解决FJSP的主流方法有如下几种。

1.Exact algorithms
第一种是精确求解,包括迭代暴力搜索,混合整数规划以及分支定界等。精确求解的优点在于求出的解是最优的,可以作为其他方法评优的baseline。缺点就在于速度慢,没有办法解决大规模问题。之前调研过表现最好的MILP方法(Roshanaei et al.,2012),作者提出了两种MILP模型,分别基于position-based和sequence-based,解决一个12*8的FJSP需要1个小时。
Exact algorithms 是把FJSP问题公式化成integer linear programming (ILP)或者mixed ILP (MILP) models.
1.1 MILP
Wagner et.al. 1959年最早提出Position-based modeling idea
Manne et.al. 1960年最早提出Sequence-based modeling idea
(MILP中表现最好的)Roshanaei 2012 et al. developed two novel effective position-based and sequence-based MILP models to deal with the FJSP to minimize make span. 之前调研过表现最好的MILP方法,2012年的文章,提出了两种MILP模型,分别基于position-based和sequence-based。
2. Heuristics
(Ziaee, 2014).rule-based中表现最好的,速度快,但是和最优平均有5%左右的差距。数据集越大差距越明显
(Li, 2016)2016年华中科技大学提出来的方法,将GA和TS结合。简单来说就是在GA的过程中,对每一个子代个体进行tabu search优化。在90%问题集以上可以找到最优解。在时间表现方面,文中最大的测试样本是la-36,包含30JOB和10machine。时间在67S。
Meta-heuristics
1.Population-based meta-heuristics
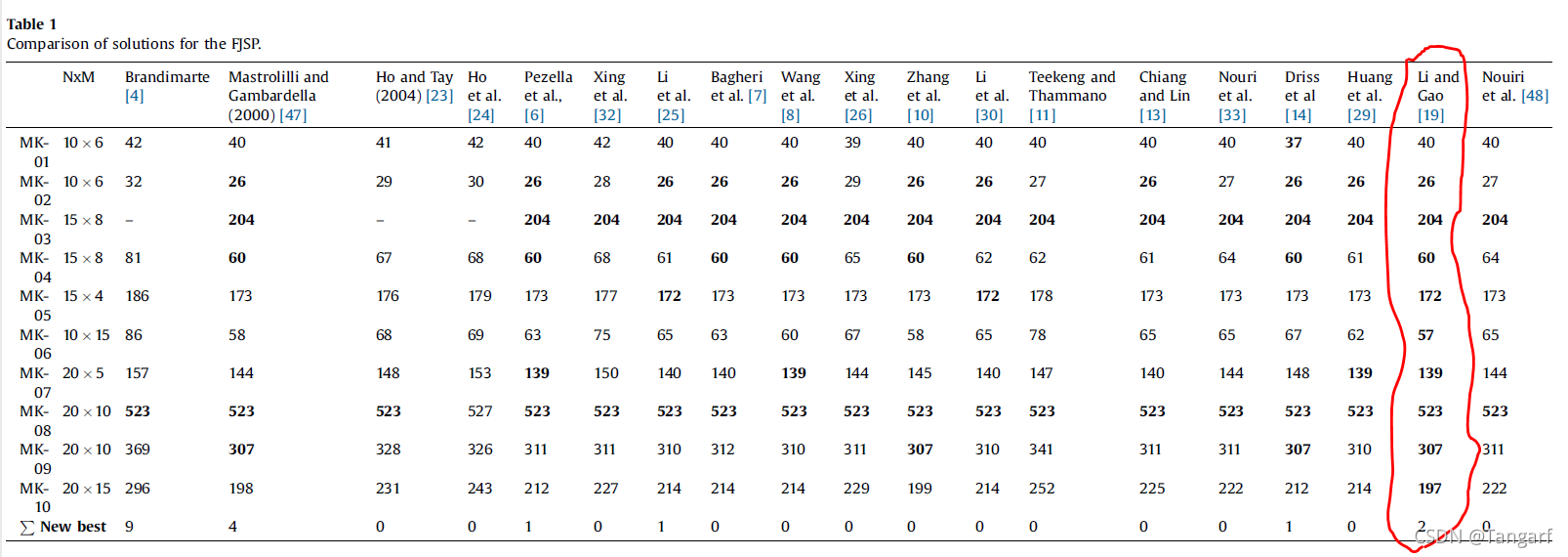
(混合启发式最好的)Li and Gao [80] proposed a hybrid algorithm which hybrid is the GA and TS for the FJSP。2016年华中科技大学提出来的方法,将GA和TS结合。简单来说就是在GA的过程中,对每一个子代个体进行tabu search优化。在SFJS01-SFJS10, MFJS01-MFJS10,MK01-MK10以及setb问题集都可以找到最优解(Denkena,2021)。在其他的问题集上,90%以上可以找到最优解。在时间表现方面,文中最大的测试样本是la-36,包含30JOB和10machine。时间在67S。
Machine learning
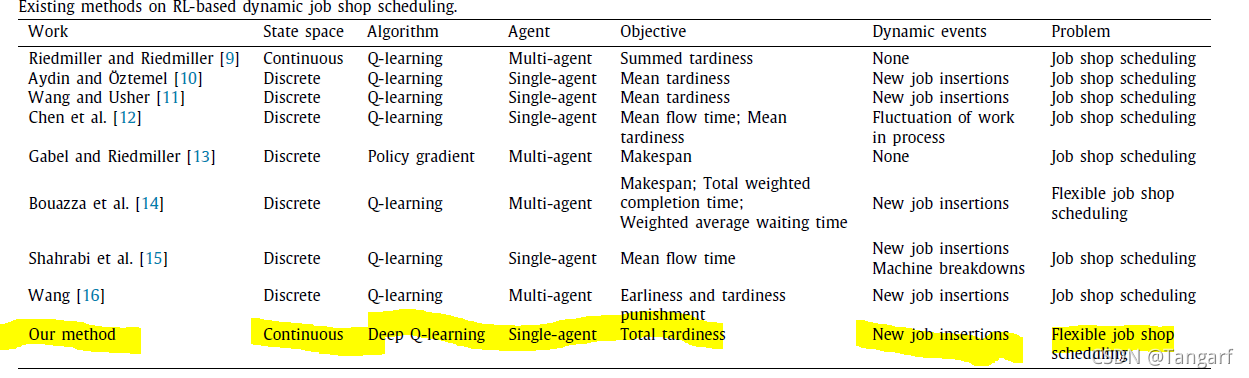
目前使用强化学习解决FJSP问题一共有两篇文献。第一篇是” A distributed approach solving partially flexible job-shop scheduling problem with a Q-learning effect ” (Bouazza, 2017)。文章基于Q-learning算法,没有给出具体的公式。对比的方法只有First In First Out, Shortest Job First, Highest Priority First and Last In First Out。第二篇是“Dynamic scheduling for flexible job shop with new job insertions by deep reinforcement learning”(Shu Luo,2020)文章使用DQN深度强化学习算法解决动态柔性车间调度问题,里面对DQN使用了一种不同于every C step的目标网络更新方法,而是一种软策略soft target update policy。算法使用DQN寻找dispatching rule,相对比其他几种rule-based的方法表现较优。但没有在标准数据集上进行测试。
Quantum Annealer
Quantum algorithms for process parallel flexible job shop scheduling (Denkena,2021)
文章基于Fujitsu量子退火计算机求解了FJSP问题。在MK-01-MK-10数据集上接近最优解。在20JOB*15MACHINE的数据集上需要27.06秒。
Reference
Aramon, M., Rosenberg, G., Valiante, E., Miyazawa, T., Tamura, H., & Katzgraber, H. G. (2019). Physics-inspired optimization for quadratic unconstrained problems using a digital annealer. Frontiers in Physics, 7, 48.
Bowman, E. H. (1959). The Schedule-Sequencing Problem. Operations Research, 7(5), 621–624. http://www.jstor.org/stable/167010
Neukart, F., Compostella, G., Seidel, C., Von Dollen, D., Yarkoni, S., & Parney, B. (2017). Traffic flow optimization using a quantum annealer. Frontiers in ICT, 4, 29.
Roshanaei, V., Azab, A., ElMaraghy, H.: ‘Mathematical modelling and a meta-heuristic for flexible job shop scheduling’, Int. J. Prod. Res., 2013, 51, (20), pp. 6247–6274
Venturelli, D., Marchand, D. J., & Rojo, G. (2015). Quantum annealing implementation of job-shop scheduling. arXiv preprint arXiv:1506.08479.
Wagner, H., 1959. An integer linear-programming model for machine scheduling. Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, 6(2), pp.131-140.




 本文介绍了FJSP(柔性车间调度问题)的主流解决方案,包括精确算法如MILP模型,启发式方法如遗传算法与禁忌搜索的结合,以及机器学习中的强化学习应用。此外,还探讨了使用量子退火技术在解决大型问题上的潜力,特别是在接近最优解方面的表现。
本文介绍了FJSP(柔性车间调度问题)的主流解决方案,包括精确算法如MILP模型,启发式方法如遗传算法与禁忌搜索的结合,以及机器学习中的强化学习应用。此外,还探讨了使用量子退火技术在解决大型问题上的潜力,特别是在接近最优解方面的表现。

















 7394
7394










