一、join
在多表关联查询场景中,join是常用的方式。join,汉译为“连接”。连接分为内连接(inner join)和外连接(out join)。外连接分为左外连接和右外连接和全外连接,它们由分别简称为“左连接(left join)”、“右连接(right join)”和“全连接(full join)”。当只使用关键字“join”时,等同于内连接(inner join)。
0.准备数据
-- 1.学生表:学号,姓名,性别,年龄
-- 1)建表:
create table t_student(p_id int(4),name varchar(10),gender char(2),age int(2));
-- 2)插入数据:
insert into t_student values (1,'小红','女',13);
insert into t_student values (2,'小明','男',14);
insert into t_student values (4,'小刘','男',13);
-- 2.考试成绩表:学号,语文成绩,数学成绩,英语成绩,学期,学年
-- 1)建表:
create table t_result(student_id int(4),chinese_result int(3),math_result int(3),english_result int(3),trimester int(1),year int(4));
-- 2)插入数据:
insert into t_result values (1,95,69,98,1,2019);
insert into t_result values (1,97,77,95,2,2019);
insert into t_result values (1,95,80,90,1,2020);
insert into t_result values (1,86,73,91,2,2020);
insert into t_result values (2,68,89,49,1,2019);
insert into t_result values (2,74,96,66,1,2020);
insert into t_result values (2,85,98,59,2,2020);
insert into t_result values (3,95,99,99,1,2019);
insert into t_result values (3,96,100,100,2,2019);
insert into t_result values (3,97,100,100,1,2020);
insert into t_result values (3,98,100,100,2,2020);1.内连接(inner join)or join
select t1.name,t2.chinese_result,t2.math_result,t2.english_result,t2.trimester,t2.year
from t_student t1 join t_result t2
on t1.p_id=t2.student_id;
select t1.name,t2.chinese_result,t2.math_result,t2.english_result,t2.trimester,t2.year
from t_student t1 inner join t_result t2
on t1.p_id=t2.student_id;
查询结果:

2.left join
select t1.name,t2.chinese_result,t2.math_result,t2.english_result,t2.trimester,t2.year
from t_student t1 left join t_result t2
on t1.p_id=t2.student_id;查询结果:

3.right join
select t1.name,t2.chinese_result,t2.math_result,t2.english_result,t2.trimester,t2.year
from t_student t1 RIGHT join t_result t2
on t1.p_id=t2.student_id;查询结果:

4.full join
select t1.name,t2.chinese_result,t2.math_result,t2.english_result,t2.trimester,t2.year
from t_student t1 left join t_result t2
on t1.p_id=t2.student_id
union
select t1.name,t2.chinese_result,t2.math_result,t2.english_result,t2.trimester,t2.year
from t_student t1 RIGHT join t_result t2
on t1.p_id=t2.student_id;
-- 由于我使用的是MySQL数据库服务,其不支持“full join”
-- 因此我们使用left join + union + right join来实现(上面一段代码)。等同于:
select t1.name,t2.chinese_result,t2.math_result,t2.english_result,t2.trimester,t2.year
from t_student t1 full join t_result t2
on t1.p_id=t2.student_id;5.小结
5.0 原始数据
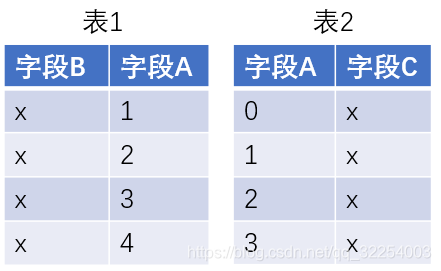
5.1 inner join

5.2 left join

5.3 right join

5.4 full join

二、开窗函数
0.数据准备
数据表(Oracle):T_Person 表保存了人员信息,FName 字段为人员姓名,FCity 字段为人员所在的城市名,FAge 字段为人员年龄,FSalary 字段为人员工资
-- 1)建表
CREATE TABLE T_Person (FName string,FCity string,FAge INT,FSalary INT)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
-- 2)插入数据
INSERT INTO T_Person VALUES('Tom','BeiJing',20,3000);
INSERT INTO T_Person VALUES('Tim','ChengDu',21,4000);
INSERT INTO T_Person VALUES('Jim','BeiJing',22,3500);
INSERT INTO T_Person VALUES('Lily','London',21,2000);
INSERT INTO T_Person VALUES('John','NewYork',22,1000);
INSERT INTO T_Person VALUES('YaoMing','BeiJing',20,3000);
INSERT INTO T_Person VALUES('Swing','London',22,2000);
INSERT INTO T_Person VALUES('Guo','NewYork',20,2800);
INSERT INTO T_Person VALUES('YuQian','BeiJing',24,8000);
INSERT INTO T_Person VALUES('Ketty','London',25,8500);
INSERT INTO T_Person VALUES('Kitty','ChengDu',25,3000);
INSERT INTO T_Person VALUES('Merry','BeiJing',23,3500);
INSERT INTO T_Person VALUES('Smith','ChengDu',30,3000);
INSERT INTO T_Person VALUES('Bill','BeiJing',25,2000);
INSERT INTO T_Person VALUES('Jerry','NewYork',24,3300);
1.聚合开窗函数
聚合开窗函数可以使用SUM、AVG、MAX、MIN、COUNT等聚合函数,但是需要注意聚合开窗函数只能使用PARTITION BY子句,ORDER BY不能与聚合开窗函数一同使用。
1.1 求满足条件的数据的总行数
count(*)over()
查询每个工资小于 5000 元的员工信息(城市以及年龄),并且在每行中都显示所有工资小于 5000 元的员工个数:
select fname, fcity, fsalary,
count(*) over() a -- 总人数
from t_person
where fsalary < 5000;
-- 类似于如下 使用子查询 实现的效果:
select fname,
fcity,
fsalary,
(select count(*) from t_person where fsalary < 5000) -- 工资少于5000员工总数
from t_person
where fsalary < 5000;运行结果:
Guo NewYork 2800 13
Swing London 2000 13
YaoMing BeiJing 3000 13
John NewYork 1000 13
Lily London 2000 13
Jim BeiJing 3500 13
Jerry NewYork 3300 13
Bill BeiJing 2000 13
Smith ChengDu 3000 13
Merry BeiJing 3500 13
Kitty ChengDu 3000 13
Tim ChengDu 4000 13
Tom BeiJing 3000 131.2 求各个分区的总行数
count(*) over(partition by fcity)
select fname,
fcity,
fage,
fsalary,
count(*) over(partition by fcity) a -- 所在分区的行数
from t_person;运行结果:
Tom BeiJing 20 3000 6
YuQian BeiJing 24 8000 6
YaoMing BeiJing 20 3000 6
Jim BeiJing 22 3500 6
Bill BeiJing 25 2000 6
Merry BeiJing 23 3500 6
Kitty ChengDu 25 3000 3
Tim ChengDu 21 4000 3
Smith ChengDu 30 3000 3
Lily London 21 2000 3
Swing London 22 2000 3
Ketty London 25 8500 3
Jerry NewYork 24 3300 3
Guo NewYork 20 2800 3
John NewYork 22 1000 31.3 求到当前行 对应列 的数值之和
sum(fsalary) over(order by fsalary rows between unbounded preceding and current row) a
(注解:unbounded preceding -- 无上界,从第一行开始;current row -- 当前行)
select fname,
fcity,
fage,
fsalary,
sum(fsalary) over(order by fsalary rows between unbounded preceding and current row) a -- 到当前行工资的和
from t_person;运行结果:
John NewYork 22 1000 1000
Swing London 22 2000 3000
Lily London 21 2000 5000
Bill BeiJing 25 2000 7000
Guo NewYork 20 2800 9800
Smith ChengDu 30 3000 12800
Kitty ChengDu 25 3000 15800
YaoMing BeiJing 20 3000 18800
Tom BeiJing 20 3000 21800
Jerry NewYork 24 3300 25100
Jim BeiJing 22 3500 28600
Merry BeiJing 23 3500 32100
Tim ChengDu 21 4000 36100
YuQian BeiJing 24 8000 44100
Ketty London 25 8500 526001.4 小结
聚合函数() over()这里的“聚合函数() over()”,前者“聚合函数()”用来控制“对哪些列?做什么聚合?”,后者“over()”表示“对哪些行?”。

聚合函数
聚合函数可以使用SUM、AVG、MAX、MIN、COUNT等聚合函数,来实现聚合操作。
控制列
列通过在调用聚合函数时传入实参(函数后面的括号)来指定。
控制行
行通过over()的括号中传入“一些操作”来实现。一些操作:可以是空,表示*,即对所有数据进行聚合操作;可以是分区函数“PARTITION BY”子句用来定义“在行的分区内部进行聚合计算”。
2.排名开窗函数
2.1 各排名函数的特点
| 特点 | 函数名 |
| 排名并列算两个 | rank() |
| 排名并列算一个 | dense_rank() |
| 排名不并列 | row_number() |
例如:
| 姓名 | 地区 | 分数 | rank | dense_rank | row_number |
| 小李 | 安徽 | 91 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 小丁 | 安徽 | 90 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 小赵 | 安徽 | 90 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| 小丑 | 安徽 | 77 | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| 小甲 | 安徽 | 68 | 5 | 4 | 5 |
| 小子 | 广东 | 98 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 小卯 | 广东 | 96 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 小孙 | 广东 | 85 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 小丙 | 广东 | 67 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 小红 | 江苏 | 98 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 小明 | 江苏 | 98 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 小钱 | 江苏 | 98 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 小乙 | 江苏 | 81 | 4 | 2 | 4 |
| 小寅 | 江苏 | 79 | 5 | 3 | 5 |
排名的数值上的特点:

2.2 使用方法
语法:
select *, rank() over(partition by 分组列 order by 排名列 desc)as 排名
from 成绩表;
select *, dense_rank() over(partition by 分组列 order by 排名列 desc)as 排名
from 成绩表;
select *, row_number() over(partition by 分组列 order by 排名列 desc)as 排名
from 成绩表;实例:
select *, rank() over(partition by 地区 order by 分数 desc)as 排名
from 成绩表;
select *, dense_rank() over(partition by 地区 order by 分数 desc)as 排名
from 成绩表;
select *, row_number() over(partition by 地区 order by 分数 desc)as 排名
from 成绩表;如果需要获取指定排名或之前的数据,可配合子查询实现。
select * from (
select *, rank() over(partition by 分组列 order by 排名列 desc)as 排名
from 成绩表) as t
where 排名=N;
select * from (
select *, rank() over(partition by 分组列 order by 排名列 desc)as 排名
from 成绩表) as t
where 排名<N;























 568
568

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








