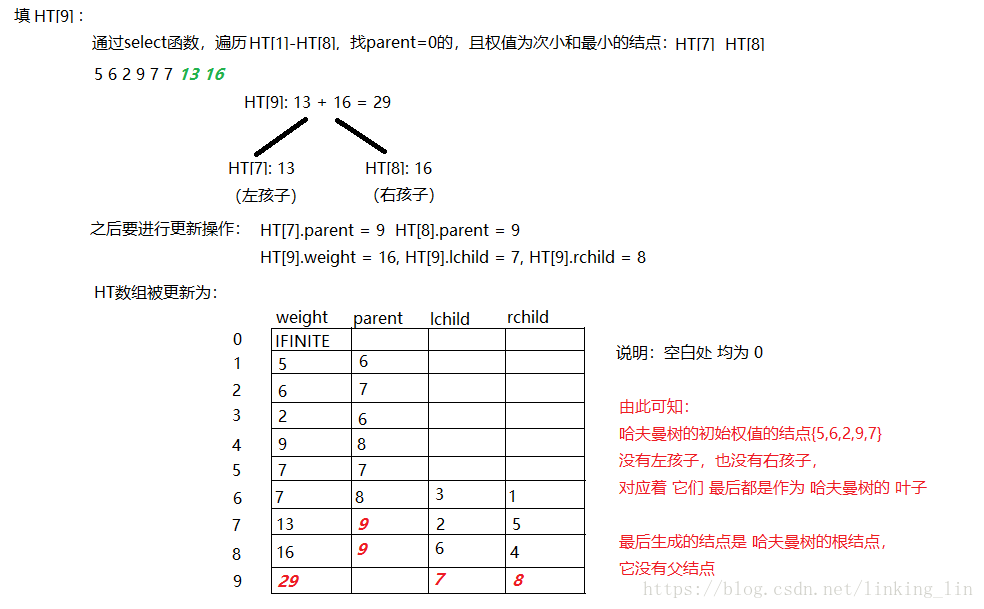
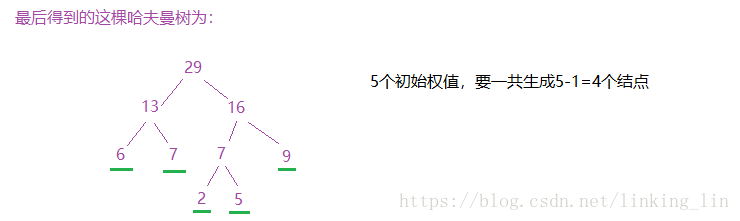
讲述哈夫曼树的构建过程(按照代码的思路):

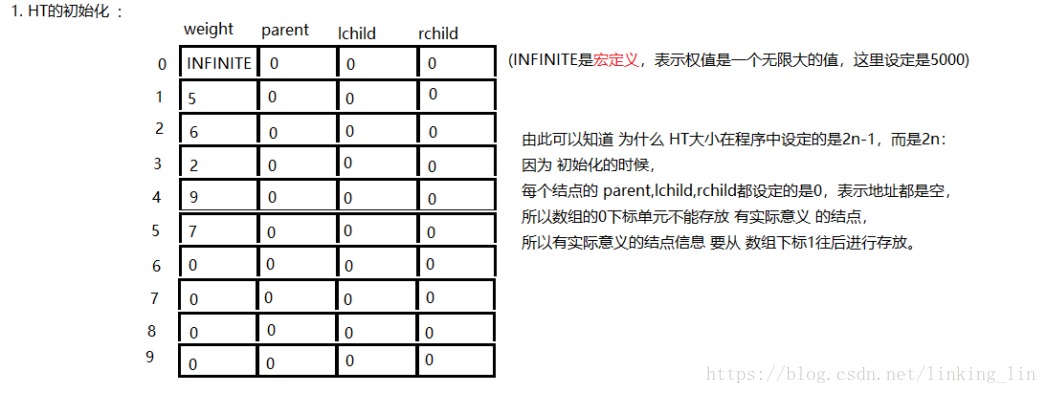
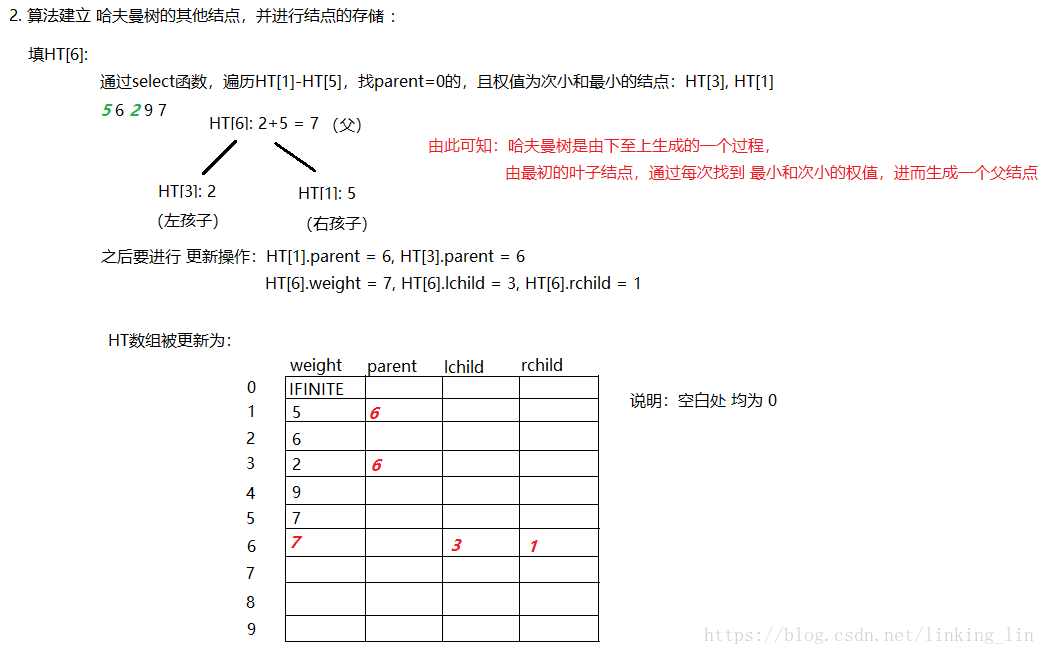
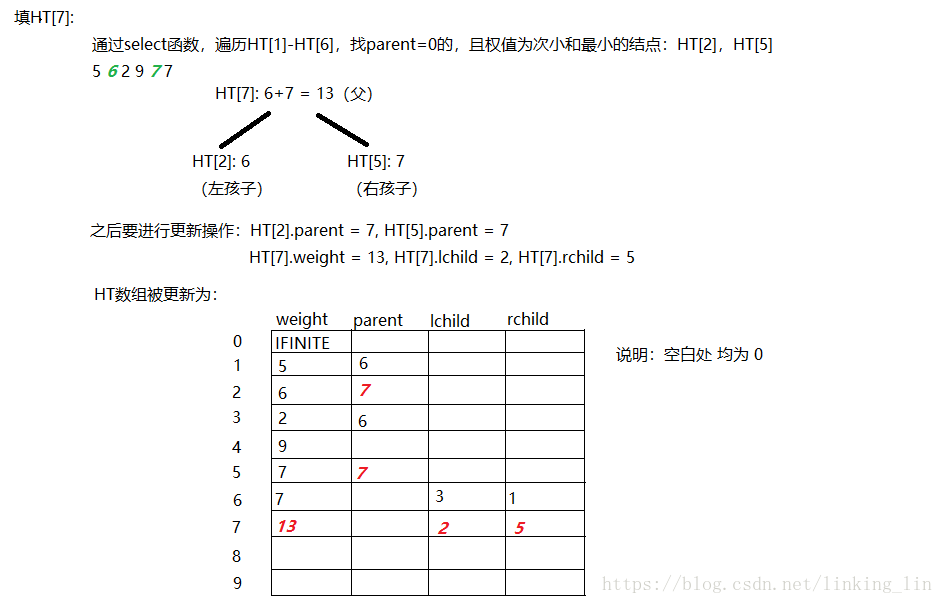
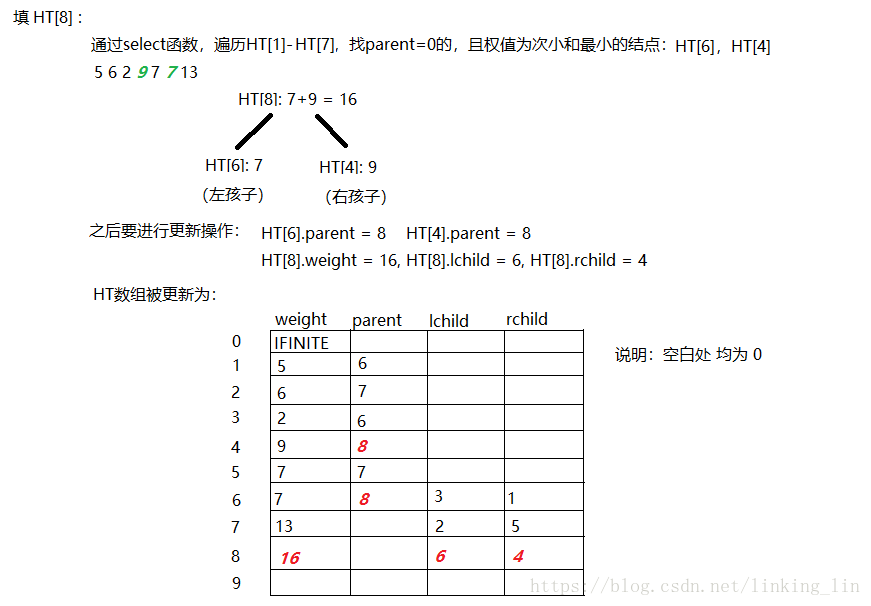
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
typedef struct{
int weight;
int parent;
int lchild;
int rchild;
}HTNode, *HTree;
#define INFINITE 5000
void select(HTree HT, int n, int *smallest_index, int *second_smallest_index)
{
// int tmp = *smallest_index;
int i;
HTree p = HT;
for(i=1;i<=n;++i){
if(p[i].parent == 0){
if(p[i].weight < p[*smallest_index].weight){
*second_smallest_index = *smallest_index;
*smallest_index = i;
}else if(p[i].weight < p[*second_smallest_index].weight){
*second_smallest_index = i;
}
}
}
}
// n: the number of leaves in a Huffman Tree
// w: an array which stores weights
void huffman_coding(int n,int m,int *w, HTree HT)
{
if(n < 1 || HT == NULL){
return;
}
*HT = (HTNode){INFINITE,0,0,0};
HTree p = HT+1;
int i;
for(i = 1; i <= n; ++i,++p,++w){
*p=(HTNode){*w,0,0,0};
// HTNode tmp ={*w,0,0,0};
// *p=tmp;
// p->weight = *w;
// p->parent = 0;
// p->lchild = 0;
// p->rchild = 0;
}// i在这个for循环中只是计数作用
for(;i<=m;++i,++p){
*p=(HTNode){0,0,0,0};
}// i在这个for循环中只是计数作用
int *s1 = 0;
int *s2 = 0;
for(i=n;i<=m-1;++i){
select(HT,i,s1,s2);
HT[*s1].parent = i+1;
HT[*s2].parent = i+1;
HT[i+1].lchild = *s1;
HT[i+1].rchild = *s2;
HT[i+1].weight = HT[*s1].weight+HT[*s2].weight;
}
}
int main()
{
int w[5] = {5,6,2,9,7};
int n = 5;
int m = 2*n-1;
HTree HT = (HTree)malloc((m+1)*sizeof(HTNode));
huffman_coding(n,m,w,HT);
}





 本文详细探讨了哈夫曼树的构建方法,通过代码解析思路,深入理解哈夫曼树的生成过程,帮助读者掌握数据结构中的这一重要概念。
本文详细探讨了哈夫曼树的构建方法,通过代码解析思路,深入理解哈夫曼树的生成过程,帮助读者掌握数据结构中的这一重要概念。
















 921
921

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








