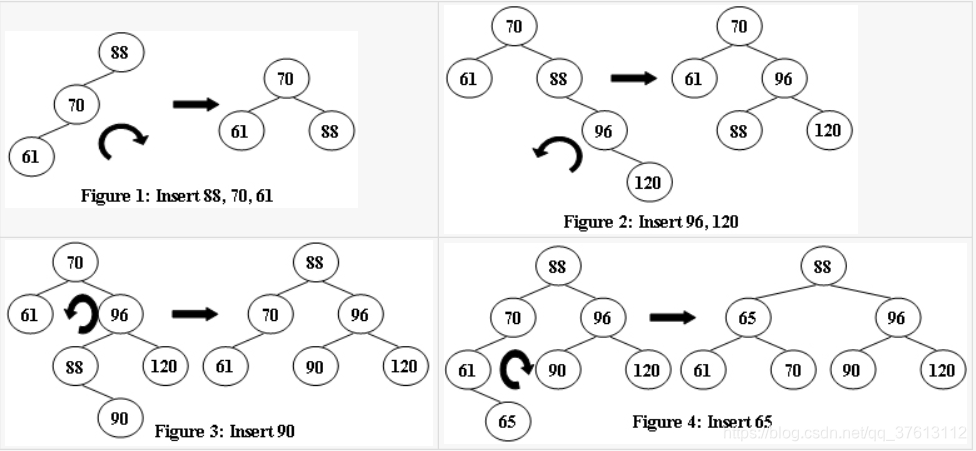
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
 Now given a sequence of insertions, you are supposed to output the level-order traversal sequence of the resulting AVL tree, and to tell if it is a complete binary tree.
Now given a sequence of insertions, you are supposed to output the level-order traversal sequence of the resulting AVL tree, and to tell if it is a complete binary tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤ 20). Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, insert the keys one by one into an initially empty AVL tree. Then first print in a line the level-order traversal sequence of the resulting AVL tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line. Then in the next line, print YES if the tree is complete, or NO if not.
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
typedef struct node {
int data, depth = 1;
node* l = NULL, * r = NULL;
}*tree;
int n;
int getDepth(tree t) {
if (t == NULL)return 0;
else
return getDepth(t->r) > getDepth(t->l) ? getDepth(t->r) + 1 : getDepth(t->l) + 1;
}
int getDegree(tree t) {
return getDepth(t->l) - getDepth(t->r);
}
void R(tree &t) {
tree temp = t->l;
t->l = temp->r;
temp->r = t;
temp->depth = getDepth(temp);
t->depth = getDepth(t);
t = temp;
}
void L(tree& t) {
tree temp = t->r;
t->r = temp->l;
temp->l = t;
temp->depth = getDepth(temp);
t->depth = getDepth(t);
t = temp;
}
void insert(tree& t,int data) {
if (t == NULL) {
t = new node();
t->data = data;
return;
}
if (data < t->data) {
insert(t->l, data);
if (getDegree(t) == 2) {
if (getDegree(t->l) == 1) {
R(t);
}
else if (getDegree(t->l) == -1) {
L(t->l);
R(t);
}
}
}
else {
insert(t->r, data);
if (getDegree(t) == -2) {
if (getDegree(t->r) == -1) {
L(t);
}
else if (getDegree(t->r) == 1) {
R(t->r);
L(t);
}
}
}
}
void level(tree t,bool &isCBT) {
queue<tree>q;
q.push(t);
int i = 0;
bool flag = false;
while (!q.empty()) {
tree temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if (temp != NULL) {
if (i != n - 1)cout << temp->data << " ";
else
cout << temp->data << endl;
i++;
if (flag)isCBT = false;
q.push(temp->l);
q.push(temp->r);
}
else
flag = true;
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
tree t = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int d;
cin >> d;
insert(t, d);
}
bool isCBT = true;
level(t, isCBT);
if (isCBT)cout << "YES" << endl;
else
cout << "NO" << endl;
return 0;
}





















 711
711

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








