1 简介
The removal of mixed noise is a stiff problem since the distribution of the noise cannot be predicted accurately. The most common mixed noise is the combination of Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) and Impulse Noise (IN). Many methods first attempt to remove IN but it might collapse the texture of the image. In this paper, we propose a new learning-based method using convolutional neural network (CNN) for removing mixed gaussian-impulse noise. Since our denoising network can remove various level of mixed noise, neither the preprocessing for removing IN nor noise-level estimation is necessary.
2 部分代码
% Use this code when trainingtraining_image_list = {};for a=1000:2:1200training_image_list = [training_image_list,['image/train/train_image_gray', num2str(a) ,'.png']];endpatch_size = 33;train_data = zeros(patch_size, patch_size, 1000000, 'single');train_label = zeros(patch_size, patch_size, 1000000, 'single');num_patches = 0;% Make training datafor image_index = 1 : length(training_image_list)fprintf('Reading %s\n', training_image_list{image_index});for impulse_loop =1for impulse_noise_rate = 0:5:45for gaussian_noise_sigma = 0:10:50img_original = im2single(imread(training_image_list{image_index}));img_original = padarray(img_original, ceil(size(img_original)/patch_size)*patch_size-size(img_original) ,'symmetric','post');% AWGNimg_noisy = img_original + (gaussian_noise_sigma / 255) * randn(size(img_original));% RVINimg_noise_position = rand(size(img_original)) < impulse_noise_rate / 100;img_noisy(repmat(img_noise_position,1,1)) = rand(1, sum(img_noise_position(:)));if impulse_noise_rate>0if gaussian_noise_sigma >0if rand<0.15% SPINimg_noise_position = rand(size(img_original)) < randi(30) / 100;img_noisy(repmat(img_noise_position,1,1)) = rand(1, sum(img_noise_position(:)))>0.5;endendendtmp_data = im2col(img_noisy, [patch_size, patch_size], 'distinct');tmp_data = reshape(tmp_data, patch_size, patch_size, []);tmp_label = im2col(img_original, [patch_size, patch_size], 'distinct');tmp_label = reshape(tmp_label, patch_size, patch_size, []);train_data(:, :, num_patches + 1 : num_patches + size(tmp_data, 3)) = tmp_data;train_label(:, :, num_patches + 1 : num_patches + size(tmp_label, 3)) = tmp_label;num_patches = num_patches + size(tmp_data, 3);endendendendtrain_data = train_data(:, :, 1 : num_patches);train_label = train_label(:, :, 1 : num_patches);% reshape to MxNx1xCtrain_data = reshape(train_data, patch_size, patch_size, 1, []);train_label = reshape(train_label, patch_size, patch_size, 1, []);% save('mixed_data.mat','train_data','train_label');% clear allfprintf('Complete.\n');
3 仿真结果
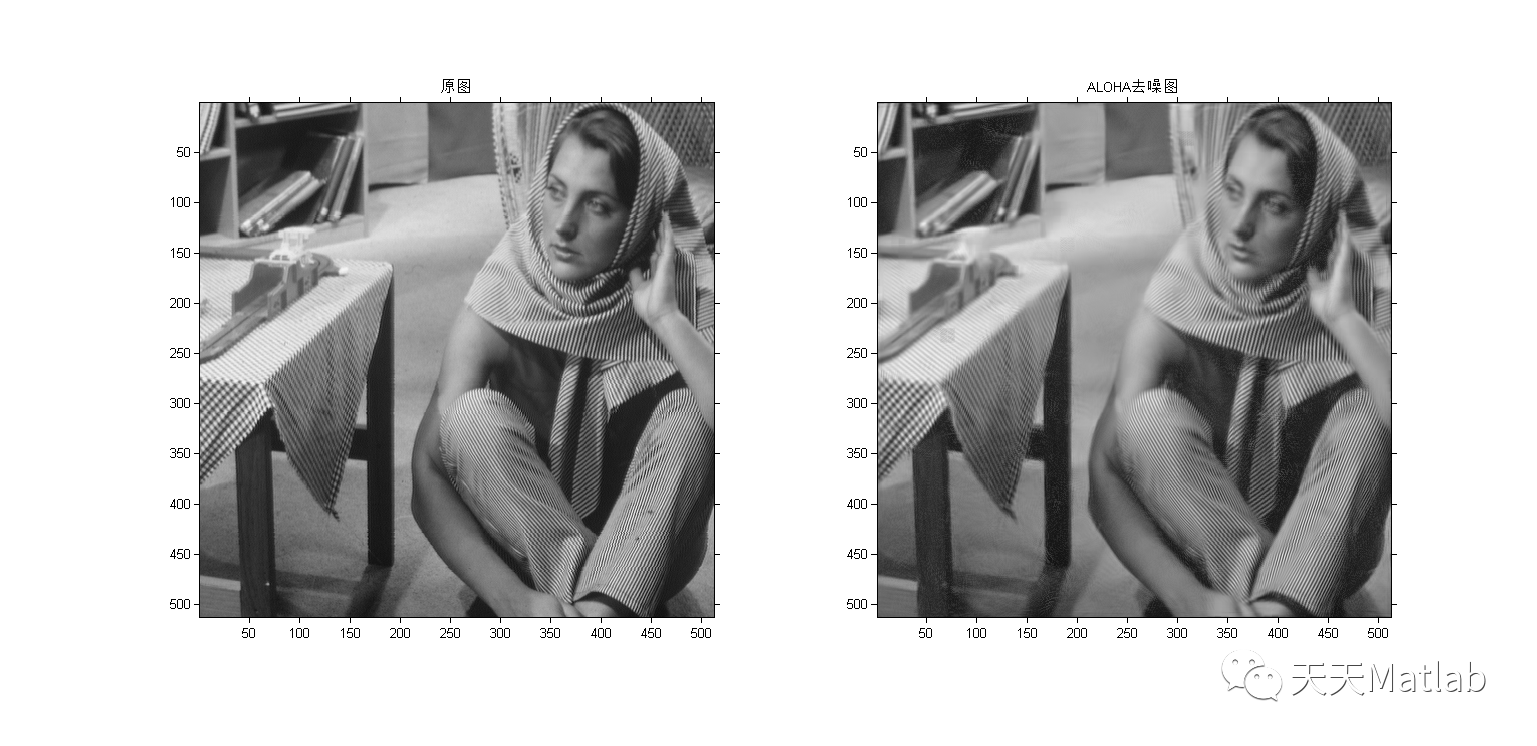
4 参考文献
Ryo Abiko, and Masaaki Ikehara. "Blind Denoising of Mixed Gaussian-impulse Noise by Single CNN." ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). IEEE, 2019.
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。





 本文提出了一种基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的学习方法,用于有效去除图像中的混合高斯-脉冲噪声。该方法无需预处理去除脉冲噪声或精确的噪声水平估计,能处理不同级别的噪声。通过生成大量带有不同噪声水平的训练数据,训练CNN模型进行去噪。实验结果验证了方法的有效性。
本文提出了一种基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的学习方法,用于有效去除图像中的混合高斯-脉冲噪声。该方法无需预处理去除脉冲噪声或精确的噪声水平估计,能处理不同级别的噪声。通过生成大量带有不同噪声水平的训练数据,训练CNN模型进行去噪。实验结果验证了方法的有效性。

















 857
857

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










