This is an interactive problem.
Vladik has favorite game, in which he plays all his free time.
Game field could be represented as n × m matrix which consists of cells of three types:
- «.» — normal cell, player can visit it.
- «F» — finish cell, player has to finish his way there to win. There is exactly one cell of this type.
- «*» — dangerous cell, if player comes to this cell, he loses.
Initially player is located in the left top cell with coordinates (1, 1).
Player has access to 4 buttons "U", "D", "L", "R", each of them move player up, down, left and right directions respectively.
But it’s not that easy! Sometimes friends play game and change functions of buttons. Function of buttons "L" and "R" could have been swapped, also functions of buttons "U" and "D" could have been swapped. Note that functions of buttons can be changed only at the beginning of the game.
Help Vladik win the game!
First line contains two space-separated integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 100) — number of rows and columns respectively.
Each of next n lines contains m characters describing corresponding row of field. Set of characters in field is described above.
Guaranteed that cell with coordinates (1, 1) is normal and there is at least one way from initial cell to finish cell without dangerous cells.
You can press buttons no more than 2·n·m times.
To press a button you should print "U", "D", "L", "R" in new line. It’s necessary to print newline character and flush output. After flushing buffer you should read answer from input data. Answer is the pair of space-separated integers x, y — new position of player. In case, if there is no cell in direction of moving, position will not change. If after any move player lost, in other words player move to dangerous cell, then x and y will be equal to - 1.
If after any move player is in finish or dangerous cell, then you should terminate your program.
To finish output buffer (i. e. for operation flush) right after printing direction and newline you should do next:
- fflush(stdout) in C++
- System.out.flush() in Java
- stdout.flush() in Python
- flush(output) in Pascal
- read documentation for other languages.
Hacks
To perform a hack you should use this format:
n m swapLR swapUD a_1 a_2 ... a_n
Where n, m — number of rows and columns in game field. swapLR is equal to 1 in case, when directions "L’’ and "R’’ is swapped, and equal to 0 otherwise. swapUD is equal to 1, when directions "U’’ and "D’’ is swapped, and equal to 0 otherwise. a1, a2, ..., an — description of corresponding rows of game field.
4 3 ... **. F*. ... 1 1 1 2 1 3 1 3 2 3 3 3 4 3 4 2 4 1 3 1
R L L D U U U R R D
In first test case all four directions swapped with their opposite directions. Protocol of interaction In more convenient form:
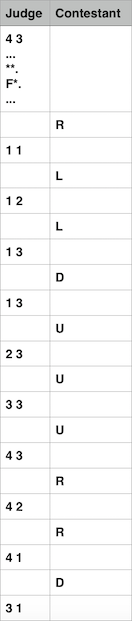
This test could be presenter for hack in following way:
4 3 1 1 ... **. F*. ...
题目大意:
现在给你一个n*m大小的图,你输出一个方向之后,系统反馈给你一个坐标,表示走完这步之后到的位子,我们需要在2*n*m步之内走到终点,问怎样走才行(多解输出任意一个即可)。
我们一开始的位子是(1,1),终点位子是“F”,‘*’表示不能走的位子,游戏开始的时候,有一些小伙伴比较调皮,会将U和D互换,就是说假设我们操作了U,但是实际是走到了D.或者也可能将L和R互换,当然也可能都没有互换过,当然也可能都互换过。
然你模拟整个过程。
思路:
预处理Bfs随便跑出来一个可行解,然后我们按照这个过程模拟的去走,如果发现下一步走到的位子和预期走到的位子不同,那么肯定这个键子就被小伙伴们调皮的换过了,
那么此时我们反过去走就行。
Ac代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int x,y;
}now,nex;
char a[105][105];
int path[105*105*3][2];
int pre[105][105][2];
int vis[105][105];
int fx[4]={0,0,1,-1};
int fy[4]={1,-1,0,0};
char ans[4]{'R','L','D','U'};
int n,m;
int cnt;
void Bfs()
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
queue<node >s;
now.x=1;
now.y=1;
s.push(now);
pre[now.x][now.y][0]=1;
pre[now.y][now.y][1]=1;
vis[now.x][now.y]=1;
while(!s.empty())
{
now=s.front();
if(a[now.x][now.y]=='F')break;
s.pop();
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
nex.x=now.x+fx[i];
nex.y=now.y+fy[i];
if(nex.x>=1&&nex.x<=n&&nex.y>=1&&nex.y<=m&&a[nex.x][nex.y]!='*')
{
if(vis[nex.x][nex.y]==0)
{
vis[nex.x][nex.y]=1;
s.push(nex);
pre[nex.x][nex.y][0]=now.x;
pre[nex.x][nex.y][1]=now.y;
}
}
}
}
}
void Slove()
{
/*
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
printf("(%d,%d) ",pre[i][j][0],pre[i][j][1]);
}
printf("\n");
}*/
int ex,ey;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]=='F')
{
ex=i,ey=j;
}
}
}
cnt=0;
while(1)
{
path[cnt][0]=ex;
path[cnt][1]=ey;
int tmpx=ex,tmpy=ey;
ex=pre[tmpx][tmpy][0];
ey=pre[tmpx][tmpy][1];
cnt++;
if(ex==1&&ey==1)
{
path[cnt][0]=ex;
path[cnt][1]=ey;
cnt++;
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m))
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%s",a[i]+1);
Bfs();
Slove();
int now=cnt-1;
/*
for(int i=cnt-1;i>=0;i--)
{
printf("%d %d\n",path[i][0],path[i][1]);
}
*/
while(now>0)
{
int flag=-1;
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
{
int xx=path[now][0]+fx[j];
int yy=path[now][1]+fy[j];
if(xx==path[now-1][0]&&yy==path[now-1][1])flag=j;
}
printf("%c\n",ans[flag]);
fflush(stdout);
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
if(x==path[now-1][0]&&y==path[now-1][1])now--;
else
{
if(ans[flag]=='L'||ans[flag]=='R')swap(ans[0],ans[1]);
else swap(ans[2],ans[3]);
}
}
}
}







 本文介绍了一个互动游戏问题,玩家需要在一个矩阵地图中找到从起点到终点的路径,同时避开危险区域。文章提供了完整的AC代码实现,并详细解释了如何通过预处理BFS找出一条可行路径的方法。
本文介绍了一个互动游戏问题,玩家需要在一个矩阵地图中找到从起点到终点的路径,同时避开危险区域。文章提供了完整的AC代码实现,并详细解释了如何通过预处理BFS找出一条可行路径的方法。
















 797
797

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








