一. 引言
在 AI 应用开发中,与大语言模型的交互不再是简单的单轮问答,而是涉及复杂的、结构化的提示词组装。提示词的质量直接影响大模型输出效果。LangChain作为构建LLM应用的核心框架,其提示词模板正是实现这一过程的基石。本文将带你如何使用LangChain来构建最基础的提示词模板。
二. 为什么要使用提示词模板
- 可复用性与一致性
模板一旦定义,就可以在应用的任何地方反复使用。这确保了传递给模型的指令格式是统一的,避免了因提示词微小的不一致而导致模型输出结果的波动,对于保证应用质量至关重要。 - 关注点分离与可维护性
开发者可以将精力集中在设计高质量的提示词结构上(静态部分),而将具体的内容(动态部分)交给业务逻辑来处理。当需要优化提示词时,只需修改一个模板文件,而无需在整个代码库中搜索和替换。 - 复杂提示词的模块化
对于包含系统消息、少样本示例、用户查询等复杂结构的提示词,模板能使其变得清晰、易管理。 - 集成与链式调用
这是LangChain的核心优势。提示词模板是LCEL链中的关键一环。它可以无缝地与大模型、输出解析器、工具等其他组件连接。
三. LangChain常用的提示词模板
3.1 PromptTemplate(字符串提示词模板)
特点:
- 支持通过占位符 { } 定义动态提示结构,将固定文本与动态参数分离。
- 通过format方法传入参数即可生成具体提示,避免硬编码,提升复用性。
- 支持动态模板语法,包括f-string和jinja2。
使用场景:
- 用于文本补全模型,输入是纯文本。
- 适用于简单的任务,例如生成一段文本、回答问题或执行指令。
示例:
"""
python版本:3.12.10
langchain版本:1.0
安装 uv python包管理工具
pip3 install uv
安装langchain库
uv add langchain
安装openai库
uv add langchain_openai
"""
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from pydantic import SecretStr
# 创建LLM客户端
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="kimi-k2-0711-preview", # 模型名称
base_url="https://api.moonshot.cn/v1", # 设置api端点
api_key=SecretStr("your api key"), # api密钥
streaming=True # 启用流式输出模式
)
# 创建基本模板
template = "你是一名{role},请使用{language}语言,{task_description}"
prompt_template = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["role", "language", "task_description"],
template=template
)
# 动态填充变量生成提示词
formatted_prompt = prompt_template.format(
role="资深程序员",
language="python",
task_description="写一个冒泡排序算法"
)
# 执行流式调用获取结果
resp = llm.stream(formatted_prompt)
for chunk in resp:
print(chunk.content, end="")
输出:
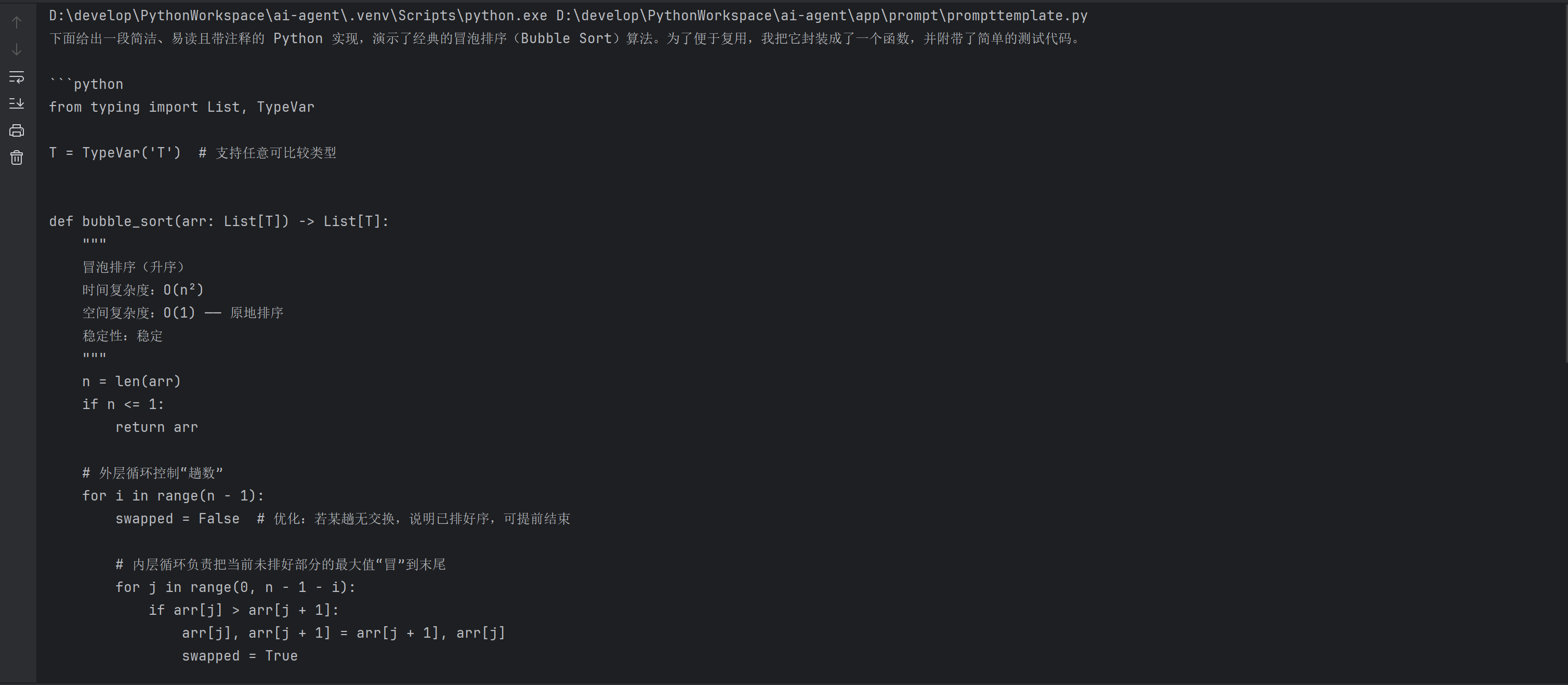
3.2 ChatPromptTemplate(聊天提示词模板)
特点:
- 多角色支持,系统、用户、AI等多种消息类型。
- 维护历史对话,支持多轮对话场景。
- 支持模板保存和复用,减少重复编码。
使用场景:
- 用于聊天模型,输入是多轮对话的消息列表(SystemMessage、HumanMessage、AIMessage 等)。
示例:
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, HumanMessagePromptTemplate, SystemMessagePromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from pydantic import SecretStr
# 创建LLM客户端
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="kimi-k2-0711-preview",
base_url="https://api.moonshot.cn/v1",
api_key=SecretStr("your api key"),
streaming=True
)
system_template = "你是一个精通{domain}的专家助手,用{style}风格回答"
# 构建系统角色消息模板
system_prompt = SystemMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(system_template)
human_template = "我的问题是:{question}"
# 构建用户消息模板
human_prompt = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(human_template)
# 构建聊天模型的提示模板
chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([system_prompt, human_prompt])
# 动态填充变量生成提示词
formatted_prompt = chat_prompt.format_messages(
domain="人工智能",
style="简洁严谨",
question="解释Transformer架构的核心思想"
)
# 执行流式调用
resp = llm.stream(formatted_prompt)
for chunk in resp:
print(chunk.content, end="")
输出:
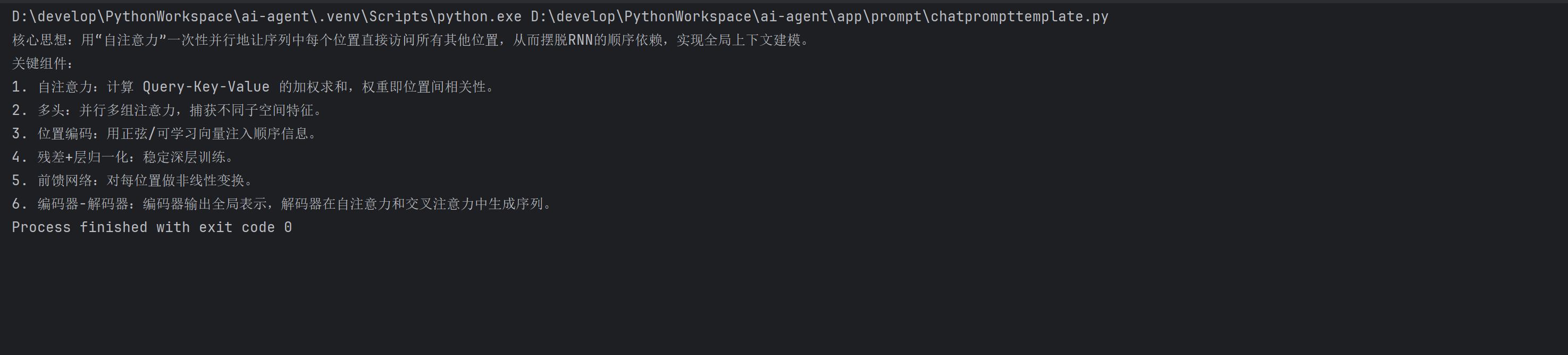
3.3 FewShotPromptTemplate(少样本学习提示词模板)
特点:
- 通过提供少量样本显式指导语言模型理解任务规则和输出格式,避免因指令描述而产生歧义性。
- 支持ExampleSelector自动筛选与当前输入最相关的示例。
- 模块化组件设计,通过前缀prefix和后缀suffix等参数定义任务指令和输入占位符。
使用场景:
- 用于少量样本学习,通过列举的示例,帮助大模型理解任务。
- 适用于复杂任务,需要通过示例引导大模型行为。
示例:
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate, FewShotPromptTemplate, ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from pydantic import SecretStr
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="kimi-k2-0711-preview",
base_url="https://api.moonshot.cn/v1",
api_key=SecretStr("your api key"),
streaming=True
)
translation_examples = [
{
"english": "Hello, how have you been recently?",
"chinese": "你好,最近你过得怎么样?"
},
{
"english": "My ideal is to be a teacher.",
"chinese": "我的理想是当一名教师。"
},
{
"english": "What a hot day it is today.",
"chinese": "今天的天气真热啊。"
}
]
example_template = "输入:{input}\n输出:{output}"
examples = [
{"input": "将'china'翻译成中文", "output": "中国"},
{"input": "将'japan'翻译成中文", "output": "日本"}
]
# 构建FewShotPromptTemplate模板
few_shot_prompt = FewShotPromptTemplate(
examples=examples,
example_prompt=PromptTemplate.from_template(example_template),
prefix="请将以下英文翻译成中文:",
suffix="输入: {text}\n输出:",
input_variables=["text"]
)
# 动态填充变量生成提示词
prompt = few_shot_prompt.format(text="america")
print(prompt)
response = llm.stream(prompt)
for chunk in response:
print(chunk.content, end="")
输出:
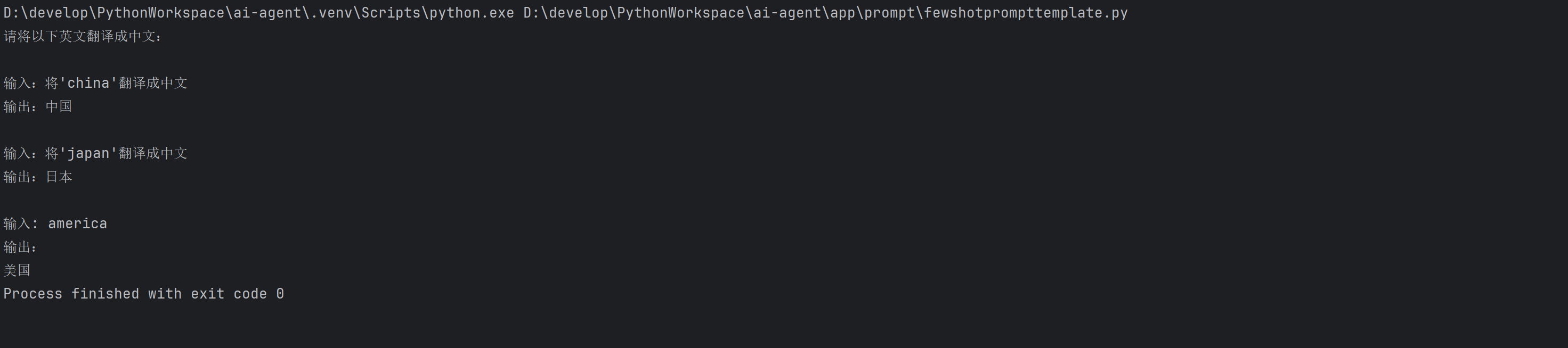
四. 总结
本文通过样例代码介绍了LangChain构建提示词模板基础用法。LangChain提示词模板远不止是字符串格式化的工具,它可以让大模型能够更加清晰理解我们的意图。LangChain提示词模板通过抽象和封装,让开发者能从繁琐的字符串操作中解放出来,更专注于核心的提示工程与业务逻辑设计。




















 1181
1181

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








