接前一篇文章:Linux内核进程管理子系统有什么第六回 —— 进程主结构详解(2)
本文内容参考:
Linux内核进程管理专题报告_linux rseq-优快云博客
《趣谈Linux操作系统 核心原理篇:第三部分 进程管理》—— 刘超
《图解Linux内核 基于6.x》 —— 姜亚华 机械工业出版社
特此致谢!
进程管理核心结构 —— task_struct
上一回给出了Linux内核源码中struct task_struct的定义,并且说明了理解和掌握此巨大的结构的方法。

那么从本回开始,就要深入到task_struct结构中,研究其各个成员了。
1. 任务ID相关成员
首先来看任务ID相关的成员。包括以下几个成员:
pid_t pid;
pid_t tgid;
struct task_struct *group_leader;
struct list_head thread_group;这几个字段的描述如下:
| 字段 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| pid | pid_t | 进程id(准确地说应该是任务id) |
| tgid | pid_t | 进程所属的线程组的id |
| group_leader | struct task_struct * | 进程所处的线程组的领导进程 |
| thread_group | list_head | 将进程链接到线程组中,链表的表头为新城组领导进程的thread_group字段 |
前文书讲了进程和线程,Linux实际上并没有从本质上将进程和线程分开,线程又被称为轻量级进程(Low Weight Process,LWP)。这一点,从前文书(Linux内核进程管理子系统有什么第三回 —— 进程进阶知识(上)-优快云博客)所讲的进程和线程的区别中,就可见一斑。

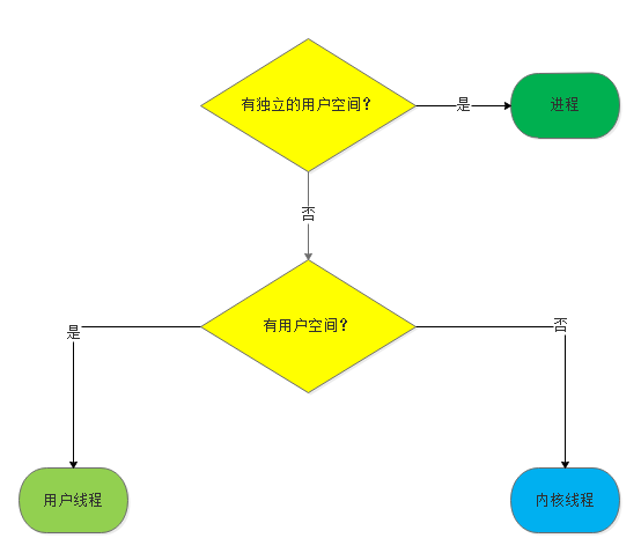
在Linux中,无论进程还是线程,到了内核里头,都统一称作任务(Task),由一个统一的结构,就是这个struct task_struct进行管理。每一个任务就都应该有一个任务ID,作为该任务的唯一标识的ID(就像人们的身份证一样)。
讲到这,有的读者可能会有疑问了:既然是唯一标识的ID,那么有一个不就可以了,怎么上边有个pid_t pid,还有个pid_t tgid?弄俩干什么?
别着急,咱们先从一个代码讲起。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void *thread1(void *p)
{
while (1)
{
printf("thread1 running\n");
sleep(2);
}
}
void *thread2(void *p)
{
while (1)
{
printf("thread2 running\n");
sleep(2);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pid_t pid;
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
int ret;
if ((pid = fork()) < 0)
{
printf("fork() failed\n");
return -1;
}
else if (pid == 0) //child process
{
ret = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thread1, NULL);
if (ret)
{
printf("thread1 create failed");
return -1;
}
ret = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thread2, NULL);
if (ret != 0)
{
printf("thread2 create failed");
pthread_cancel(tid1); //请求取消线程
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
return -1;
}
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
}
else //parent process
{
while(1)
sleep(5);
}
return 0;
}
以上代码的功能大体说明如下:
1)首先,调用fork()创建一个子进程。如果fork()返回错误,则退出。否则往下进行;
2)如果返回值大于0,说明是父进程,则循环等待,每次循环休眠5秒;
3)如果返回值等于0,说明是子进程,那么创建两个线程;
4)在两个线程中也执行while循环,每次循环休眠2秒。
将此代码使用以下命令进行编译:
gcc process_test.c -lpthread -o process_test编译完成后,在此终端下运行process_test:
./process_test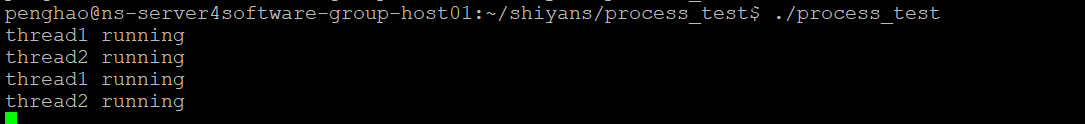
另起一个终端,执行以下命令:
ps -eLo pid,ppid,pgid,sid,lwp,nlwp,comm | grep process_test实际命令及结果如下:
$ ps -eLo pid,ppid,pgid,sid,lwp,nlwp,comm | grep process_test
765335 764210 765335 764210 765335 1 process_test
765336 765335 765335 764210 765336 3 process_test
765336 765335 765335 764210 765337 3 process_test
765336 765335 765335 764210 765338 3 process_test
对于该结果的分析、以及struct task_struct中任务ID相关成员的讲解,请看下回。


























 1594
1594

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










