昨天我用深度优先算法写了一道迷宫问题,见下链接
今天我想试一下广度优先算法看dfs与bfs算法,看哪种运算速度更快;(结果一个小错误没发现,做了好久。。。。。)

但好歹写出来了:
深度优先算法

广度优先算法

确实广度优先算法要快一些(当然还得根据不同代码及所占内存分析)
广度优先算法解题思路如下:
使用queue常用函数,应用队列的思想来处理数据
将每一个点的坐标及移动方向用结构体存储
广度优先搜索有点像辐射,从一个节点向另一个节点传递,一层一层的辐射直至目标节点被找到;
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
string str;
int flag[100][100];
int map[30][50] =
{
0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,
0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,
0,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,
0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,
0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
1,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,
0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,
0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,
1,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,
0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,
1,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,
1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,
1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,
1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,
1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,
0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,
1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,
0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,
1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,
0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,
1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,
0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,
1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,
0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,
1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,
1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,
0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,
1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0
};
int row = 30;
int col = 50;
char dir[4] = { 'D','L','R','U' };
int dirx[4] = { 1,0,0,-1 };
int diry[4] = { 0,-1,1,0 };
struct node {
int x, y;
string s;
};
bool check(int x, int y)
{
if (x >= 0 && x < 30 && y >= 0 && y < 50 && !map[x][y] && !flag[x][y])
return true;
return false;
}
void bfs()
{
queue<node>q;
q.push({ 0,0,"" });
flag[0][0] = 1;
while (q.size())
{
node t = q.front();
q.pop();
if (t.x == (row-1) && t.y == (col-1))
{
cout << t.s << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int tx = t.x + dirx[i];
int ty = t.y + diry[i];
if (check(tx,ty))
{
q.push({ tx,ty, t.s+ dir[i] });
flag[tx][ty] = 1;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
bfs();
return 0;
}其实对迷宫的初始化我也学到一种比较优雅的方法(我其实感觉初始化这个一堆0和1的迷宫感到很别扭)代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
#include<time.h>
clock_t start_time = clock();
using namespace std;
string str;
int flag[100][100],map[100][100];
int row = 30;
int col = 50;
char dir[4] = { 'D','L','R','U' };
int dirx[4] = { 1,0,0,-1 };
int diry[4] = { 0,-1,1,0};
struct node {
int x, y;
string s;
};
bool check(int x, int y)
{
if (x >= 0 && x < 30 && y >= 0 && y < 50 && !map[x][y] && !flag[x][y])
return true;
return false;
}
void bfs()
{
queue<node>q;
q.push({ 0,0,"" });
flag[0][0] = 1;
while (q.size())
{
node t = q.front();
q.pop();
if (t.x == (row-1) && t.y == (col-1))
{
cout << t.s << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int tx = t.x + dirx[i];
int ty = t.y + diry[i];
if (check(tx,ty))
{
q.push({ tx,ty, t.s+ dir[i] });
flag[tx][ty] = 1;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
cin >> str;
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
if (str[j] == '1')
map[i][j] =1;
}
}
bfs();
clock_t end_time = clock();
cout<< "Running time is: "<<static_cast<double>(end_time-start_time)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC*1000<<"ms"<<endl;
return 0;
}是的我认为
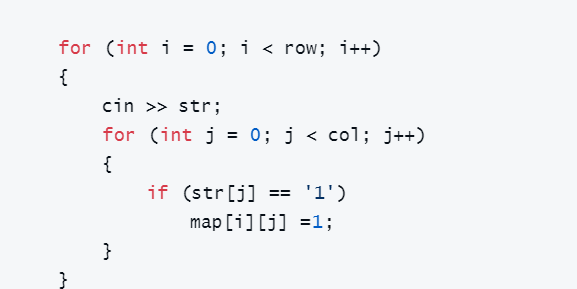
这一段非常
优雅❤
但是它又有一点缺陷

运算时间太长😅😅😅😅😅
好了,希望自己明天能有一个超级棒的状态学习,不虚度光阴!




 作者分享了使用深度优先搜索(DFS)和广度优先搜索(BFS)解决迷宫问题的C++实现。通过比较,发现BFS在解决此类问题时通常速度更快。文章还提到了迷宫初始化的优化方法,但指出这可能导致较高的运行时间。
作者分享了使用深度优先搜索(DFS)和广度优先搜索(BFS)解决迷宫问题的C++实现。通过比较,发现BFS在解决此类问题时通常速度更快。文章还提到了迷宫初始化的优化方法,但指出这可能导致较高的运行时间。
















 323
323

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








