Some Points:
Implement Steps:
1.Pick a neural network architecture.
- number of input units = dimension of features
- number of output units = number of classes
- number of hidden layer = 1(Default), if you have more than 1 hidden layer, it recommended that every hidden layer have the same number of units
- number of hidden units per layer = .. Usually the more the better
2. Randomly initialize the weights so that they are not competely identical. Formally says "break symmetry"
3. Implement a for-loop for t = 1: m and place the steps 3.1 - 3.3 below inside the for-loop. With the t-th iteration performing the calculation on the t-th trainng example (x(t), y(t)).
- 3.1 Implement forward propagation to get vector a(unit) and vector z(unit) for each layer.
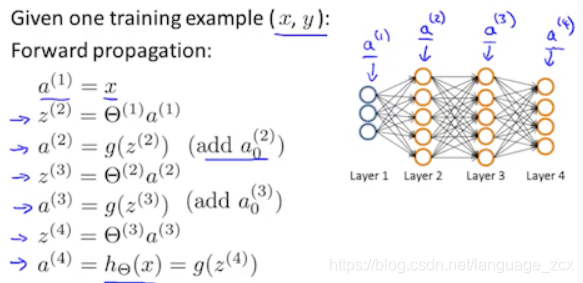
- 3.2 Implement cost function for the t-th example.
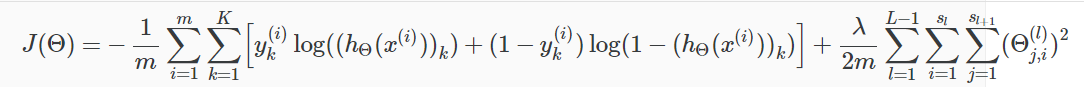
- 3.3 Implement back propagation to get vector
 (unit) and matrix
(unit) and matrix  (weight).
(weight).
![]()

4. Get the averages of cost function and matrix  , add regurlarization portion.Attention the index begin at 1, ignoring the bias units.
, add regurlarization portion.Attention the index begin at 1, ignoring the bias units.
5.Use gradient checking to confirm that your backprpa works well.
6. Use gradient descent or other advanced optimization algorithms e.g. fmincg to get the mininum cost-point.
7. In my eyes, decrease the value of 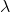 may weaken the effect of regularization, which will improve the accuracy of training set detection and is harmful to the prediction of new data.
may weaken the effect of regularization, which will improve the accuracy of training set detection and is harmful to the prediction of new data.
The Results:
- nnCostFunction.m
function [J grad] = nnCostFunction(nn_params, ...
input_layer_size, ...
hidden_layer_size, ...
num_labels, ...
X, y, lambda)
Theta1 = reshape(nn_params(1:hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1)), ...
hidden_layer_size, (input_layer_size + 1));
Theta2 = reshape(nn_params((1 + (hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1))):end), ...
num_labels, (hidden_layer_size + 1));
% Setup some useful variables
m = size(X, 1);
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
Theta1_grad = zeros(size(Theta1));
Theta2_grad = zeros(size(Theta2));
X = [ones(m, 1), X]; % 5000*401
a2 = sigmoid(X * Theta1'); % 5000*25
a2 = [ones(size(a2,1),1), a2]; % 5000*26
h = sigmoid(a2 * Theta2'); % 5000*10
%for i=1:num_labels
% pos = log(h(:, i)); % 5000*1
% neg = log(1-h(:, i)); % 5000*1
% y_temp = y==i;
% J = J + (-1 / m) * (y_temp' * pos + (1 - y_temp)' * neg);
%end
for i=1:m
pos = log(h(i, :)); %1*10
neg = log(1-(h(i, :))); %1*10
y_temp = zeros(num_labels, 1); %10*1
y_temp(y(i,1), 1) = 1; %10*1
J = J + (pos * y_temp + neg * (1 - y_temp));
end
J = (-1 / m) * J;
% -------------------------------------------------------------
y_temp = [];
for i=1:num_labels
y_temp = [y_temp, y==i]; % 5000*10
end
for i=1:m
delta3 = (h(i, :) - y_temp(i, :))'; % 10*1
delta2 = Theta2' * delta3 .* a2(i, :)' .* (1- a2(i, :))'; % 26*1
Theta2_grad = Theta2_grad + delta3 * a2(i, :); % 10*26
Theta1_grad = Theta1_grad + delta2(2:end, 1) * X(i, :); % 25*401
end
Theta2_grad = Theta2_grad / m; % 10*26
Theta1_grad = Theta1_grad / m; % 25*401
% =========================================================================
sum1 = sum(sum(Theta1(:,2:end) .^ 2));
sum2 = sum(sum(Theta2(:,2:end) .^ 2));
J = J + (lambda / (2 * m)) * (sum1 + sum2);
Theta2_grad = Theta2_grad + lambda / m * [zeros(size(Theta2,1),1), Theta2(:, 2:end)]; % 10*26
Theta1_grad = Theta1_grad + lambda / m * [zeros(size(Theta1,1),1), Theta1(:, 2:end)]; % 25*401
% Unroll gradients
grad = [Theta1_grad(:) ; Theta2_grad(:)];
end
- sigmoidGradient.m
function g = sigmoidGradient(z)
g = zeros(size(z));
g = sigmoid(z) .* (1 - sigmoid(z));
end





 本文详细介绍了神经网络的训练过程,包括选择网络架构、初始化权重、前向传播、计算成本函数、反向传播、梯度检查及优化算法应用等步骤。通过具体函数实现,如前向传播、成本计算和梯度更新,展示了神经网络训练的完整流程。
本文详细介绍了神经网络的训练过程,包括选择网络架构、初始化权重、前向传播、计算成本函数、反向传播、梯度检查及优化算法应用等步骤。通过具体函数实现,如前向传播、成本计算和梯度更新,展示了神经网络训练的完整流程。
















 899
899

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








