第五十周学习笔记
论文阅读概述
- SemStyle: Learning to Generate Stylised Image Captions using Unaligned Text: This article introduces a novel model dubbed SemStyle to generate diverse image caption based on paired factual data and unpaired stylistic corpus by two-stage method which firstly map image to semantic term sequence and then feed it to language model to generate captions. By extracting semantic term with NLP package from Unpaired stylistic corpus to train the second model, SemStyle incorporates stylistic data to achieve good performance.
- Dense Captioning with Joint Inference and Visual Context: This article comes up with joint inference(which simultaneosly generate region captions and region) and context fusion(which provides contextual information for region captioning) to address the problem of highly overlapping target regions in dataset and difficulty in recognizing each region by appearance alone, achieving SoTA on VG.
- Semantic Compositional Networks for Visual Captioning: This article introduces a novel model named SCN to effectively incorporate high-level semantic concepts in image captioning system by using softmax output of multi-label concept(object) detection to weight weights of LSTM analogous to an esemble LSTM model, achieving top3 performance then.
- Incorporating Copying Mechanism in Image Captioning for Learning Novel Objects: This article introduces a novel model called LSTM-C(Copy) to incorporate external visual recognition dataset by linearly combining traditional decoder output next word probability distribution and object detection-based distribution to generate next word to achieve the goal of novel object captioning.
- Captioning Images with Diverse Objects: This article introduces a novel model to simultaneosly target at object detection,next word generation and image captioning with shared model and parameters to incorporate external visual detection dataset and text dataset.
- Top-down Visual Saliency Guided by Captions: This article tries to investigate the internal mechanism of image captioning model by replacing contextual vector with single region feature and comparing language model output distribution of both to explain the dependency between specific word and specific region and figure out whether encoder-decoder could adaptively find the connection between them which the answer is ‘yes’.
- Bidirectional Beam Search: Forward-Backward Inference in Neural Sequence Models for Fill-in-the-Blank Image Captioning: This article comes up with bidirectional beam search for fill-in-the-blank image captioning as an attempt to explore bidirectional decoding method.
- Beyond instance-level image retrieval:Leveraging captions to learn a global visual representation for semantic retrieval: This article exploits caption dataset to supervise semantic image encoding model for semantic image retrieval and achieve better performance.
- Areas of Attention for Image Captioning: This article comes up with a novel language model to generate captions by modeling the interplay of region feature, current input word and hidden state with different region feature(spatial, proposal, transform) to find a better attention mechanism for image captioning.
- An Empirical Study of Language CNN for Image Captioning: This article introduces Language CNN as decoder for image caption to deal with long-term dependency which is a challenge in RNN-based decoder, by using layer-wise transformation of fixed window size in CNN(followed by a rnn cell to model local information) to model the structure and global information in all previous generated sequence.
- Scene Graph Generation from Objects, Phrases and Region Captions(amazing one): This article firstly emphasizes the connection between three difference level visual understanding task——object detection, scene graph generation and region captioning then design an end-to-end model to be simultaneosly trained on these three tasks by refining different tasks’ visual feature as connected node on a hierachical dynamic tree as mutual compensation, boosting all of three tasks’ performance.
- Improved Image Captioning via Policy Gradient optimization of SPIDEr: This article introduces a robust policy gradient algorithm to directly optimize on image captioning metric for more human-consensus caption and a better optimization SPIDEr which is the linear combination of SPICE and CIDEr.
- Speaking the Same Language:Matching Machine to Human Captions by Adversarial Training: This article comes up with a new question to generate caption set from a single image to better use the one-to-many dataset of image captioning by adversarial training, achieving both accuracy and diversity.
- Paying Attention to Descriptions Generated by Image Captioning Models: This article investigate the difference of saliency between human and image captioning model and prove that model sharing more consensus on saliency with human can achieve better performance.
- Boosting Image Captioning with Attributes: Again, this article emphasizes the importance of semantic level information for better image caption generation by detecting and inputting multi-label object detection distribution to decoder to achieve SoTA performance.
代码运行结果
感谢ruotianluo,运行了一些主流的image captioning模型,得到的结果如图(图太多就先放一张cider的把),350k iteration之前是XE优化,之后是CIDEr optimization,分别使用了spatial attantion特征和bottom-up attention特征
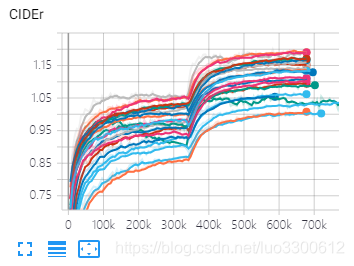
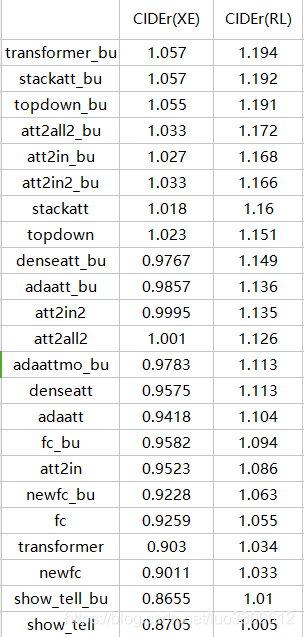
结果表明
- 所有模型使用bottom-up特征的都比spatial特征的最终结果好
- transformer是本次实验的最好模型(暂时凭CIDEr),其次是top-down模型
- 特别的是show tell模型,它的XE训练结果的spatial特征比bottom-up特征要好
- bottom-up特征能帮助屌丝模型实现逆袭,参见transformer
暂时还漏了几个模型没跑,下周一起跑完了把所有metric放一起详细分析下,并对比论文结果
本周小结
上周任务完成度
- 读完17-19年image captioning的CVPR论文 √
- 整理近年来的SoTA image captioning model ~(ongoing)
- 整理先前阅读的所有论文 ×
- 整理论文的书写方法 ~
- 整理重要的引用文献 ~
- 研究CIDEr optimization和top-down model的细节 ×
- 所有模型跑一个CIDEr optimization的版本 √
- 跑基于top-down feature的模型 √
各种整理任务均在进行中,完成时间还是往后推迟,每周放在计划里先作一个提醒
下周目标
- 读完17ICCV 18年ECCV的image captioning论文
- 整理近年来的SoTA image captioning model
- 整理先前阅读的论文
- 整理论文的书写方法
- 整理重要的引用文献
- 研究策略梯度、CIDEr optimization和top-down model的细节
- 完成基本模型的运行任务,比对其原论文详细分析结果
























 1997
1997

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








