背景:
分析audio系统框架整体系统源码,需要找到一个合适切入点。那么这个切入点是直接选择audio服务的AudioFlinger,AudioPolicy合适,还是从最简单基础的AudioTrack切入呢?对于大部分音频没有很好基础的同学当然是从最简单AudioTrack切入,一直分析到数据到hal写入的整个流程最好。
下面开始从AudioTrack来开始进行源码分析,代码基于aosp15。
AudioTrack的StreamType构造模式
public AudioTrack(int streamType, int sampleRateInHz, int channelConfig, int audioFormat,
int bufferSizeInBytes, int mode)
throws IllegalArgumentException {
this(streamType, sampleRateInHz, channelConfig, audioFormat,
bufferSizeInBytes, mode, AUDIO_SESSION_ID_GENERATE);
}
调用到了另一个构造方法
public AudioTrack(int streamType, int sampleRateInHz, int channelConfig, int audioFormat,
int bufferSizeInBytes, int mode, int sessionId)
throws IllegalArgumentException {
// mState already == STATE_UNINITIALIZED
this((new AudioAttributes.Builder())
.setLegacyStreamType(streamType) //StreamType转换成AudioAttributes对象
.build(),
(new AudioFormat.Builder())
.setChannelMask(channelConfig)
.setEncoding(audioFormat)
.setSampleRate(sampleRateInHz)
.build(),
bufferSizeInBytes,
mode, sessionId);
deprecateStreamTypeForPlayback(streamType, "AudioTrack", "AudioTrack()");
}
这里可以看出java层面最后AudioTrack构造都会调用到AudioAttributes方式来构造。
那么这里是如何吧StreamType转换成AudioAttributes对象呢?核心方法就是上面的setLegacyStreamType(streamType)部分:
public Builder setLegacyStreamType(int streamType) {
//省略部分
setInternalLegacyStreamType(streamType);
return this;
}
实际转换方法setInternalLegacyStreamType如下:
public Builder setInternalLegacyStreamType(int streamType) {
mContentType = CONTENT_TYPE_UNKNOWN;
mUsage = USAGE_UNKNOWN;
//注意首先AudioProductStrategy查询是否有对应StreamType
if (AudioProductStrategy.getAudioProductStrategies().size() > 0) {
// 获取策略中StreamType对应的AudioAttributes
AudioAttributes attributes =
AudioProductStrategy.getAudioAttributesForStrategyWithLegacyStreamType(
streamType);
if (attributes != null) {
mUsage = attributes.mUsage;
// on purpose ignoring the content type: stream types are deprecated for
// playback, making assumptions about the content type is prone to
// interpretation errors for ambiguous types such as STREAM_TTS and STREAM_MUSIC
//mContentType = attributes.mContentType;
//注意新版本已经不在考虑对mContentType内容进行设置了
mFlags = attributes.getAllFlags();
mMuteHapticChannels = attributes.areHapticChannelsMuted();
mIsContentSpatialized = attributes.isContentSpatialized();
mSpatializationBehavior = attributes.getSpatializationBehavior();
mTags = attributes.mTags;
mBundle = attributes.mBundle;
mSource = attributes.mSource;
}
}
switch (streamType) {
case AudioSystem.STREAM_VOICE_CALL:
mContentType = CONTENT_TYPE_SPEECH;
break;
case AudioSystem.STREAM_SYSTEM_ENFORCED:
mFlags |= FLAG_AUDIBILITY_ENFORCED;
// intended fall through, attributes in common with STREAM_SYSTEM
case AudioSystem.STREAM_SYSTEM:
mContentType = CONTENT_TYPE_SONIFICATION;
break;
case AudioSystem.STREAM_RING:
mContentType = CONTENT_TYPE_SONIFICATION;
break;
case AudioSystem.STREAM_ALARM:
mContentType = CONTENT_TYPE_SONIFICATION;
break;
case AudioSystem.STREAM_NOTIFICATION:
mContentType = CONTENT_TYPE_SONIFICATION;
break;
case AudioSystem.STREAM_BLUETOOTH_SCO:
mContentType = CONTENT_TYPE_SPEECH;
mFlags |= FLAG_SCO;
break;
case AudioSystem.STREAM_DTMF:
mContentType = CONTENT_TYPE_SONIFICATION;
break;
case AudioSystem.STREAM_TTS:
mContentType = CONTENT_TYPE_SONIFICATION;
mFlags |= FLAG_BEACON;
break;
case AudioSystem.STREAM_ACCESSIBILITY:
mContentType = CONTENT_TYPE_SPEECH;
break;
case AudioSystem.STREAM_ASSISTANT:
mContentType = CONTENT_TYPE_SPEECH;
break;
case AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC:
//新版本针对music没有进行ContentType设定
// leaving as CONTENT_TYPE_UNKNOWN
break;
default:
Log.e(TAG, "Invalid stream type " + streamType + " for AudioAttributes");
}
//最后如果上面策略中没有设置usage,则使用默认的转换函数StreamType转成usage
if (mUsage == USAGE_UNKNOWN) {
mUsage = usageForStreamType(streamType);
}
return this;
}
这里的usageForStreamType方法如下,也是一样的switch case:
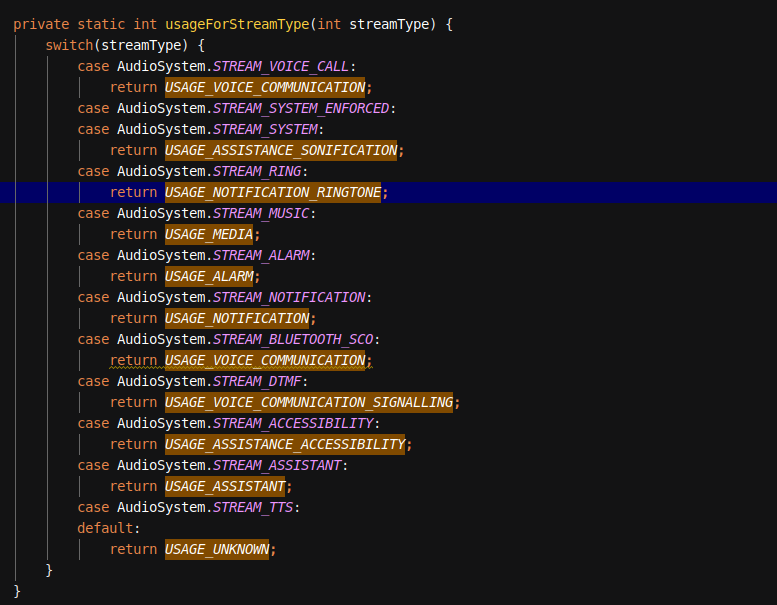
上面主要分为一下几个分部分:
1、首先从系统的AudioProductStrategy中,通过StreamType获取的对应的AudioAttributes
2、经过第一部的获取设置后,但ContentType没有被设置,则按照默认的switch规则设置
3、如果发现Usage没有设置,那么也是按照固定的默认的switch规则设置
ps:
在aosp15最新版本上,如果StreamType是music情况下,那么他的ContentType是不会被设置的,但是以前是有进行固定的设置,这个修改提交也有对应的提交:
commit 2eb20ebb6aef488945ec2aba4c32f3730777ad27
Author: Jean-Michel Trivi <jmtrivi@google.com>
Date: Tue Sep 19 15:39:58 2023 -0700
AudioAttributes: set content type to UNKNOWN for init from stream
When creating AudioAttributes from a legacy stream type, do
not read the content type from the audio strategies, or set
it to a specific value for STREAM_MUSIC.
Instead use CONTENT_TYPE_UNKNOWN which more correctly
represents the fact that stream types are not enough information
to express the content type for STREAM_MUSIC.
Bug: 301100160
Test: atest android.media.audio.cts.AudioAttributesTest
Test: atest android.media.audio.cts.AudioManagerTest
Test: atest android.media.audio.cts.VolumeInfoTest
Test: atest android.media.audio.cts.NonDefaultDeviceForStrategyTest
Change-Id: I7299465a690aeeac953edf61aab0fa9d350c8f65
但是在aosp13版本是有硬性的进行设置
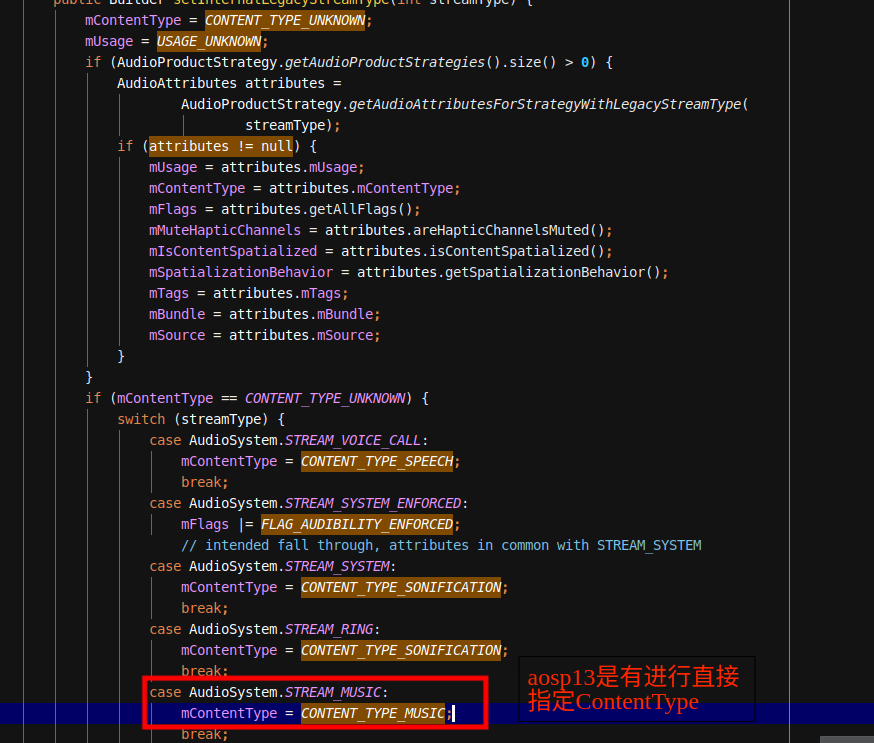
AudioTrack的AudioAttributes构造模式
无论是StreamType还是AudioAttributes方式最后都是到了如下的AudioTrack构造方法
private AudioTrack(@Nullable Context context, AudioAttributes attributes, AudioFormat format,
int bufferSizeInBytes, int mode, int sessionId, boolean offload, int encapsulationMode,
@Nullable TunerConfiguration tunerConfiguration)
throws IllegalArgumentException {
//省略
// native initialization
try (ScopedParcelState attributionSourceState = attributionSource.asScopedParcelState()) {
//最后java层面参数都是会通过native_setup方法传递到native层面
int initResult = native_setup(new WeakReference<AudioTrack>(this), mAttributes,
sampleRate, mChannelMask, mChannelIndexMask, mAudioFormat,
mNativeBufferSizeInBytes, mDataLoadMode, session,
attributionSourceState.getParcel(), 0 /*nativeTrackInJavaObj*/, offload,
encapsulationMode, tunerConfiguration, getCurrentOpPackageName());
//省略
}
}
上面可以看出java层面AudioTrack的构造最后都是吧所有参数调用了native_setup,让底层native层面用这些参数构造出native层面的AudioTrack,本质上Java层面的AudioTrack其实是个包装壳,最后都是要构造出native层面的AudioTrack。
下面来看看native_setup
frameworks/base/core/jni/android_media_AudioTrack.cpp
static jint android_media_AudioTrack_setup(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, jobject weak_this,
jobject jaa, jintArray jSampleRate,
jint channelPositionMask, jint channelIndexMask,
jint audioFormat, jint buffSizeInBytes, jint memoryMode,
jintArray jSession, jobject jAttributionSource,
jlong nativeAudioTrack, jboolean offload,
jint encapsulationMode, jobject tunerConfiguration,
jstring opPackageName) {
//省略
// if we pass in an existing *Native* AudioTrack, we don't need to create/initialize one.
sp<AudioTrack> lpTrack;
const auto lpJniStorage = sp<AudioTrackJniStorage>::make(clazz, weak_this, offload);
if (nativeAudioTrack == 0) {
//这个判断java层面传递过来的AudioAttribute是否为null,如果为null则会报错
if (jaa == 0) {
ALOGE("Error creating AudioTrack: invalid audio attributes");
return (jint) AUDIO_JAVA_ERROR;
}
//省略一些其他参数检验
android::content::AttributionSourceState attributionSource;
attributionSource.readFromParcel(parcelForJavaObject(env, jAttributionSource));
//正式构建一个native层面的AudioTrack,只不过这个参数用的是AttributionSourceState
lpTrack = sp<AudioTrack>::make(attributionSource);
//把java层面的AudioAttributes对象转换成native层面的AudioAttributes对象
// read the AudioAttributes values
auto paa = JNIAudioAttributeHelper::makeUnique();
jint jStatus = JNIAudioAttributeHelper::nativeFromJava(env, jaa, paa.get());
//接下来要把java层面那些参数,通过set方法传递到native层面的AudioTrack
switch (memoryMode) {
case MODE_STREAM:
//可以注意到这里native层面开始设置的StreamType就是default
status = lpTrack->set(AUDIO_STREAM_DEFAULT, // stream type, but more info conveyed
// in paa (last argument)
sampleRateInHertz,
format, // word length, PCM
nativeChannelMask, offload ? 0 : frameCount,
offload ? AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_COMPRESS_OFFLOAD
: AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_NONE,
lpJniStorage,
0, // notificationFrames == 0 since not using EVENT_MORE_DATA
// to feed the AudioTrack
0, // shared mem
true, // thread can call Java
sessionId, // audio session ID
offload ? AudioTrack::TRANSFER_SYNC_NOTIF_CALLBACK
: AudioTrack::TRANSFER_SYNC,
(offload || encapsulationMode) ? &offloadInfo : NULL,
attributionSource, // Passed from Java
paa.get());
break;
case MODE_STATIC:
{
// AudioTrack is using shared memory
const auto iMem = allocSharedMem(buffSizeInBytes);
//省略
status = lpTrack->set(AUDIO_STREAM_DEFAULT, // stream type, but more info conveyed
// in paa (last argument)
sampleRateInHertz,
format, // word length, PCM
nativeChannelMask, frameCount, AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_NONE,
lpJniStorage,
0, // notificationFrames == 0 since not using EVENT_MORE_DATA
// to feed the AudioTrack
iMem, // shared mem
true, // thread can call Java
sessionId, // audio session ID
AudioTrack::TRANSFER_SHARED,
nullptr, // default offloadInfo
attributionSource, // Passed from Java
paa.get());
break;
}
}
// Set caller name so it can be logged in destructor.
// MediaMetricsConstants.h: AMEDIAMETRICS_PROP_CALLERNAME_VALUE_JAVA
lpTrack->setCallerName("java");
} else { // end if (nativeAudioTrack == 0)
//省略
}
lpJniStorage->mAudioTrackCallback =
sp<JNIAudioTrackCallback>::make(env, thiz, lpJniStorage->getAudioTrackWeakRef(),
javaAudioTrackFields.postNativeEventInJava);
lpTrack->setAudioTrackCallback(lpJniStorage->mAudioTrackCallback);
nSession = env->GetIntArrayElements(jSession, nullptr /* isCopy */);
//下面就开始从native的AudioTrack获取一些数据,设置回Java层面的AudioTrack
// read the audio session ID back from AudioTrack in case we create a new session
nSession[0] = lpTrack->getSessionId();
env->ReleaseIntArrayElements(jSession, nSession, 0 /* mode */);
nSession = NULL;
{
const jint elements[1] = { (jint) lpTrack->getSampleRate() };
env->SetIntArrayRegion(jSampleRate, 0, 1, elements);
}
// save our newly created C++ AudioTrack in the "nativeTrackInJavaObj" field
// of the Java object (in mNativeTrackInJavaObj)
setFieldSp(env, thiz, lpTrack, javaAudioTrackFields.nativeTrackInJavaObj);
// save the JNI resources so we can free them later
//ALOGV("storing lpJniStorage: %x\n", (long)lpJniStorage);
setFieldSp(env, thiz, lpJniStorage, javaAudioTrackFields.jniData);
// since we had audio attributes, the stream type was derived from them during the
// creation of the native AudioTrack: push the same value to the Java object
env->SetIntField(thiz, javaAudioTrackFields.fieldStreamType, (jint) lpTrack->streamType());
return (jint) AUDIO_JAVA_SUCCESS;
//省略
}
上面的setup主要干了以下几件事:
1、校验检测java层面传递来的参数是否合法,并且把一些java层面对象转换成native层面对象
2、构造出一个native层面的AudioTrack对象,不过这个时候对象参数还没有相关详细参数
3、调用AudioTrack的set方法,把相关的详细参数设置到AudioTrack对象,在set方法中完成在AudioFlinger中相关track的创建业务,这个set方法比较复杂后续再聊
4、调用完成set后,native层面的AudioTrack信息已经完善,会获取一些参数从新设置给java的AudioTrack对象
接下来重点分析一些这里核心的set方法
AudioTrack的set方法
status_t AudioTrack::set(
audio_stream_type_t streamType,
uint32_t sampleRate,
audio_format_t format,
audio_channel_mask_t channelMask,
size_t frameCount,
audio_output_flags_t flags,
const wp<IAudioTrackCallback>& callback,
int32_t notificationFrames,
const sp<IMemory>& sharedBuffer,
bool threadCanCallJava,
audio_session_t sessionId,
transfer_type transferType,
const audio_offload_info_t *offloadInfo,
const AttributionSourceState& attributionSource,
const audio_attributes_t* pAttributes,
bool doNotReconnect,
float maxRequiredSpeed,
audio_port_handle_t selectedDeviceId)
{
mThreadCanCallJava = threadCanCallJava;
// These variables are pulled in an error report, so we initialize them early.
mSelectedDeviceId = selectedDeviceId;
mSessionId = sessionId;
mChannelMask = channelMask;
mReqFrameCount = mFrameCount = frameCount;
mSampleRate = sampleRate;
mOriginalSampleRate = sampleRate;
mAttributes = pAttributes != nullptr ? *pAttributes : AUDIO_ATTRIBUTES_INITIALIZER;
mPlaybackRate = AUDIO_PLAYBACK_RATE_DEFAULT;
// update format and flags before storing them in mFormat, mOrigFlags and mFlags
if (pAttributes != NULL) {
audio_flags_to_audio_output_flags(mAttributes.flags, &flags);
}
//省略
mFormat = format;
mOrigFlags = mFlags = flags;
mSharedBuffer = sharedBuffer;
mTransfer = transferType;
mDoNotReconnect = doNotReconnect;
// handle default values first.
if (streamType == AUDIO_STREAM_DEFAULT) {
streamType = AUDIO_STREAM_MUSIC;
}
//省略
mFrameSize = audio_bytes_per_frame(channelCount, format);
mVolume[AUDIO_INTERLEAVE_LEFT] = 1.0f;
mVolume[AUDIO_INTERLEAVE_RIGHT] = 1.0f;
mSendLevel = 0.0f;
//省略
mNotificationFramesAct = 0;
// TODO b/182392553: refactor or remove
mClientAttributionSource = AttributionSourceState(attributionSource);
callingPid = IPCThreadState::self()->getCallingPid();
//省略
// create the IAudioTrack
{
AutoMutex lock(mLock);
status = createTrack_l();
}
//省略
return status;
}
这个set方法核心部分就干了以下2个重要的事,
1、校验set方法传递进来的合法性,把参数都赋值给AudioTrack的成员变量
2、调用了createTrack_l进行AudioFlinger远程端创建对应的Track
下面重点看看createTrack_l方法实现:
status_t AudioTrack::createTrack_l()
{
//省略
const sp<IAudioFlinger>& audioFlinger = AudioSystem::get_audio_flinger();
//省略
IAudioFlinger::CreateTrackInput input;
if (mOriginalStreamType != AUDIO_STREAM_DEFAULT) {
// Legacy: This is based on original parameters even if the track is recreated.
input.attr = AudioSystem::streamTypeToAttributes(mOriginalStreamType);
} else {
input.attr = mAttributes;
}
input.config = AUDIO_CONFIG_INITIALIZER;
input.config.sample_rate = mSampleRate;
input.config.channel_mask = mChannelMask;
input.config.format = mFormat;
input.config.offload_info = mOffloadInfoCopy;
input.clientInfo.attributionSource = mClientAttributionSource;
input.clientInfo.clientTid = -1;
input.sharedBuffer = mSharedBuffer;
input.notificationsPerBuffer = mNotificationsPerBufferReq;
input.speed = 1.0;
if (audio_has_proportional_frames(mFormat) && mSharedBuffer == 0 &&
(mFlags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_FAST) == 0) {
input.speed = !isPurePcmData_l() || isOffloadedOrDirect_l() ? 1.0f :
max(mMaxRequiredSpeed, mPlaybackRate.mSpeed);
}
input.flags = mFlags;
input.frameCount = mReqFrameCount;
input.notificationFrameCount = mNotificationFramesReq;
input.selectedDeviceId = mSelectedDeviceId;
input.sessionId = mSessionId;
input.audioTrackCallback = mAudioTrackCallback;
media::CreateTrackResponse response;
status = audioFlinger->createTrack(VALUE_OR_FATAL(input.toAidl()), response);
IAudioFlinger::CreateTrackOutput output{};
if (status == NO_ERROR) {
output = VALUE_OR_FATAL(IAudioFlinger::CreateTrackOutput::fromAidl(response));
}
//省略
//获取跨进程创建track后返回的数据,挨个赋值给AudioTrack的成员变量
mFrameCount = output.frameCount;
mNotificationFramesAct = (uint32_t)output.notificationFrameCount;
mRoutedDeviceId = output.selectedDeviceId;
mSessionId = output.sessionId;
mStreamType = output.streamType;
mSampleRate = output.sampleRate;
if (mOriginalSampleRate == 0) {
mOriginalSampleRate = mSampleRate;
}
mAfFrameCount = output.afFrameCount;
mAfSampleRate = output.afSampleRate;
mAfChannelCount = audio_channel_count_from_out_mask(output.afChannelMask);
mAfFormat = output.afFormat;
mAfLatency = output.afLatencyMs;
mAfTrackFlags = output.afTrackFlags;
mLatency = mAfLatency + (1000LL * mFrameCount) / mSampleRate;
// AudioFlinger now owns the reference to the I/O handle,
// so we are no longer responsible for releasing it.
// FIXME compare to AudioRecord
std::optional<media::SharedFileRegion> sfr;
output.audioTrack->getCblk(&sfr);
sp<IMemory> iMem = VALUE_OR_FATAL(aidl2legacy_NullableSharedFileRegion_IMemory(sfr));
//省略
// invariant that mAudioTrack != 0 is true only after set() returns successfully
if (mAudioTrack != 0) {
IInterface::asBinder(mAudioTrack)->unlinkToDeath(mDeathNotifier, this);
mDeathNotifier.clear();
}
//注意这里的mAudioTrack是与af跨进程通讯的接口,不是AudioTrack对象
mAudioTrack = output.audioTrack;
mCblkMemory = iMem;
IPCThreadState::self()->flushCommands();
audio_track_cblk_t* cblk = static_cast<audio_track_cblk_t*>(iMemPointer);
mCblk = cblk;
mAwaitBoost = false;
void* buffers;
if (mSharedBuffer == 0) {
buffers = cblk + 1;
} else {
// TODO: Using unsecurePointer() has some associated security pitfalls
// (see declaration for details).
// Either document why it is safe in this case or address the
// issue (e.g. by copying).
buffers = mSharedBuffer->unsecurePointer();
//省略
}
//省略
// update proxy
if (mSharedBuffer == 0) {
mStaticProxy.clear();
mProxy = new AudioTrackClientProxy(cblk, buffers, mFrameCount, mFrameSize);
} else {
mStaticProxy = new StaticAudioTrackClientProxy(cblk, buffers, mFrameCount, mFrameSize);
mProxy = mStaticProxy;
}
mProxy->setVolumeLR(gain_minifloat_pack(
gain_from_float(mVolume[AUDIO_INTERLEAVE_LEFT]),
gain_from_float(mVolume[AUDIO_INTERLEAVE_RIGHT])));
mProxy->setSendLevel(mSendLevel);
const uint32_t effectiveSampleRate = adjustSampleRate(mSampleRate, mPlaybackRate.mPitch);
const float effectiveSpeed = adjustSpeed(mPlaybackRate.mSpeed, mPlaybackRate.mPitch);
const float effectivePitch = adjustPitch(mPlaybackRate.mPitch);
mProxy->setSampleRate(effectiveSampleRate);
AudioPlaybackRate playbackRateTemp = mPlaybackRate;
playbackRateTemp.mSpeed = effectiveSpeed;
playbackRateTemp.mPitch = effectivePitch;
mProxy->setPlaybackRate(playbackRateTemp);
mProxy->setMinimum(mNotificationFramesAct);
if (mDualMonoMode != AUDIO_DUAL_MONO_MODE_OFF) {
setDualMonoMode_l(mDualMonoMode);
}
if (mAudioDescriptionMixLeveldB != -std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity()) {
setAudioDescriptionMixLevel_l(mAudioDescriptionMixLeveldB);
}
mDeathNotifier = new DeathNotifier(this);
IInterface::asBinder(mAudioTrack)->linkToDeath(mDeathNotifier, this);
//省略
return status;
}
再来看看AudioFlinger::createTrack
status_t AudioFlinger::createTrack(const media::CreateTrackRequest& _input,
media::CreateTrackResponse& _output)
{
// Local version of VALUE_OR_RETURN, specific to this method's calling conventions.
//把传递的参数CreateTrackRequest转换成CreateTrackInput对象
CreateTrackInput input = VALUE_OR_RETURN_STATUS(CreateTrackInput::fromAidl(_input));
//这里的CreateTrackOutput作为本地输出对象
CreateTrackOutput output;
//省略
//下面都是从input对象中获取相关属性
// TODO b/182392553: refactor or make clearer
pid_t clientPid =
VALUE_OR_RETURN_STATUS(aidl2legacy_int32_t_pid_t(input.clientInfo.attributionSource.pid));
bool updatePid = (clientPid == (pid_t)-1);
const uid_t callingUid = IPCThreadState::self()->getCallingUid();
uid_t clientUid =
VALUE_OR_RETURN_STATUS(aidl2legacy_int32_t_uid_t(input.clientInfo.attributionSource.uid));
audio_io_handle_t effectThreadId = AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE;
std::vector<int> effectIds;
audio_attributes_t localAttr = input.attr;
//省略
//通过上面input获取的相关参数,调用AudioSystem::getOutputForAttr获取要播放的output线程
lStatus = AudioSystem::getOutputForAttr(&localAttr, &output.outputId, sessionId, &streamType,
adjAttributionSource, &input.config, input.flags,
&output.selectedDeviceId, &portId, &secondaryOutputs,
&isSpatialized, &isBitPerfect);
//省略
{
audio_utils::lock_guard _l(mutex());
//通过output.outputId获取到对应到的PlaybackThread
IAfPlaybackThread* thread = checkPlaybackThread_l(output.outputId);
//把clientPid注册,会构造对应的Client对象
client = registerPid(clientPid);
//省略
//把所有input相关参数,又写到output中
output.sampleRate = input.config.sample_rate;
output.frameCount = input.frameCount;
output.notificationFrameCount = input.notificationFrameCount;
output.flags = input.flags;
//注意这个时候StreamType实际是policy端确定的,会写会app层面
output.streamType = streamType;
//调用thread的createTrack_l来创建AudioFlinger的Track
track = thread->createTrack_l(client, streamType, localAttr, &output.sampleRate,
input.config.format, input.config.channel_mask,
&output.frameCount, &output.notificationFrameCount,
input.notificationsPerBuffer, input.speed,
input.sharedBuffer, sessionId, &output.flags,
callingPid, adjAttributionSource, input.clientInfo.clientTid,
&lStatus, portId, input.audioTrackCallback, isSpatialized,
isBitPerfect, &output.afTrackFlags);
//又是进行相关赋值给output
output.afFrameCount = thread->frameCount();
output.afSampleRate = thread->sampleRate();
output.afChannelMask = static_cast<audio_channel_mask_t>(thread->channelMask() |
thread->hapticChannelMask());
output.afFormat = thread->format();
output.afLatencyMs = thread->latency();
output.portId = portId;
//省略
//AudioFlinger端创建的Track要和app层面的AudioTrack进行关联,创建对应的TrackHandle赋值到output
output.audioTrack = IAfTrack::createIAudioTrackAdapter(track);
//output本地对象转换成和输入参数一样类型
_output = VALUE_OR_FATAL(output.toAidl());
上面重要地方都有相关注释,删除一些不影响主要流程的代码。
上面最重要有2个核心步骤:
核心1 :
AudioSystem::getOutputForAttr方法
它通过输入参数input,获取对应到的输出output,其实就是PlaybackThread,AudioSystem::getOutputForAttr方法相对比较复杂,这个后续在分析
核心2:
thread->createTrack_l
在获取了PlaybackThread后会调用createTrack_l进行在Thread中也创建一个Track,这个Track与app端的AudioTrack对应。
下面在重点看看thread->createTrack_l方法
// PlaybackThread::createTrack_l() must be called with AudioFlinger::mutex() held
sp<IAfTrack> PlaybackThread::createTrack_l(
const sp<Client>& client,
audio_stream_type_t streamType,
const audio_attributes_t& attr,
uint32_t *pSampleRate,
audio_format_t format,
audio_channel_mask_t channelMask,
size_t *pFrameCount,
size_t *pNotificationFrameCount,
uint32_t notificationsPerBuffer,
float speed,
const sp<IMemory>& sharedBuffer,
audio_session_t sessionId,
audio_output_flags_t *flags,
pid_t creatorPid,
const AttributionSourceState& attributionSource,
pid_t tid,
status_t *status,
audio_port_handle_t portId,
const sp<media::IAudioTrackCallback>& callback,
bool isSpatialized,
bool isBitPerfect,
audio_output_flags_t *afTrackFlags)
{
//省略
lStatus = initCheck();
//省略
track = IAfTrack::create(this, client, streamType, attr, sampleRate, format,
channelMask, frameCount,
nullptr /* buffer */, (size_t)0 /* bufferSize */, sharedBuffer,
sessionId, creatorPid, attributionSource, trackFlags,
IAfTrackBase::TYPE_DEFAULT, portId, SIZE_MAX /*frameCountToBeReady*/,
speed, isSpatialized, isBitPerfect);
lStatus = track != 0 ? track->initCheck() : (status_t) NO_MEMORY;
mTracks.add(track);
//省略
}
return track;
}
这里主要就是调用了 IAfTrack::create方法构造出了Track对象,同时构造出的track对象被放入到Thread的mTracks集合中。
更多audio系统框架基础开始学的内如参考:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/pQr-HrW0EUoi5QHTMOGEBQ
更多audio系统框架相关的实战开发分析,请关注下面“千里马学框架”






















 2154
2154

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










