可—理清功能逻辑)–安全框架
<!--thymeleaf和spring-security的一些包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-java8time</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5</artifactId>
</dependency>

8.1注意自定义API与框架现成API的区分
自己的登陆页面和springsecurity的登陆页面不同
springsecurity:url:“8080/login”
http.formLogin();

自己定义的:url:“8080/tologin”
http.formLogin().loginPage("/toLogin");//定制自己的登陆页面

注意使用自己定制的登陆页面还需要注意login.html中表单提交的登陆地址!!!具体注意点看狂神的笔记,显然springsecurity的自带的login更加方便,自定义的需要很多的注意点
8.2 登陆认证与访问权限的配置类
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//用户登录认证的方法
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
//在内存中定义,也可以在jdbc中去拿....
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder())
.withUser("kuangshen").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip2","vip3")
.and()
.withUser("root").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip1","vip2","vip3")
.and()
.withUser("guest").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip1");
}
//链式编程,用户登录后相关页面的授权的方法
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// 定制请求的授权规则
// 首页所有人可以访问
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("vip1")
.antMatchers("/level2/**").hasRole("vip2")
.antMatchers("/level3/**").hasRole("vip3");
// 开启自动配置的登录功能
// 没有权限进入登录页
// /login?error 重定向到这里表示登录失败
http.formLogin()
.usernameParameter("username")
.passwordParameter("password")
.loginPage("/toLogin").loginProcessingUrl("/lg");//定制自己的登陆页面
http.csrf().disable();//关闭csrf功能:跨站请求伪造,默认只能通过post方式提交logout请求
//开启自动注销功能,并跳转到首页
http.logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/");
// 记住我:cookie的实现(默认保存两周),自定义接收前端的参数
http.rememberMe().rememberMeParameter("remember");
}
}
@Controller
public class RouterController {
@RequestMapping({"/","/index"})
public String index(){
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/toLogin")
public String toLogin(){
return "views/login";
}
@RequestMapping("/level1/{id}")
public String level1(@PathVariable("id") int id){
return "views/level1/"+id;
}
@RequestMapping("/level2/{id}")
public String level2(@PathVariable("id") int id){
return "views/level2/"+id;
}
@RequestMapping("/level3/{id}")
public String level3(@PathVariable("id") int id){
return "views/level3/"+id;
}
}
9. Shiro(对比Spring Security)简单的安全框架–整合了数据库Mybatis的版本
9.1 具体的shiro的原理

总体了解

9.2 具体的实现逻辑代码(注意和前端以及数据库的交互—所以这个是个mybatis的框架)
自定义Realm,来自定义用户的登录认证 和 用户访问的授权
//自定义一个realm
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
//用户登录的认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
//打印一个提示
System.out.println("执行了认证方法");
//通过参数获取登录的控制器中生成的 令牌
UsernamePasswordToken token = (UsernamePasswordToken) authenticationToken;
// 用户名密码--连接真实的数据库(数据库中的用户都是合法的用户--秒a)
User user = userService.queryUserByName(token.getUsername());
//用户名认证
if (user==null){
// return null 就表示控制器中抛出的相关异常
return null;
}
Subject currentSubject= SecurityUtils.getSubject();
Session session = currentSubject.getSession();
session.setAttribute("loginUser",user);
//密码认证, Shiro 自己做,为了避免和密码的接触
//最后返回一个 AuthenticationInfo 接口的实现类,这里选择 SimpleAuthenticationInfo
// 三个参数:获取当前用户的认证 ; 密码 ; 认证名
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user, user.getPwd(), "");
}
//用户登录后相关操作的授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
//打印一个提示
System.out.println("执行了授权方法");
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
//拿到登陆的用户对象
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//来自于下面的认证里的user(shiro自己设计的两个方法的联动)
User curUser = (User) subject.getPrincipal();
info.addStringPermission(curUser.getPerms());
return info;
}
}
shiro的三要素:注意三者之间的对接—使用bean-name+Qualifier注解来联动
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
// subject -> ShiroFilterFactoryBean
@Bean(name="shiroFilterFactoryBean")
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("DefaultWebSecurityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
//关联securityManager,设置安全管理器
bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
//添加 Shiro 的内置过滤器拦截=======================
/*
anon : 无需认证,就可以访问
authc : 必须认证,才能访问
user : 必须拥有 “记住我”功能才能用
perms : 拥有对某个资源的权限才能访问
role : 拥有某个角色权限才能访问
*/
Map<String, String> filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// 设置 /user/ 下面的所有请求,只有认证过才能访问(没有认证就去登陆页面)
filterMap.put("/user/*","authc");
//授权的操作
filterMap.put("/user/add","perms[user:add]");
filterMap.put("/user/update","perms[user:update]");
bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap);
bean.setLoginUrl("/toLogin");//认证通过的用户可以进入登陆页面
bean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/unauth");//设置没有授权的跳转页面
return bean;
}
// securityManager -> DefaultWebSecurityManager
@Bean(name="DefaultWebSecurityManager")
public DefaultWebSecurityManager getDefaultWebSecurityManager(@Qualifier("userRealm1") UserRealm userRealm){
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
//关联realm
securityManager.setRealm(userRealm);
return securityManager;
}
// 创建realm对象,需要自定义类(被spring托管)---用于实现用户的认证
@Bean
public UserRealm userRealm1(){
return new UserRealm();
}
// 整合shiroDialect:用来整合shiro-thymeleaf
@Bean
public ShiroDialect getShiroDialect(){
return new ShiroDialect();
}
}
controller层的设置(用于前端与数据库以及shiro的安全框架之间的交互)
@Controller
public class Mycontroller {
@RequestMapping({"/","/index"})
public String toIndex(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","hello");
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/user/add")
public String add(){
return "user/add";
}
@RequestMapping("/user/update")
public String update(){
return "user/update";
}
@RequestMapping("/toLogin")
public String toLogin(){
return "login";
}
//登录的方法(这个实际上是post请求)
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(String username, String password, Model model) {
//获取当前用户
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//封装用户的登录数据,获得(制作成)令牌
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password);
//登录 及 异常处理
try {
//用户登录
subject.login(token);
return "index";
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {
//如果用户名不存在
System.out.println("用户名不存在");
model.addAttribute("exception", "用户名不存在");
return "login";
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
//如果密码错误
System.out.println("密码错误");
model.addAttribute("exception", "密码错误");
return "login";
}
}
//未授权的页面
@RequestMapping("/unauth")
@ResponseBody
public String unauthorized(){
return "未经授权无法访问该页面";
}
}
9.3 大体的认证与权限的安全设置的逻辑

10.Swagger(API在线文档的框架)–随着代码的改变实时更新API文档

解决版本之间不兼容问题
spring.mvc.pathmatch.matching-strategy=ant_path_matcher
不容易a
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
10.1设置要显示的配置环境的swagger–swagger开关的应用


显然在ipro的配置环境下,不会显示swagger
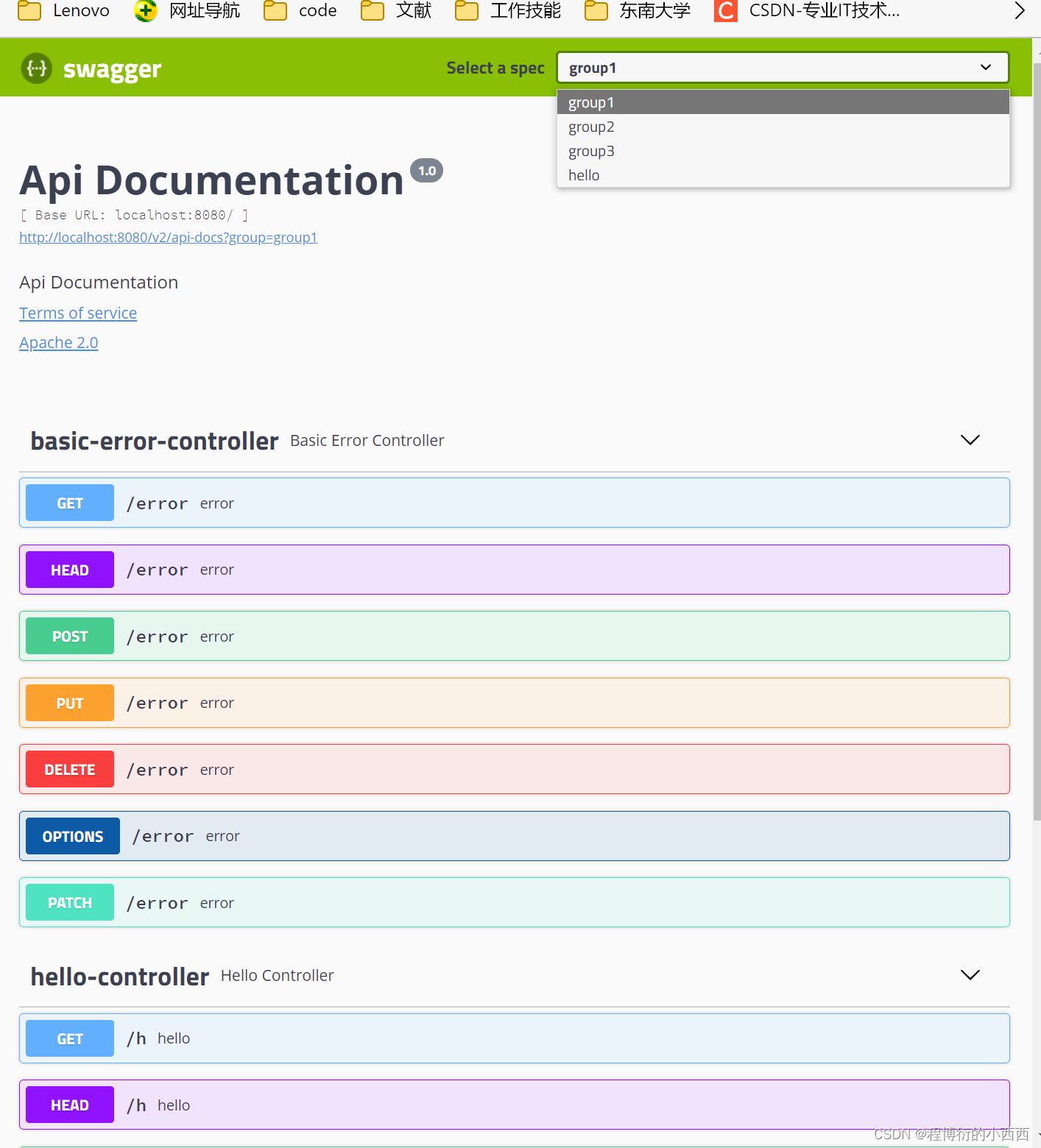
10.2 设置API文档的分组
配置多个分组只需要配置多个docket(不要重名)即可:
@Bean
public Docket docket1(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group1");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket2(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group2");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket3(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group3");
}
10.3swagger给API注释的注解

11.异步、定时、邮件(使用对应的注解)
12.分布式:Dubbo和Zookeeper+Springboot集成
12.1分布式架构


mvc三层架构:

RPC:分布式服务架构

12.2 RPC 远程过程调用

12.3 Dubbo(Java RPC框架)

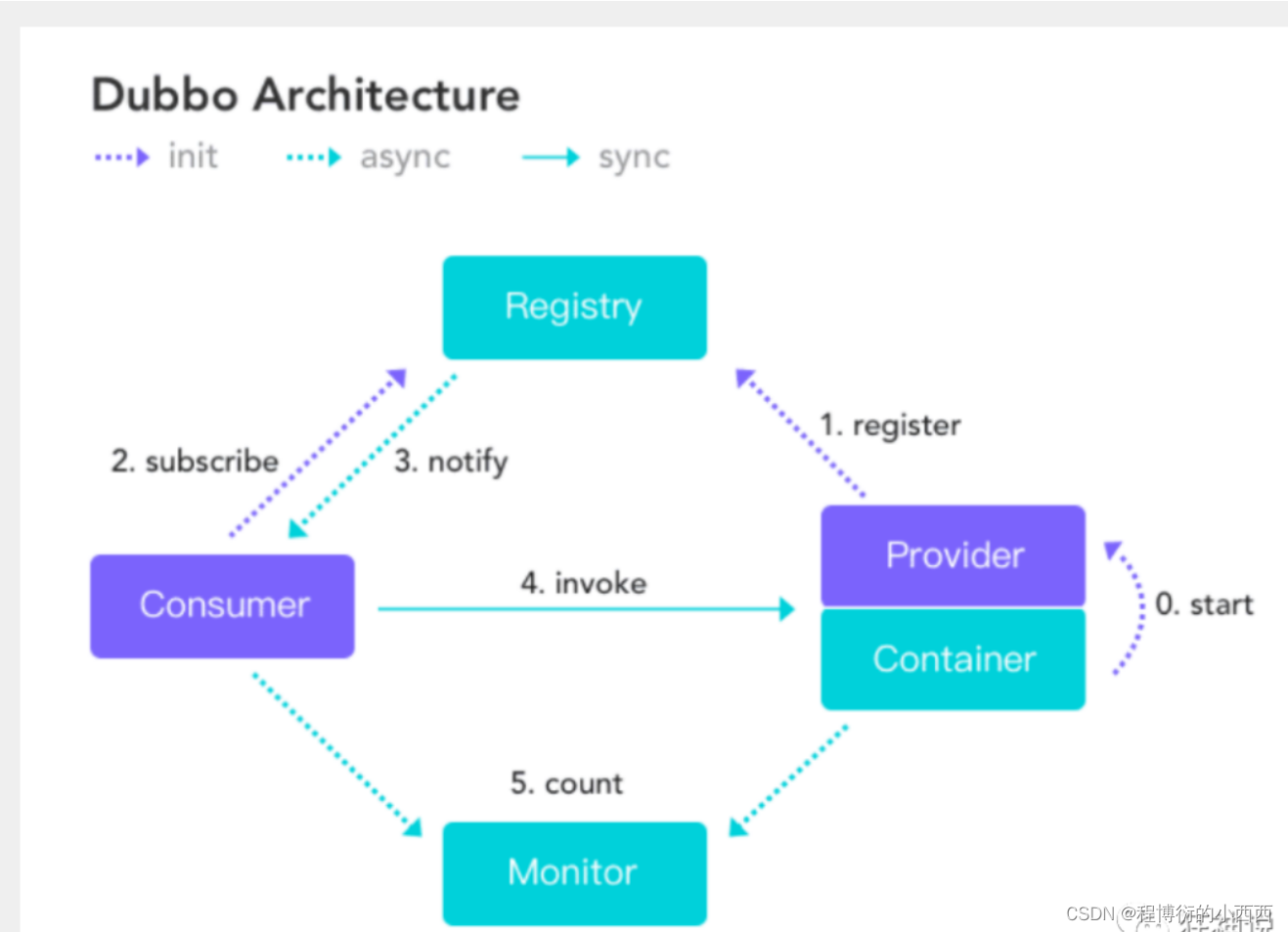

我zookeeper安装3.4失败了,3.7貌似成功了
主要是两个独立项目之间的联动,利用zookeeprer作为中间人存储一定的信息


























 654
654

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








